phosphatases and differentiation of the golgi apparatus
... zone' (Clowes, 1961), mitotic activity is apparently much lower than in some of the other cell types of the root, as are certain other metabolic activities (Jensen, 1957, 1958). Just basipetal to this region the cells, here termed apical initials, have a higher rate of mitotic activity, but are not ...
... zone' (Clowes, 1961), mitotic activity is apparently much lower than in some of the other cell types of the root, as are certain other metabolic activities (Jensen, 1957, 1958). Just basipetal to this region the cells, here termed apical initials, have a higher rate of mitotic activity, but are not ...
A Role for the Basal Forebrain Cholinergic System in Estrogen
... Estrogen-induced changes in synaptic inhibition are likely to be causally related to subsequent enhancements in excitatory synaptic function in CA1 pyramidal cells. Currently, it is unknown how or on what cells estrogen acts to regulate synaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. We used whole-cell volt ...
... Estrogen-induced changes in synaptic inhibition are likely to be causally related to subsequent enhancements in excitatory synaptic function in CA1 pyramidal cells. Currently, it is unknown how or on what cells estrogen acts to regulate synaptic inhibition in the hippocampus. We used whole-cell volt ...
PDF
... Members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors regulate the specification and differentiation of numerous cell types during embryonic development. Hand1 and Hand2 are expressed by a subset of neural crest cells in the anterior branchial arches and are involved in cranio ...
... Members of the basic helix-loop-helix (bHLH) family of transcription factors regulate the specification and differentiation of numerous cell types during embryonic development. Hand1 and Hand2 are expressed by a subset of neural crest cells in the anterior branchial arches and are involved in cranio ...
Histone methylation
... part in determining their substrate specificities. For example, histone lysine demethylase PHF8 binds to H3K4me2 and/or to H3K4me3 and demethylates H3K9me2, but the related enzyme JmjC-domain-containing histone demethylation protein 1D (JHDM1D; also known as KDM7A) is directed towards demethylating ...
... part in determining their substrate specificities. For example, histone lysine demethylase PHF8 binds to H3K4me2 and/or to H3K4me3 and demethylates H3K9me2, but the related enzyme JmjC-domain-containing histone demethylation protein 1D (JHDM1D; also known as KDM7A) is directed towards demethylating ...
Full Text - The International Journal of Developmental Biology
... would shake its foundations. Indeed the radical shift of emphasis to the cellular and subcellular levels and, from the 1950’s on, to the molecular level, transformed experimental embryology to developmental biology”. The term “decline” of experimental embryology was falsely interpreted by some autho ...
... would shake its foundations. Indeed the radical shift of emphasis to the cellular and subcellular levels and, from the 1950’s on, to the molecular level, transformed experimental embryology to developmental biology”. The term “decline” of experimental embryology was falsely interpreted by some autho ...
Microbiology
... examined by T E M after negative staining, and by SDSPAGE to identify the protein composition. TEM revealed fragments from two types of flagella differing in diameter. The high density CsCl fraction contained only the thick flagella, whereas the low density fraction contained the thin flagella (Fig. ...
... examined by T E M after negative staining, and by SDSPAGE to identify the protein composition. TEM revealed fragments from two types of flagella differing in diameter. The high density CsCl fraction contained only the thick flagella, whereas the low density fraction contained the thin flagella (Fig. ...
Identification of a novel Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response
... similarity to the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Element (ERSE). This novel ERSE (“ERSE-26”) is able to regulate PRNP endogenously in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In order to determine whether or not the ERSE-26 exists elsewhere in the genome and what is co-regulated with PR ...
... similarity to the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response Element (ERSE). This novel ERSE (“ERSE-26”) is able to regulate PRNP endogenously in response to endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress. In order to determine whether or not the ERSE-26 exists elsewhere in the genome and what is co-regulated with PR ...
Applied and Environmental Microbiology
... bacterium has been detected in roots and stems of potatoes (11) and tomatoes (42), as well as in grapevine leaves, following in vitro culture (1) and in grapevine roots under hydroponic conditions (unpublished results). However, the colonization pattern and the method used for translocation from the ...
... bacterium has been detected in roots and stems of potatoes (11) and tomatoes (42), as well as in grapevine leaves, following in vitro culture (1) and in grapevine roots under hydroponic conditions (unpublished results). However, the colonization pattern and the method used for translocation from the ...
Cell Biology IV:
... Energy of blue and red light converts purified chlorophyll to a state in which its electrons have higher potential energy. This energy is gradually released as heat (far red light, > 700 nm) and fluorescence (red light, 650-700 nm ). In chloroplasts, such energy is not lost, but is captured to power ...
