Gullstrand equation
... The distances to those points placed inside the denser medium (inside the lens), as well as the radii of any convex faces in the lens, are positive lengths. This is the sign convention employed in this work instead of the usual convention of analytical geometry (Cartesian sign convention [7, 8]). ...
... The distances to those points placed inside the denser medium (inside the lens), as well as the radii of any convex faces in the lens, are positive lengths. This is the sign convention employed in this work instead of the usual convention of analytical geometry (Cartesian sign convention [7, 8]). ...
Lenses, the eye and other applications of light
... The diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass. On the diagram, use a ruler to draw two rays from the top of the object which show how and where the image is formed. Represent the image by an arrow drawn at the correct position. ...
... The diagram shows a converging lens being used as a magnifying glass. On the diagram, use a ruler to draw two rays from the top of the object which show how and where the image is formed. Represent the image by an arrow drawn at the correct position. ...
File
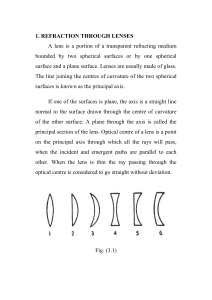
... Let a ray of monochromatic light parallel to the principal axis be incident on a thin lens at a height h above the axis and let f be the focal length of the lens. As the ray is parallel to the principal axis, after refraction it will pass through the second focus (Fig. 3.6). The deviation suffered b ...
... Let a ray of monochromatic light parallel to the principal axis be incident on a thin lens at a height h above the axis and let f be the focal length of the lens. As the ray is parallel to the principal axis, after refraction it will pass through the second focus (Fig. 3.6). The deviation suffered b ...
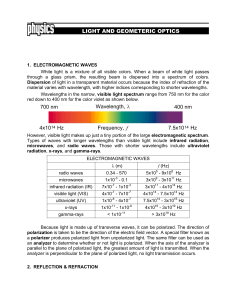
700 nm 400 nm Wavelength, λ Frequency, f 4x1014 Hz
... Because light rays do not actually pass through this image, it is known as a virtual image. In the case of a plane mirror, the image distance si from the mirror is the same as the object distance so from the mirror. The most common curved mirror is a spherical mirror. A concave or converging mirror ...
... Because light rays do not actually pass through this image, it is known as a virtual image. In the case of a plane mirror, the image distance si from the mirror is the same as the object distance so from the mirror. The most common curved mirror is a spherical mirror. A concave or converging mirror ...
Much Physics - Little Effort
... In order to have object and image in focus at the same time, they must be placed at an equal distance to the eye. In this case object distance and image distance are the same and the magnification factor is 1. It may be proved quite accurately, whether magnification 1 has in fact been obtained, if o ...
... In order to have object and image in focus at the same time, they must be placed at an equal distance to the eye. In this case object distance and image distance are the same and the magnification factor is 1. It may be proved quite accurately, whether magnification 1 has in fact been obtained, if o ...
plane mirrors - Madison Public Schools
... certain location, although the light never actually did (it was redirected by a mirror or lens to look like it did!) When a virtual image is formed, it can be seen by the human eye. However, it cannot be projected onto a screen! ...
... certain location, although the light never actually did (it was redirected by a mirror or lens to look like it did!) When a virtual image is formed, it can be seen by the human eye. However, it cannot be projected onto a screen! ...
P3.7.4.5 - LD Didactic
... filled with quartz sand is investigated (see Fig. 2). The microwave ray impinges vertically on the outer surface, which has a circular curvature, so that no refraction takes place there. Refraction does take place at the flat outer surface in the direction of air as medium, whose refractive index n2 ...
... filled with quartz sand is investigated (see Fig. 2). The microwave ray impinges vertically on the outer surface, which has a circular curvature, so that no refraction takes place there. Refraction does take place at the flat outer surface in the direction of air as medium, whose refractive index n2 ...
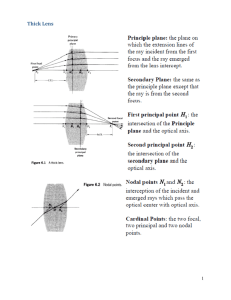
Thick Lens 1
... The following is simply a recipe for finding the aperture stop, entrance pupil, and exit pupil, given a lens system. Image all optical elements in the system into object space. Find the angle subtended by each element image at the on-axis position of the object. The element image with the smallest ...
... The following is simply a recipe for finding the aperture stop, entrance pupil, and exit pupil, given a lens system. Image all optical elements in the system into object space. Find the angle subtended by each element image at the on-axis position of the object. The element image with the smallest ...
Exposure and Imaging
... for a line, or 1.220 * 3.72 µm = 4.56 µm for a spot. – The tightest grating pitch that could be printed using this lens is therefore 2b = 7.44 µm. ...
... for a line, or 1.220 * 3.72 µm = 4.56 µm for a spot. – The tightest grating pitch that could be printed using this lens is therefore 2b = 7.44 µm. ...
Tutorial for Chapter 8
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
... A Gaussian beam of Rayleigh range z0 = 50 cm and wavelength = 488 nm is converted into another Gaussian beam with using a lens of focal length f = 5 cm at a distance z = 75 cm. Find the beam waist and location (from the lens) for the new Gaussian beam. ...
Astronomy 101 Lab: Telescopes
... Now, slowly turn the wheel to allow less and less light to pass through to the screen. 11. How does switching to smaller openings affect the image on the screen? This is the same effect that would be brought about by using a small diameter telescope rather than one with a larger diameter. This demon ...
