OPTICS
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
... a. Lenses in a slide projector or a camera produce real images C. Virtual Image-formed when the light rays from a common point pass through or are reflected by an optical system that causes them to diverge and appear to come to a single point. ...
Stop Faking It! Light
... light through matter (air or objects). Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through – i.e., glass window, water Translucent: letting light through but scattering it – i.e., wax paper Opaque: materials that do not let light through - reflects - i.e., wood, metal ...
... light through matter (air or objects). Transparent: materials that allow all light to pass through – i.e., glass window, water Translucent: letting light through but scattering it – i.e., wax paper Opaque: materials that do not let light through - reflects - i.e., wood, metal ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1D Instructions:
... A. will not undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will not undergo tota ...
... A. will not undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will not undergo tota ...
Training modules for an advanced interactive course on
... teaching of optical design. Since then a great deal of tutorial material has been prepared for conventional training methods, some of which is now available online. 2. The learning process First, it is worth looking at what a professional psychologist has to say about the learning process. Howard Ga ...
... teaching of optical design. Since then a great deal of tutorial material has been prepared for conventional training methods, some of which is now available online. 2. The learning process First, it is worth looking at what a professional psychologist has to say about the learning process. Howard Ga ...
Unit #3 - Optics Activity: D21 Observing Lenses (pg. 449) Lenses
... eyeglasses have one convex surface and one concave surface ...
... eyeglasses have one convex surface and one concave surface ...
Lect03_Bi177_MicroscopeOptics
... For object directly on focal point, rays focused to infinity. Where would this be useful? ...
... For object directly on focal point, rays focused to infinity. Where would this be useful? ...
Microscope Objective
... only way to focus is to move the specimen or move the entire optical system (objective, tube lenses, eyepiece). ...
... only way to focus is to move the specimen or move the entire optical system (objective, tube lenses, eyepiece). ...
General Introduction of Optical
... In many cases, the best coupling you can get occurs when you match the f/# between optical systems. Realistic f/#’s: ...
... In many cases, the best coupling you can get occurs when you match the f/# between optical systems. Realistic f/#’s: ...
Universal Description of Spherical Aberration Free Lenses
... small enough aperture; the two derivations must agree on the lens central radius of curvature. Ray tracing confirms this formula applies for both positive and negative index and correctly gives a change in the concavity at n = 1. Because this formula is antisymmetric about n = 1, (Fig. 3), we cannot ...
... small enough aperture; the two derivations must agree on the lens central radius of curvature. Ray tracing confirms this formula applies for both positive and negative index and correctly gives a change in the concavity at n = 1. Because this formula is antisymmetric about n = 1, (Fig. 3), we cannot ...
Physics 263 Experiment 6 Geometric Optics 1 Refraction
... 2. Move the lens to a position where an image of the object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. 3. Repeat the above procedure for a least 3 additional, different object distances. Enter the data into a spreadsheet. Plot 1/do vs. 1/di . Use trend-line informat ...
... 2. Move the lens to a position where an image of the object is formed on the screen. Measure the image distance and the object distance. 3. Repeat the above procedure for a least 3 additional, different object distances. Enter the data into a spreadsheet. Plot 1/do vs. 1/di . Use trend-line informat ...
Chapter 33
... A convex meniscus lens is made from glass with n = 1.50. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is 22.4 cm and that of the concave surface is 46.2 cm. (a) What is the focal length? (b) Where will the image be for an object 2.00 m away? ...
... A convex meniscus lens is made from glass with n = 1.50. The radius of curvature of the convex surface is 22.4 cm and that of the concave surface is 46.2 cm. (a) What is the focal length? (b) Where will the image be for an object 2.00 m away? ...
Hmwk 2 - People Server at UNCW
... Due: February 11 (Friday COB) Instructions: Complete the following problems showing all work. Please write as legibly as possible. If your handwriting is a problem use a text editor. 1. a. Write down the lens equation. b. Under what condition is the focal length equal to z’ ( distance of image plane ...
... Due: February 11 (Friday COB) Instructions: Complete the following problems showing all work. Please write as legibly as possible. If your handwriting is a problem use a text editor. 1. a. Write down the lens equation. b. Under what condition is the focal length equal to z’ ( distance of image plane ...
Exercise 13 Geometrical and Technical Optics WS 2013/2014
... refractive lens should be 6 mm. First, the diffractive lens should only have a parabolic phase function =2ar2 and a=-1/(2df’2) (focal length of the diffractive lens f’2). b) Calculate the phase function of the diffractive lens in such a way that it corrects the spherical aberration for the wavele ...
... refractive lens should be 6 mm. First, the diffractive lens should only have a parabolic phase function =2ar2 and a=-1/(2df’2) (focal length of the diffractive lens f’2). b) Calculate the phase function of the diffractive lens in such a way that it corrects the spherical aberration for the wavele ...
Optical Telescopes
... That happened in 1608, when the German-born Dutch eyeglass maker had guessed to combine several lenses and created the first telescope [PRAS]. This occasion is now almost forgotten, because no inventions were made but a Dutchman. His device was not used for astronomical purposes, and it found its ap ...