... Energy of blue and red light converts purified chlorophyll to a state in which its electrons have higher potential energy. This energy is gradually released as heat (far red light, > 700 nm) and fluorescence (red light, 650-700 nm ). In chloroplasts, such energy is not lost, but is captured to power ...
Materials and Methods - Word file
... A linear and purified Avr II- SspI DNA fragment of the pcDNA-Fabpl-netrin-1 construct was then microinjected into the male fertilized pronucleus obtained from C57BL/6 mice. Mice founders were obtained by SEAT transgenesis center (CNRS - Villejuif, France). Germline transmission and genotyping were d ...
... A linear and purified Avr II- SspI DNA fragment of the pcDNA-Fabpl-netrin-1 construct was then microinjected into the male fertilized pronucleus obtained from C57BL/6 mice. Mice founders were obtained by SEAT transgenesis center (CNRS - Villejuif, France). Germline transmission and genotyping were d ...
mast cells and basophils
... of histamine [1, 2]. The release of histamine, and other inflammatory mediators, from these cells is a critical early step in the complex series of cellular and molecular events which make up the allergic response [3–6]. The basophil has often been described as a circulating mast cell, but, in reali ...
... of histamine [1, 2]. The release of histamine, and other inflammatory mediators, from these cells is a critical early step in the complex series of cellular and molecular events which make up the allergic response [3–6]. The basophil has often been described as a circulating mast cell, but, in reali ...
NuMA assembles into an extensive filamentous structure when
... nuclear matrix (Yang et al., 1992; Zeng et al., 1994a), that it participates in the re-assembly of the daughter cell nuclei at the end of mitosis (Compton and Cleveland, 1993), and that it is a component of splicing complexes (Zeng et al., 1994b). In addition to these proposed specific functions for ...
... nuclear matrix (Yang et al., 1992; Zeng et al., 1994a), that it participates in the re-assembly of the daughter cell nuclei at the end of mitosis (Compton and Cleveland, 1993), and that it is a component of splicing complexes (Zeng et al., 1994b). In addition to these proposed specific functions for ...
Journal of Bacteriology
... Attachment of rhizobia to developing root hairs is one of the first steps of the nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis between rhizobia and the leguminous host plants. Recently, we reported that both cellulose fibrils and a Ca2+-dependent adhesin of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae cells are invol ...
... Attachment of rhizobia to developing root hairs is one of the first steps of the nitrogen-fixing root nodule symbiosis between rhizobia and the leguminous host plants. Recently, we reported that both cellulose fibrils and a Ca2+-dependent adhesin of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. viciae cells are invol ...
Diazonamide A and a Synthetic Structural Analog
... [3H]colchicine and [3H]vinblastine were from Perkin Elmer Life Sciences (Boston, MA); GTP and [8-14C]GTP were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO) and Moravek Radiochemicals (Brea, CA), respectively, and both nucleotides were repurified from about 90 to ⬎98% purity by triethylammonium bicarbonate gradient chr ...
... [3H]colchicine and [3H]vinblastine were from Perkin Elmer Life Sciences (Boston, MA); GTP and [8-14C]GTP were from Sigma (St. Louis, MO) and Moravek Radiochemicals (Brea, CA), respectively, and both nucleotides were repurified from about 90 to ⬎98% purity by triethylammonium bicarbonate gradient chr ...
Gene Therapy That Safely Targets and Kills Tumor Cells Throughout
... the risk of chromosomal integration or germ line modification of patients and also makes them highly efficient for gene transfer throughout the body. The Sindbis viral vectors we used in these studies are replication incompetent, so they cannot infect, replicate, and cause viremia unless recombinati ...
... the risk of chromosomal integration or germ line modification of patients and also makes them highly efficient for gene transfer throughout the body. The Sindbis viral vectors we used in these studies are replication incompetent, so they cannot infect, replicate, and cause viremia unless recombinati ...
Ion channels in the immune system as targets for
... identified a new generation of highly potent blockers currently being pursued in the pharmaceutical industry [33,34,35•,36–46]. In 1989, two groups reported that peptide scorpion toxins can block the type n KV channel at nanomolar concentrations [33,34]. At the time, the pharmacology of K+ channels ...
... identified a new generation of highly potent blockers currently being pursued in the pharmaceutical industry [33,34,35•,36–46]. In 1989, two groups reported that peptide scorpion toxins can block the type n KV channel at nanomolar concentrations [33,34]. At the time, the pharmacology of K+ channels ...
DNA Methylation Changes during Maize Leaf
... The former methylates CG sites during DNA replication, whereas the latter methylates CHG (H = A, C or T) sites located in chromatin in which histone 3 is dimethylated on lysine 9 (H3K9Me2) (Goll and Bestor, 2005). De novo DMTs methylate previously unmethylated DNA, and are DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLT ...