... Now, slowly turn the wheel to allow less and less light to pass through to the screen. 11. How does switching to smaller openings affect the image on the screen? This is the same effect that would be brought about by using a small diameter telescope rather than one with a larger diameter. This demon ...
PPT
... • Rays passing through the center are not deviated • All parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f Slide by Steve Seitz ...
... • Rays passing through the center are not deviated • All parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f Slide by Steve Seitz ...
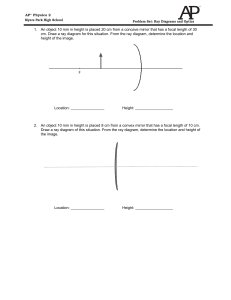
AP® Physics 2 Myers Park High School Problem Set: Ray Diagrams
... a. toward the normal b. away from the normal c. at an angle of 49° d. only if it is polarized 5. When a light beam emerges from water into air, the light speed _____. a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases 6. The image of the arrow is smaller than the arrow itself in which of the following ca ...
... a. toward the normal b. away from the normal c. at an angle of 49° d. only if it is polarized 5. When a light beam emerges from water into air, the light speed _____. a. increases b. remains the same c. decreases 6. The image of the arrow is smaller than the arrow itself in which of the following ca ...
How Do Lenses and Mirrors Affect Light?
... kinds of images. What are some objects that use lenses? What are the lenses being used for in these objects? Why do lenses work the way they do? Recall what you learned about light in Lesson 1. • Light always travels in straight lines. • Light travels more slowly through glass or plastic than air. • ...
... kinds of images. What are some objects that use lenses? What are the lenses being used for in these objects? Why do lenses work the way they do? Recall what you learned about light in Lesson 1. • Light always travels in straight lines. • Light travels more slowly through glass or plastic than air. • ...
Check focal lengths of board ray optics set Equipment o Graph
... o Board Laser Optics set with extension cord ...
... o Board Laser Optics set with extension cord ...
A crash course in optics
... 1/f (f measured in m): power of the lens, measured in diopters. 1 D = 1/m ...
... 1/f (f measured in m): power of the lens, measured in diopters. 1 D = 1/m ...
lecture 31 - magnifier, telescope
... If intermediate image were formed exactly at the focal point of the eyepiece, final image would be at . As it is, it will just be very far away. Regardless of how far away it is, though, the angle is given by the blue ray. ...
... If intermediate image were formed exactly at the focal point of the eyepiece, final image would be at . As it is, it will just be very far away. Regardless of how far away it is, though, the angle is given by the blue ray. ...
Ophthalmic lens
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
... Bull’s eye effect causes poor cosmetic appearance More conspicuous than other lens. ...
Lens Aberrations and Ray Tracing 1 Background
... Figure 9: Spherical aberration studies with a Michelson interferometer. Aberrations cannot be measured for smaller diameter lenses via the method used thus far. Diffraction will interfere with attempts to characterize smaller lenses if the beam diameter is comparable to the size of the lens. The bea ...
... Figure 9: Spherical aberration studies with a Michelson interferometer. Aberrations cannot be measured for smaller diameter lenses via the method used thus far. Diffraction will interfere with attempts to characterize smaller lenses if the beam diameter is comparable to the size of the lens. The bea ...
Seven Important Factors When Selecting a Machine
... The opening created by the iris of the lens. The relative size of the opening is described as the f-number. ...
... The opening created by the iris of the lens. The relative size of the opening is described as the f-number. ...
... that do not change the temporal and spatial characteristics of the pulses, or, if they must, that they do so in a well-characterized manner. In many experiments pulses need to be focused on an axis to achieve high intensity, normally a lens is used for this purpose, however, lenses have chromatic an ...
Physics II - Magnetism
... Here is a virtual image formed by a converging lens. Notice that the object is inside the focal point. When an object is placed at the focal point no image forms. This is shown in the next drawing. This is because all the rays are refracted in such a way that they are parallel to one another. They n ...
... Here is a virtual image formed by a converging lens. Notice that the object is inside the focal point. When an object is placed at the focal point no image forms. This is shown in the next drawing. This is because all the rays are refracted in such a way that they are parallel to one another. They n ...
concave lens
... when surrounded by material with a lower index of refraction it refracts parallel light rays so that the rays meet at a point. This is a concave lens because it is thinner in the middle than at the edges. A concave lens often is called a diverging lens because when surrounded by material with a lowe ...
... when surrounded by material with a lower index of refraction it refracts parallel light rays so that the rays meet at a point. This is a concave lens because it is thinner in the middle than at the edges. A concave lens often is called a diverging lens because when surrounded by material with a lowe ...
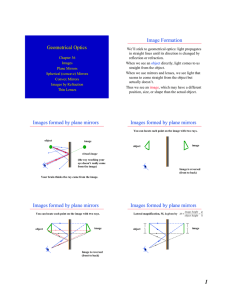
Geometrical Optics Image Formation Images formed by plane
... Note: every ray which leaves the tip of the object will go through the tip of the image! All other rays leaving from other locations on the object will go through that corresponding location on the image!!! Thus, the image looks like the object to the eye. ...
... Note: every ray which leaves the tip of the object will go through the tip of the image! All other rays leaving from other locations on the object will go through that corresponding location on the image!!! Thus, the image looks like the object to the eye. ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.