Aberration-Free Ultrathin Flat Lenses and Axicons at Telecom
... and 2, we design two lenses with radius r = 0.45 mm and focal lengths f = 3 cm (NA = 0.015) and f = 6 cm (NA = 0.075), respectively, and an axicon with the same radius and an angle β = 0.5°. The devices are fabricated by patterning one face of a double-side-polished undoped silicon wafer with gold n ...
... and 2, we design two lenses with radius r = 0.45 mm and focal lengths f = 3 cm (NA = 0.015) and f = 6 cm (NA = 0.075), respectively, and an axicon with the same radius and an angle β = 0.5°. The devices are fabricated by patterning one face of a double-side-polished undoped silicon wafer with gold n ...
ECEN 4616/5616 Optoelectronic Design
... Laying out a Coronagraph Another serious design constraint is to determine the rate at which the PSF from the first lens decays, and whether that is enough to mask the image from the dim object(s). The larger the first lens, the smaller the angular extent of the PSF, so the PSF dropoff and angular ...
... Laying out a Coronagraph Another serious design constraint is to determine the rate at which the PSF from the first lens decays, and whether that is enough to mask the image from the dim object(s). The larger the first lens, the smaller the angular extent of the PSF, so the PSF dropoff and angular ...
solar.gmu.edu
... • Stretch your arm forward and extend your thumb, thumb facing your eyes • Close one eye and move your thumb so that, looking with your open eye , you see your thumbnail covering the landmark A • Then open the eye you had closed and close the one with which you looked before, without moving your thu ...
... • Stretch your arm forward and extend your thumb, thumb facing your eyes • Close one eye and move your thumb so that, looking with your open eye , you see your thumbnail covering the landmark A • Then open the eye you had closed and close the one with which you looked before, without moving your thu ...
10_Lenses - Savita Pall and Chemistry
... As with mirrors, once the principal focus, (a.k.a.: focal point), has been located, three key rays passing through the lens, close to the principal axis are chosen, to locate the image: Ray 1: starts at the top of the object, (usually a solid, erect arrow), travels parallel to the principal axis and ...
... As with mirrors, once the principal focus, (a.k.a.: focal point), has been located, three key rays passing through the lens, close to the principal axis are chosen, to locate the image: Ray 1: starts at the top of the object, (usually a solid, erect arrow), travels parallel to the principal axis and ...
Lab 2: Abbe Theory of Imaging
... The set-up is now ready for the examination of slides. The image will be observed on an index card in another modified target assembly. The location of the observation plane will be about 450mm after the last lens and will give an image about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the b ...
... The set-up is now ready for the examination of slides. The image will be observed on an index card in another modified target assembly. The location of the observation plane will be about 450mm after the last lens and will give an image about twice the size as the object slide when the card at the b ...
Intraocular Lenses
... plate is proportional to , so different colors focus at different distances from the zone plate. Ordinary refractive lenses have chromatic aberration as well, but much less pronounced than zone plates. For example: +10 D lens made of glass with an Abbe number of 30 (high dispersion) has CA ~ 0.3 D ...
... plate is proportional to , so different colors focus at different distances from the zone plate. Ordinary refractive lenses have chromatic aberration as well, but much less pronounced than zone plates. For example: +10 D lens made of glass with an Abbe number of 30 (high dispersion) has CA ~ 0.3 D ...
Document
... Flint glass is an optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number. Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45-2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is com ...
... Flint glass is an optical glass that has relatively high refractive index and low Abbe number. Flint glasses are arbitrarily defined as having an Abbe number of 50 to 55 or less. The currently known flint glasses have refractive indices ranging between 1.45-2.00. A concave lens of flint glass is com ...
2 Modeling and Design of Lens Systems
... This property of the optical system is useful e.g. for measurement tasks: if the image plane is fixed at the position O’ a change of the object distance would only lead to a defocus but the lateral magnification of the image remains constant! Placing the stop in the front focal plane F would give an ...
... This property of the optical system is useful e.g. for measurement tasks: if the image plane is fixed at the position O’ a change of the object distance would only lead to a defocus but the lateral magnification of the image remains constant! Placing the stop in the front focal plane F would give an ...
DVD Optical System Design
... Before outlining different approaches, let me first point out some considerations: • Due to the fact that I will be dealing with conventional DVD discs, I will have to deal with pits that reflect, so if I choose a design that has a normal incidence beam onto the disc, I have to figure out a way to d ...
... Before outlining different approaches, let me first point out some considerations: • Due to the fact that I will be dealing with conventional DVD discs, I will have to deal with pits that reflect, so if I choose a design that has a normal incidence beam onto the disc, I have to figure out a way to d ...
Chapter O5
... for the muscles of the eye. To focus at the near point the eye muscles must pull quite hard and this results in a great deal of eye strain. It is much more comfortable to relax the eye and view images located infinitely far away. This configuration reduces the magnification slightly but is much less ...
... for the muscles of the eye. To focus at the near point the eye muscles must pull quite hard and this results in a great deal of eye strain. It is much more comfortable to relax the eye and view images located infinitely far away. This configuration reduces the magnification slightly but is much less ...
Light microscopy
... a millimetre. By aligning the two scales as shown below you can work out how the divisions of the graticule correspond to micrometres at this magnification. ...
... a millimetre. By aligning the two scales as shown below you can work out how the divisions of the graticule correspond to micrometres at this magnification. ...
Optical Instruments - Dr. Dr. Bill`s Page
... A radiuscope produces a virtual object conjugate to the eye of the observer. The observer adjusts the instrument up and down until he finds two different positions at which he can see the image of that object clearly. The radius of curvature of the surface is the physical distance the instrument mov ...