... The former methylates CG sites during DNA replication, whereas the latter methylates CHG (H = A, C or T) sites located in chromatin in which histone 3 is dimethylated on lysine 9 (H3K9Me2) (Goll and Bestor, 2005). De novo DMTs methylate previously unmethylated DNA, and are DOMAINS REARRANGED METHYLT ...
Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions
... groups or subfamilies of HopZ1—HopZ1a, HopZ1b, and HopZ1c—were identified (Ma et al. 2006). A survey of 96 P. syringae strains isolated from a variety of plant hosts worldwide revealed that 42% of these strains produce a functional HopZ T3SE. Evolutionary analysis demonstrated that HopZ1, ancient to ...
... groups or subfamilies of HopZ1—HopZ1a, HopZ1b, and HopZ1c—were identified (Ma et al. 2006). A survey of 96 P. syringae strains isolated from a variety of plant hosts worldwide revealed that 42% of these strains produce a functional HopZ T3SE. Evolutionary analysis demonstrated that HopZ1, ancient to ...
Stress and Protists: No life without stress
... dissolved ENM species. Once in the vicinity of the microorganism, different ENM forms react with sensitive receptor sites (adsorption, 3, Fig. 3) on the biological membrane, and then (but not necessarily) can diffuse through the membrane (internalization, 4, Fig. 3). Once inside the cell, ENMs can i ...
... dissolved ENM species. Once in the vicinity of the microorganism, different ENM forms react with sensitive receptor sites (adsorption, 3, Fig. 3) on the biological membrane, and then (but not necessarily) can diffuse through the membrane (internalization, 4, Fig. 3). Once inside the cell, ENMs can i ...
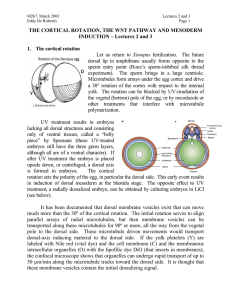
the cortical rotation, the wnt pathway
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
... dual-kinase mechanism. First Casein Kinase 1α (one of the first protein kinases to be discovered) phosphorylates a serine, and only then GSK-3 can phosphorylate the other Ser/Thr residurs. Once the two most amino-terminal Ser are phosphorylated, the protein is recognized by β-Trcp (Slimb in Drosophi ...
Roles of CDK and DDK in Genome Duplication and
... require diversity in cyclin and CDK interactions but is rather directly driven by CDK activity levels. This quantitative model of the cell cycle proposes that S phase and mitosis rely on low and high CDK activity thresholds, respectively, and that no qualitatively different cyclin-CDK complexes are ...
... require diversity in cyclin and CDK interactions but is rather directly driven by CDK activity levels. This quantitative model of the cell cycle proposes that S phase and mitosis rely on low and high CDK activity thresholds, respectively, and that no qualitatively different cyclin-CDK complexes are ...
Chromosomes with Two Intact Axial Cores Are Induced by G2
... dent duplexes to form two chromatid arms, each with an axial core. Alternatively, it is possible that the information necessary to form the two chromatids with axial cores has been templated independently, and before, the decatenation event. Here we have approached the problem of the interdependence ...
... dent duplexes to form two chromatid arms, each with an axial core. Alternatively, it is possible that the information necessary to form the two chromatids with axial cores has been templated independently, and before, the decatenation event. Here we have approached the problem of the interdependence ...
- UCL Discovery
... node21,43–45. Twelve differentially expressed genes were identified, encoding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation (ERNI17,21, Churchill43, Sox3, Otx246), known and putative receptors (TrkC and Asterix45), a putative RNA-binding protein (Obelix45), the retinoid regulator Cyp26A146 and prot ...
... node21,43–45. Twelve differentially expressed genes were identified, encoding proteins involved in transcriptional regulation (ERNI17,21, Churchill43, Sox3, Otx246), known and putative receptors (TrkC and Asterix45), a putative RNA-binding protein (Obelix45), the retinoid regulator Cyp26A146 and prot ...
HGF and TGFβ1 differently influenced Wwox regulatory function on
... parental MDA-MB231 breast carcinoma cells and the derived 1833-bone metastatic clone. The comparative study of transcriptomic profile of the two cell lines identifies a gene set whose expression is associated with, and promotes the formation of metastasis to bone [20]. MDAMB231 cells are invasive, a ...
... parental MDA-MB231 breast carcinoma cells and the derived 1833-bone metastatic clone. The comparative study of transcriptomic profile of the two cell lines identifies a gene set whose expression is associated with, and promotes the formation of metastasis to bone [20]. MDAMB231 cells are invasive, a ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.