
Chapter 18
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
Thin Lenses
... OBJECTIVE: To study and verify some of the laws of optics applicable to thin lenses by forming images with a positive and negative lens, and by determining the focal length of the positive lens. THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflect ...
... OBJECTIVE: To study and verify some of the laws of optics applicable to thin lenses by forming images with a positive and negative lens, and by determining the focal length of the positive lens. THEORY: Each point of a self-luminous object (such as the Sun or the filament of a light bulb) or reflect ...
Experiment 15
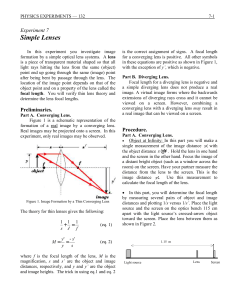
... is a piece of transparent material shaped so that all light rays hitting the lens from the same (object) point end up going through the same (image) point after being bent by passage through the lens. The location of the image point depends on that of the object point and on a property of the lens c ...
... is a piece of transparent material shaped so that all light rays hitting the lens from the same (object) point end up going through the same (image) point after being bent by passage through the lens. The location of the image point depends on that of the object point and on a property of the lens c ...
Experimental Phys - Delta University!
... Experiment No. (01) Power of Spherical Lenses ---------------------------------------------------------------- 3 1. Determination of the Focal Length and the Power of a Converging (Convex) Lens ------------------------- 3 1.1. Coincidence Method: ----------------------------------------------------- ...
... Experiment No. (01) Power of Spherical Lenses ---------------------------------------------------------------- 3 1. Determination of the Focal Length and the Power of a Converging (Convex) Lens ------------------------- 3 1.1. Coincidence Method: ----------------------------------------------------- ...
Applied physics viva
... A1 No, two lines of force never intersect each other . If they intersect each other , then at the point of intersection, two tangents can be drawn and thus we have two directions of magnetic field at that point , which is impossible. Q2. What is neutral point? A2 The points where net magnetic field ...
... A1 No, two lines of force never intersect each other . If they intersect each other , then at the point of intersection, two tangents can be drawn and thus we have two directions of magnetic field at that point , which is impossible. Q2. What is neutral point? A2 The points where net magnetic field ...
Introduction
... image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the system exits the sy ...
... image location and magnification. This graphical approach relies on two simple properties of an optical system. First, a ray that enters the system parallel to the optical axis crosses the optical axis at the focal point. Second, a ray that enters the first principal point of the system exits the sy ...
Waves and Optics One
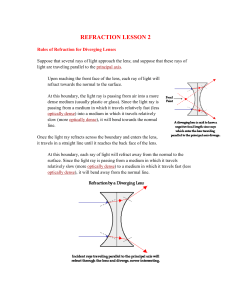
... When light passes from one medium to another, e.g. air to glass, there will be a change of __________. This is due to the __________ of light being less in glass than air. The light ray will bend _________ the normal. When the light ray moves from glass to air it will bend _________ __________ the n ...
... When light passes from one medium to another, e.g. air to glass, there will be a change of __________. This is due to the __________ of light being less in glass than air. The light ray will bend _________ the normal. When the light ray moves from glass to air it will bend _________ __________ the n ...
microscope instructions ppt
... Setting up Köhler illumination (focusing the condenser) Now look through the oculars and slowly lower the condenser until you see a sharp outline of the field diaphragm (it looks like a circle-shaped polygon.) ...
... Setting up Köhler illumination (focusing the condenser) Now look through the oculars and slowly lower the condenser until you see a sharp outline of the field diaphragm (it looks like a circle-shaped polygon.) ...
Assignment #2 - Rose
... in the z = 0 plane, with the beam waist radii w0x and w0y in the x and y-directions respectively. The contours of constant intensity are therefore ellipses instead of circles. Write expressions for the beam depth of focus, angular divergence, and radii of curvature in the x and y-directions, as func ...
... in the z = 0 plane, with the beam waist radii w0x and w0y in the x and y-directions respectively. The contours of constant intensity are therefore ellipses instead of circles. Write expressions for the beam depth of focus, angular divergence, and radii of curvature in the x and y-directions, as func ...
4.Bending Light PhET
... Google the phrase, “Bending Light PhET” and click on the first link. Click the “Download Now!” button. In the last unit, you learned that reflection occurs when light bounces off of a surface. Refraction occurs when light changes direction (bends) when entering a new medium. The laser is pointing to ...
... Google the phrase, “Bending Light PhET” and click on the first link. Click the “Download Now!” button. In the last unit, you learned that reflection occurs when light bounces off of a surface. Refraction occurs when light changes direction (bends) when entering a new medium. The laser is pointing to ...
1 - Hodge Hill College
... An endoscope is a tube which allows a doctor to look into the passageways of the body without having to operate. Endoscopes consist of a flexible tube containing glass fibres called optical fibres. The endoscope allows the transmission of light into and out of the body. It has a light source attache ...
... An endoscope is a tube which allows a doctor to look into the passageways of the body without having to operate. Endoscopes consist of a flexible tube containing glass fibres called optical fibres. The endoscope allows the transmission of light into and out of the body. It has a light source attache ...
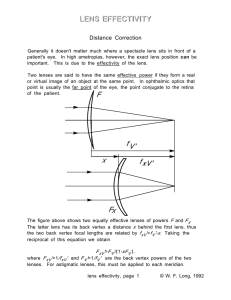
Lens Effectivity (WP)
... his distance prescription so he would not have to accommodate at all for an object 25cm from the spectacle plane. Pretend that we have a real +4.00D lens in front of the patients +3.00-3.00x180 distance prescription. As shown in the diagram, the +3.00-3.00x180 lens sees collimated light-just as it w ...