... A radiuscope produces a virtual object conjugate to the eye of the observer. The observer adjusts the instrument up and down until he finds two different positions at which he can see the image of that object clearly. The radius of curvature of the surface is the physical distance the instrument mov ...
Sign convention
... 1. A ray through the center of the lens is undeviated 2. An incident ray parallel to the optic axis appears to emerge from the front focal point 3. An incident ray directed towards the back focal point emerges parallel to the optic axis. and occasionally useful 4. Two rays that are parallel in front ...
... 1. A ray through the center of the lens is undeviated 2. An incident ray parallel to the optic axis appears to emerge from the front focal point 3. An incident ray directed towards the back focal point emerges parallel to the optic axis. and occasionally useful 4. Two rays that are parallel in front ...
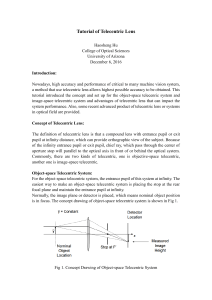
Tutorial of Telecentric Lens
... This photo comparison shows the difference image function between angular field of view conventional lens and zero angle field of view telecentric lens clearly. The photo taken by zero angle field of view telecentric lens is hard to tell which cube is in front of the other, but for the photo taken b ...
... This photo comparison shows the difference image function between angular field of view conventional lens and zero angle field of view telecentric lens clearly. The photo taken by zero angle field of view telecentric lens is hard to tell which cube is in front of the other, but for the photo taken b ...
cameras - Purdue Engineering
... are 400-800 km) and you want to see lots of detail in the scene? ...
... are 400-800 km) and you want to see lots of detail in the scene? ...
Chapter 1 - Liceo Crespi
... electromagnetic waves and light Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with electric and magnetic field components, which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a me ...
... electromagnetic waves and light Electromagnetic waves are transverse waves with electric and magnetic field components, which oscillate in phase perpendicular to each other and to the direction of wave propagation. Unlike a wave on a string or a sound wave, electromagnetic waves do not require a me ...
09Optics
... – Image formed is VIRTUAL (appears behind mirror where no light actually falls.) – Image is upright. ...
... – Image formed is VIRTUAL (appears behind mirror where no light actually falls.) – Image is upright. ...
A method for characterizing longitudinal chromatic aberration of
... us to remove the chromatic effect of the collimating lens from the final results presented in the following figures. It should be noted, however, that for most objective lenses the effect of the collimating lens on the overall longitudinal chromatic aberration was negligible. Indeed, we believe the ...
... us to remove the chromatic effect of the collimating lens from the final results presented in the following figures. It should be noted, however, that for most objective lenses the effect of the collimating lens on the overall longitudinal chromatic aberration was negligible. Indeed, we believe the ...
F - mjburns.net
... light moving from air into glass will move toward the normal light moving from glass back into air will move away from the normal virtual focus ...
... light moving from air into glass will move toward the normal light moving from glass back into air will move away from the normal virtual focus ...
The Camera
... A lens focuses light onto the film • Rays passing through the center are not deviated • All parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f Slide by Steve Seitz ...
... A lens focuses light onto the film • Rays passing through the center are not deviated • All parallel rays converge to one point on a plane located at the focal length f Slide by Steve Seitz ...
Chapter 3 Geometric Optics
... measured relative to the normal to the surfaces. In the geometric optics picture, a ray of light travels through a uniform medium in a straight line until a new interface is reached. The ray is deflected according to Equations 3.1 and 3.2, and this process is repeated until the light reaches its fin ...
... measured relative to the normal to the surfaces. In the geometric optics picture, a ray of light travels through a uniform medium in a straight line until a new interface is reached. The ray is deflected according to Equations 3.1 and 3.2, and this process is repeated until the light reaches its fin ...
Ray Optics - UMD Physics
... Similarly, the focal length is the distance from the lens at which rays will refract out of the lens parallel to the optical axis. ...
... Similarly, the focal length is the distance from the lens at which rays will refract out of the lens parallel to the optical axis. ...
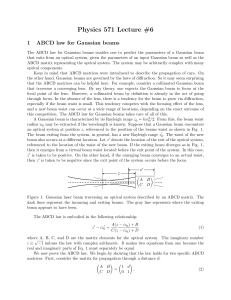
ABCD law for Gaussian laser beams
... through a distance d and transmission through a thin lens with focal length f (or a concave mirror with focal length f ). From these elements we can derive more complicated systems. The ABCD matrix for a thick lens cannot be constructed from just these two elements. However, we can construct the mat ...
... through a distance d and transmission through a thin lens with focal length f (or a concave mirror with focal length f ). From these elements we can derive more complicated systems. The ABCD matrix for a thick lens cannot be constructed from just these two elements. However, we can construct the mat ...
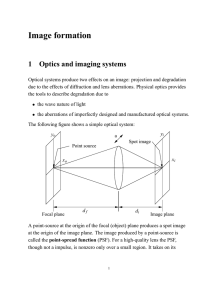
pupil function - UCT Digital Image Processing
... A point-source at the origin of the focal (object) plane produces a spot image at the origin of the image plane. The image produced by a point-source is called the point-spread function (PSF). For a high-quality lens the PSF, though not a impulse, is nonzero only over a small region. It takes on its ...
... A point-source at the origin of the focal (object) plane produces a spot image at the origin of the image plane. The image produced by a point-source is called the point-spread function (PSF). For a high-quality lens the PSF, though not a impulse, is nonzero only over a small region. It takes on its ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.