lecture1
... Distortion in lens in which there is a failure to focus different wavelength rays to converge on same point. • In light it’s the different color wavelengths • In electrons shorter wavelength electrons are more energetic and have a longer focal length than longer wavelength electrons. ...
... Distortion in lens in which there is a failure to focus different wavelength rays to converge on same point. • In light it’s the different color wavelengths • In electrons shorter wavelength electrons are more energetic and have a longer focal length than longer wavelength electrons. ...
Designing an Experimental Prototype to Support Geometric Optics
... spherical and no spherical surfaces, possibly constructed ...
... spherical and no spherical surfaces, possibly constructed ...
light microscopy
... resolution in the plane perpendicular to the optical axis. Another important aspect to resolution is the axial (or longitudinal) resolving power of an objective, which is measured parallel to the optical axis and is most often referred to as depth of field. • Depth of field is determined by the dist ...
... resolution in the plane perpendicular to the optical axis. Another important aspect to resolution is the axial (or longitudinal) resolving power of an objective, which is measured parallel to the optical axis and is most often referred to as depth of field. • Depth of field is determined by the dist ...
Chapter 9. Computer vision
... frequency, then the sinusoid will continue to be a sinusoid and the contras will continue to be one. The ideal mathematical model ignores the effect of noise in the signal. Noise will be an important factor in coherent imaging. The presence of foreign particulates in the optical system will cause li ...
... frequency, then the sinusoid will continue to be a sinusoid and the contras will continue to be one. The ideal mathematical model ignores the effect of noise in the signal. Noise will be an important factor in coherent imaging. The presence of foreign particulates in the optical system will cause li ...
GGN PUBLIC SCHOOL, LUDHIANA XII PHYSICS ASSIGNMENT
... will the lens behave when μL >μM. 4. A diverging lens of focal length f is cut into two identical parts each forming a plano-concave lens. What is the focal length of each part? 5. Why the scratches on the lens of a photographic camera do not appear on the photograph? 6. What happens to the focal le ...
... will the lens behave when μL >μM. 4. A diverging lens of focal length f is cut into two identical parts each forming a plano-concave lens. What is the focal length of each part? 5. Why the scratches on the lens of a photographic camera do not appear on the photograph? 6. What happens to the focal le ...
AQA GCSE Physics P3 Revision Worksheet
... A body is said to be accelerating when its velocity is changing. So the moon is accelerating all the time, although its speed remains the same. The direction of this acceleration is always towards the centre of the circle. What is the name given to this (centre-seeking) acceleration? ...
... A body is said to be accelerating when its velocity is changing. So the moon is accelerating all the time, although its speed remains the same. The direction of this acceleration is always towards the centre of the circle. What is the name given to this (centre-seeking) acceleration? ...
Plane Mirrors
... Two types of lenses are biconvex lenses, which are converging lenses and biconcave lenses, which are diverging lenses. Converging6 lenses are thicker in the center than at the edges, while diverging lenses are thicker at the edges that in the center. ...
... Two types of lenses are biconvex lenses, which are converging lenses and biconcave lenses, which are diverging lenses. Converging6 lenses are thicker in the center than at the edges, while diverging lenses are thicker at the edges that in the center. ...
Acknowledgments
... measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved basis. In many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the s ...
... measurements. Optical techniques are widely used in many areas of the thermal sciences for measuring system temperatures, velocities, and species on a time- and space-resolved basis. In many cases these non-intrusive optical devices have significant advantages over physical probes that perturb the s ...
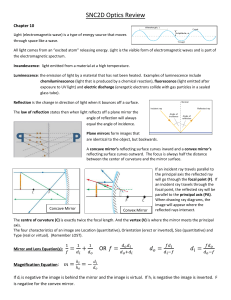
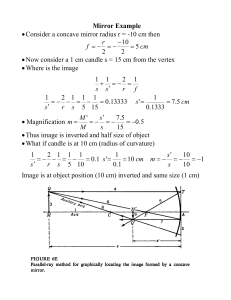
Mirror Example • Consider a concave mirror radius r =
... Image appears to be behind the mirror by 5 cm Image is virtual – light is expanding from mirror Image is erect and twice object size Do not see image if place something at image position With graphical method must project C & F lines to right side Shows size of image there For convex m ...
... Image appears to be behind the mirror by 5 cm Image is virtual – light is expanding from mirror Image is erect and twice object size Do not see image if place something at image position With graphical method must project C & F lines to right side Shows size of image there For convex m ...
chapter9-Section4
... 2. The ray that passes through the focal point (F’) on the same side of the lens as the object emerges parallel to the optical axis. 3. The ray that goes exactly through the center of the lens is undeviated because the two interfaces it encounters are parallel. ...
... 2. The ray that passes through the focal point (F’) on the same side of the lens as the object emerges parallel to the optical axis. 3. The ray that goes exactly through the center of the lens is undeviated because the two interfaces it encounters are parallel. ...
the optical (light) microscope
... Tungsten-halogen filament lamps are also widely used for their high intensity and high colour temperature. Light intensity can be controlled by varying the current or by use of neutral-density filters. Other light sources, such as the zirconium-arc, sodium-arc, quartziodine, or mercury-vapor lam ...