... his distance prescription so he would not have to accommodate at all for an object 25cm from the spectacle plane. Pretend that we have a real +4.00D lens in front of the patients +3.00-3.00x180 distance prescription. As shown in the diagram, the +3.00-3.00x180 lens sees collimated light-just as it w ...
Chapter 23
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
Lesson-2 Light Microscopy
... Conjugate foci: Object placed at one end of lens will form a clear image on a screen kept at other side of lens. Conjugate foci vary in position. If object is nearer the lens, the image will be formed further away, at a greater magnification and inverted. This “real” image is formed by objective len ...
... Conjugate foci: Object placed at one end of lens will form a clear image on a screen kept at other side of lens. Conjugate foci vary in position. If object is nearer the lens, the image will be formed further away, at a greater magnification and inverted. This “real” image is formed by objective len ...
Optics Lesson 6
... note that a converging lens and concave mirror are also capable of producing virtual images if the object is within the focal length. ...
... note that a converging lens and concave mirror are also capable of producing virtual images if the object is within the focal length. ...
The Truth About Base Curves - ABO-NCLE
... (Fig. 2). Considering the pupil is between 3 to 5 mm. in diameter however, spherical aberration is not important since only a small portion of the lens is used at a given time7. Coma occurs when broad light rays pass obliquely through a lens. The axial light ray does not intersect at the same point ...
... (Fig. 2). Considering the pupil is between 3 to 5 mm. in diameter however, spherical aberration is not important since only a small portion of the lens is used at a given time7. Coma occurs when broad light rays pass obliquely through a lens. The axial light ray does not intersect at the same point ...
Telescopes
... Only one side of mirror has to be polished/flawless Mirror can be bigger than lenses because they can be supported from behind No chromatic aberration. ...
... Only one side of mirror has to be polished/flawless Mirror can be bigger than lenses because they can be supported from behind No chromatic aberration. ...
Light - PhysicsDCS
... Optical fibres: An optical fibre is a long, thin, transparent rod made of glass or plastic. Light is internally reflected from one end to the other, making it possible to send large chunks of information ...
... Optical fibres: An optical fibre is a long, thin, transparent rod made of glass or plastic. Light is internally reflected from one end to the other, making it possible to send large chunks of information ...
Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]
... This is a standard integral. Its value is π J1 ( ρ ) / ρ where J1 is the Bessel function of the first kind, order one. The ratio J1 ( ρ ) / ρ → 12 as ρ → 0 . The irradiance/intensity distribution is therefore given by ...
... This is a standard integral. Its value is π J1 ( ρ ) / ρ where J1 is the Bessel function of the first kind, order one. The ratio J1 ( ρ ) / ρ → 12 as ρ → 0 . The irradiance/intensity distribution is therefore given by ...
Advanced Optics Lab at San Jose State University Ramen
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
... illuminate a substantial part of the grating which will result in higher resolution. • (b) building a telescope The students select two doublet lenses for the telescope keeping in mind the fact that they have to overfill the pupil of their eyes so that the spectrum does not disappear on moving one's ...
CP2: Optics Why study optics? The problem of teaching optics
... • A converging lens will form a real image of an object on the opposite side of the lens, as long as the object is placed at least one focal length away. • A real image can be directly detected using, for example, photographic film, a CCD chip, or just a piece of paper • A real image can also be det ...
... • A converging lens will form a real image of an object on the opposite side of the lens, as long as the object is placed at least one focal length away. • A real image can be directly detected using, for example, photographic film, a CCD chip, or just a piece of paper • A real image can also be det ...
Image Formation by Spherical Lenses
... Spherical Lens : It is the segment of a sphere, and it refracts rays of light equally in all meridians.. Concave Lens: A concave lens causes light to spread out or diverge in which the reflecting surface curves inward. Convex Lens : A convex lens is a lens that is curved outward. The ends ...
... Spherical Lens : It is the segment of a sphere, and it refracts rays of light equally in all meridians.. Concave Lens: A concave lens causes light to spread out or diverge in which the reflecting surface curves inward. Convex Lens : A convex lens is a lens that is curved outward. The ends ...
L and M notes
... (nearsightedness) but larger if it is convex (farsightedness). Surgical techniques (e.g., laser surgery) have been developed to compensate for many eye problems. An eyeglass lens will form a virtual image at the person’s near-point where it can be seen clearly. The eye is not focusing on the object; ...
... (nearsightedness) but larger if it is convex (farsightedness). Surgical techniques (e.g., laser surgery) have been developed to compensate for many eye problems. An eyeglass lens will form a virtual image at the person’s near-point where it can be seen clearly. The eye is not focusing on the object; ...
1 CHAPTER 4 OPTICAL ABERRATIONS 4.1 Introduction We have
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
... The angle of incidence of the ray at R is 25.442 358 40 degrees to the normal, and the angle of refraction is 43.421 850 83 degrees. The net result of this is that there is a short linear “image” at T perpendicular to the tangential plane, and a short linear “image” at S perpendicular to the sagitta ...
Depth-of-Focus in Microscopy
... The basis of this formula is as follows. Consider two light emitting points along the axis of the optical system: one in-focus at position R and one out-of-focus at position R+∆z. Each point produces (according to the Huygens’ model) a spherical wavefront of light. Given a pupil that subtends an ang ...
... The basis of this formula is as follows. Consider two light emitting points along the axis of the optical system: one in-focus at position R and one out-of-focus at position R+∆z. Each point produces (according to the Huygens’ model) a spherical wavefront of light. Given a pupil that subtends an ang ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.











![Scalar Diffraction Theory and Basic Fourier Optics [Hecht 10.2.410.2.6, 10.2.8, 11.211.3 or Fowles Ch. 5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008906603_1-55857b6efe7c28604e1ff5a68faa71b2-300x300.png)