... That happened in 1608, when the German-born Dutch eyeglass maker had guessed to combine several lenses and created the first telescope [PRAS]. This occasion is now almost forgotten, because no inventions were made but a Dutchman. His device was not used for astronomical purposes, and it found its ap ...
Chapter 5: Geometrical Optics
... Image: If a cone of rays emitted from a point source S arrives at a certain point P, then P is called the image of S. Diffraction-limited image: The size of the image for a point source is not zero. The limited size of an optical system causes the blur of the image point due to diffraction effect: ...
... Image: If a cone of rays emitted from a point source S arrives at a certain point P, then P is called the image of S. Diffraction-limited image: The size of the image for a point source is not zero. The limited size of an optical system causes the blur of the image point due to diffraction effect: ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they converge at a common focal point in front of the mirror. Convex mirrors produce diverging rays with a foc ...
... incidence for a reflected ray of light. The angles are defined with respect to the direction perpendicular to the reflecting surface called the normal. 2. Concave mirrors focus rays so that they converge at a common focal point in front of the mirror. Convex mirrors produce diverging rays with a foc ...
File
... 3. (a) The image formed by a spherical mirror may be larger, smaller, or equal in size to the object. If the magnification of the mirror is negative, describe the image of the object. ...
... 3. (a) The image formed by a spherical mirror may be larger, smaller, or equal in size to the object. If the magnification of the mirror is negative, describe the image of the object. ...
EE119 Homework 7: Microscopes, Projectors and Photomultiplier
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
... The positive solution to this quadratic equation is fo = 0.5. Notice that if the working distance were larger, then fo could be larger too. But let’s use fo = 0.5here. This means that the eyepiece focal length should be 8/(3×0.5)=16/3=5.333 cm. Now we need to find some diameters for these lenses. Fo ...
You want to project a real image of an object using
... placed below the principal axis of the mirror. The diagram below illustrates the situation. ...
... placed below the principal axis of the mirror. The diagram below illustrates the situation. ...
Subject: Precision Optics II Grade: 10
... 1. Investigating the EM spectrum: interactions between light and matter. 1. Analyze a situation and identify the type of EM 2. Light’s journey from air into and out of glass: What happens at the radiation at play. boundaries and in the bulk? 2. Qualitatively predict the path of light from air 3. Law ...
... 1. Investigating the EM spectrum: interactions between light and matter. 1. Analyze a situation and identify the type of EM 2. Light’s journey from air into and out of glass: What happens at the radiation at play. boundaries and in the bulk? 2. Qualitatively predict the path of light from air 3. Law ...
PDF - Bridgend Astronomical Society
... available to amateurs. But first things first, all astronomical telescopes invert images. Some laterally reverse (mirror image) them too! The reason is simple, the more lenses used, the more the image is degraded. So inverting lenses (used in terrestrial telescopes) are omitted. The problem with all ...
... available to amateurs. But first things first, all astronomical telescopes invert images. Some laterally reverse (mirror image) them too! The reason is simple, the more lenses used, the more the image is degraded. So inverting lenses (used in terrestrial telescopes) are omitted. The problem with all ...
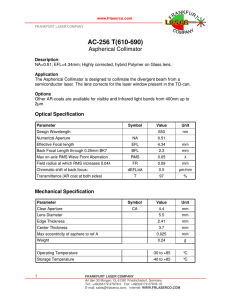
AC-256 T(610-690) - Frankfurt Laser Company
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
... The Aspherical Collimator is designed to collimate the divergent beam from a semiconductor laser. The lens corrects for the laser window present in the TO-can. Options Other AR-coats are available for visible and Infrared light bands from 400nm up to 2µm ...
chapter3lenses
... rules are an approximation. For this approximation to be accurate, the paraxial rays should be closer to the axis, and the object should be small compared to the mirror radius. • We’ve drawn these examples in an exaggerated manner, because it is easier to see. • This is still a very useful technique ...
... rules are an approximation. For this approximation to be accurate, the paraxial rays should be closer to the axis, and the object should be small compared to the mirror radius. • We’ve drawn these examples in an exaggerated manner, because it is easier to see. • This is still a very useful technique ...
Chapter 34 – Geometric Optics and Optical Instruments
... Two identical spherical mirrors with radius R are separated by a distance equal to their focal length, f = R/2. An object is placed on the surface of one of the mirrors. After undergoing two reflections, where will the image be located, and what kind of image is it? If a small hole is made in the mi ...
... Two identical spherical mirrors with radius R are separated by a distance equal to their focal length, f = R/2. An object is placed on the surface of one of the mirrors. After undergoing two reflections, where will the image be located, and what kind of image is it? If a small hole is made in the mi ...
RIT CIS - Rochester Institute of Technology
... uncertainty, involving statistical evaluations of data. However, it is always essential for the experimentalist to compare such statistical estimates of uncertainty with his or her qualitative judgment of uncertainty. It is never correct to justify results by saying "that's what the computer said". ...
... uncertainty, involving statistical evaluations of data. However, it is always essential for the experimentalist to compare such statistical estimates of uncertainty with his or her qualitative judgment of uncertainty. It is never correct to justify results by saying "that's what the computer said". ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.