... Tungsten-halogen filament lamps are also widely used for their high intensity and high colour temperature. Light intensity can be controlled by varying the current or by use of neutral-density filters. Other light sources, such as the zirconium-arc, sodium-arc, quartziodine, or mercury-vapor lam ...
Optical laser beam scanner lens relay system
... with standard, i.e. commonly available lenses. Nevertheless, a very good performance can be obtained with a little bit of care in the design. Even a very simple design using achromats is adequate, although significantly improved performance can be obtained if meniscus lenses are added. The general r ...
... with standard, i.e. commonly available lenses. Nevertheless, a very good performance can be obtained with a little bit of care in the design. Even a very simple design using achromats is adequate, although significantly improved performance can be obtained if meniscus lenses are added. The general r ...
Overview of various methods for measuring a lens focal length
... The lens power is measured for different positions of the source. The author of this method claims that routinely measurements are made with less than 0.5% accuracy. ...
... The lens power is measured for different positions of the source. The author of this method claims that routinely measurements are made with less than 0.5% accuracy. ...
Light Revision
... Hint: your cornea and water have a similar refractive index Light refracts when travelling from air through the cornea of your eye, but water and the cornea have the same refractive index , so light does not refract. By wearing goggles however light which hits your eye is coming from air, so t ...
... Hint: your cornea and water have a similar refractive index Light refracts when travelling from air through the cornea of your eye, but water and the cornea have the same refractive index , so light does not refract. By wearing goggles however light which hits your eye is coming from air, so t ...
Interference I - Galileo and Einstein
... very short focal length. The optics are just those of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification ...
... very short focal length. The optics are just those of the magnifying glass discussed above. • The simplest compound microscope has two convex lenses: the first (objective) forms a real (inverted) image, the second (eyepiece) acts as a magnifying glass to examine that image. • The total magnification ...
Physics for Scientists & Engineers 2
... ! We start with a ray along the optical axis of the lens that passes straight through the lens that defines the bottom of the image. ! A second ray is then drawn from the top of the object parallel to the optical axis • This ray is focused through the focal point on the other side of the lens ...
... ! We start with a ray along the optical axis of the lens that passes straight through the lens that defines the bottom of the image. ! A second ray is then drawn from the top of the object parallel to the optical axis • This ray is focused through the focal point on the other side of the lens ...
RAY OPTICS I
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
... Note that in Figure 6.2, we have drawn the rays as if the lens bends them suddenly at the exact center of the lens. Actually, each ray is bent a certain amount when it enters the lens and a certain amount more when it leaves the lens. If the lens is very thin compared to its focal length (or other i ...
lens theory - Laser Components
... excellent as far as the positioning of the elements is concerned. However, due to diffraction, the magnifications encountered may be completely different than those calculated from geometric optics. Use the familiar ABCD matrix formalism. If you treat the lenses as thin lenses, use distances between ...
... excellent as far as the positioning of the elements is concerned. However, due to diffraction, the magnifications encountered may be completely different than those calculated from geometric optics. Use the familiar ABCD matrix formalism. If you treat the lenses as thin lenses, use distances between ...
Many other important inventions involve the use of
... Egyptian hieroglyphs in the 6th century BC, which depict "simple glass meniscal lenses". The earliest written record of magnification dates back to the 1st century AD, when Seneca the Younger, a tutor of Emperor Nero who wrote that letters, however small and indistinct, are seen enlarged and more cl ...
... Egyptian hieroglyphs in the 6th century BC, which depict "simple glass meniscal lenses". The earliest written record of magnification dates back to the 1st century AD, when Seneca the Younger, a tutor of Emperor Nero who wrote that letters, however small and indistinct, are seen enlarged and more cl ...
Forensic Science
... •A microscope is an optical instrument that uses a lens or a combination of lenses to magnify and resolve the fine details of an object. •The earliest methods for examining physical evidence relied solely on the microscope. •The magnified image seen by looking through a lens is known as a virtual im ...
... •A microscope is an optical instrument that uses a lens or a combination of lenses to magnify and resolve the fine details of an object. •The earliest methods for examining physical evidence relied solely on the microscope. •The magnified image seen by looking through a lens is known as a virtual im ...
Chapter 23
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
... Two converging lenses having focal lengths of 10.0 cm and 20.0 cm are placed 50.0 cm apart, as shown in the figure. The final image is to be located between the lenses, at the position indicated. (a) How far to the left of the first lens should the object be positioned? (b) What is the overall magni ...
Presentation
... displays. A twisted nematic (TN) cell liquid crystal is used as polarization switch to control the optical path length through the system. Different polarization state leads to different path length in the proposed optical system, which in turn results in different focal length. ...
... displays. A twisted nematic (TN) cell liquid crystal is used as polarization switch to control the optical path length through the system. Different polarization state leads to different path length in the proposed optical system, which in turn results in different focal length. ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.