
F - DCS Physics
... A converging lens is used as a magnifying glass. Draw a ray diagram to show how an erect image is formed by a magnifying glass. A diverging lens cannot be used as a magnifying glass. Explain why. The converging lens has a focal length of 8 cm. Determine the two positions that an object can be ...
... A converging lens is used as a magnifying glass. Draw a ray diagram to show how an erect image is formed by a magnifying glass. A diverging lens cannot be used as a magnifying glass. Explain why. The converging lens has a focal length of 8 cm. Determine the two positions that an object can be ...
$doc.title
... Airy disk. It extends to the first dark ring whose size is given by the first zero of the Bessel function, namely, ρ = 3.832 . The angular radius of the first dark ring is thus given by 3.832 1.22λ sin θ = ...
... Airy disk. It extends to the first dark ring whose size is given by the first zero of the Bessel function, namely, ρ = 3.832 . The angular radius of the first dark ring is thus given by 3.832 1.22λ sin θ = ...
Science Olympiad 2011 Practice Optics C
... collimated light source has a radius of curvature of exactly 30 cm, and the surface facing away from the light source has a radius of curvature of exactly 70 cm. The thickness of the lens at its axis is exactly 1 mm. The lens is made of Pyrex, which has a refractive index of exactly 1.474. Use the l ...
... collimated light source has a radius of curvature of exactly 30 cm, and the surface facing away from the light source has a radius of curvature of exactly 70 cm. The thickness of the lens at its axis is exactly 1 mm. The lens is made of Pyrex, which has a refractive index of exactly 1.474. Use the l ...
Correcting chromatic aberrations using a diffraction grating in a
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
... In 1800 Thomas Young demonstrated interference patterns in light [3]. He shone monochromatic light at two screens. The first had one narrow slit in it, which had the effect of only letting light from a small part of the source through, and resulted in the transmitted light being fairly coherent. The ...
Imaging
... The light gathering capacity of a camera lens is determined by its aperture. Aperture can be no larger than the diameter of the lens itself, and it is usually made smaller this by means of a diaphragm – a circular hole of adjustable size, incorporated into the lens. It is normal to express the aper ...
... The light gathering capacity of a camera lens is determined by its aperture. Aperture can be no larger than the diameter of the lens itself, and it is usually made smaller this by means of a diaphragm – a circular hole of adjustable size, incorporated into the lens. It is normal to express the aper ...
GEOMETRIC OPTICS I. What is GEOMTERIC OPTICS In geometric
... focal point-the point on the axis of a lens or mirror to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction or reflection radius of curvature-a point beyond the focal point that indicates how curved a lens or mirror is virtual image-an optical image from whic ...
... focal point-the point on the axis of a lens or mirror to which parallel rays of light converge or from which they appear to diverge after refraction or reflection radius of curvature-a point beyond the focal point that indicates how curved a lens or mirror is virtual image-an optical image from whic ...
LAB #10 - GEOCITIES.ws
... To relate image and object distances to focal lengths for various lenses. To be able to determine focal length, image size, brightness, and f-numbers for various lenses. To understand the differences between telescopic systems and astronomical telescopes of various types. To construct a simple refra ...
... To relate image and object distances to focal lengths for various lenses. To be able to determine focal length, image size, brightness, and f-numbers for various lenses. To understand the differences between telescopic systems and astronomical telescopes of various types. To construct a simple refra ...
LM Ch 4: Optics
... 1600’s invented microscopes that used single simple lenses of his own design. Some of his lenses had a magnification in the range of 400X! Using Figure 4.15 his microscopes, Leuwenhook made the first observations of many simple organisms. Compound Lenses There are four basic lens shapes: double conv ...
... 1600’s invented microscopes that used single simple lenses of his own design. Some of his lenses had a magnification in the range of 400X! Using Figure 4.15 his microscopes, Leuwenhook made the first observations of many simple organisms. Compound Lenses There are four basic lens shapes: double conv ...
Chapt23_VG0
... based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original components. See Chapter 24.3 ...
... based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original components. See Chapter 24.3 ...
Newton`s Rings - Manchester HEP
... interference of light will be used to determine the wavelength, , of a light source. The interference fringe system here is a pattern of concentric circles, the diameter of which you will measure with a travelling microscope (which has a Vernier scale). If a clean convex lens is placed on a clean ...
... interference of light will be used to determine the wavelength, , of a light source. The interference fringe system here is a pattern of concentric circles, the diameter of which you will measure with a travelling microscope (which has a Vernier scale). If a clean convex lens is placed on a clean ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1E Instructions:
... A. will undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will undergo total intern ...
... A. will undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will undergo total intern ...
Glossary
... MTF…"Modulation Transfer Function". Indicates the contrast of a B/W pattern at a given [high] spatial frequency relative to the contrast at low spatial frequencies. It's used to measure and quantify the resolution of a lens. ND…"Neutral Density" A material (usually a filter) that blocks some light ...
... MTF…"Modulation Transfer Function". Indicates the contrast of a B/W pattern at a given [high] spatial frequency relative to the contrast at low spatial frequencies. It's used to measure and quantify the resolution of a lens. ND…"Neutral Density" A material (usually a filter) that blocks some light ...
Lecture 14: Lenses
... beam and a concave lens forms a diverging beam. The centre of the lens is called the optical centre and the direction through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens is called the principal axis. A beam parallel to the principal axis will form a converging beam with a convex lens and a dive ...
... beam and a concave lens forms a diverging beam. The centre of the lens is called the optical centre and the direction through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens is called the principal axis. A beam parallel to the principal axis will form a converging beam with a convex lens and a dive ...
APPENDIX When designing shape magnification into a lens, the two
... nomograph (see Figure A1) is a simple graphic way to represent the relationship between magnification, ...
... nomograph (see Figure A1) is a simple graphic way to represent the relationship between magnification, ...
Exam 4 Solutions
... Solution: We learned that when thin lenses are put next to one another the total focal length is found from 1/ f = 1/ f1 + 1/ f 2 . This gives the values shown. You can also work it out manually. If an object is placed a distance p from f1, then the image location q is found from 1/q = 1/ f1 "1/ p . ...
... Solution: We learned that when thin lenses are put next to one another the total focal length is found from 1/ f = 1/ f1 + 1/ f 2 . This gives the values shown. You can also work it out manually. If an object is placed a distance p from f1, then the image location q is found from 1/q = 1/ f1 "1/ p . ...
Image Formation & Optical Instruments
... A ray parallel to the mirror axis reflects through the focal point f A ray passing through the focus reflects parallel to the axis A ray that strikes the center of the mirror reflects symmetrically A ray passing through the center of curvature c, returns on itself ...
... A ray parallel to the mirror axis reflects through the focal point f A ray passing through the focus reflects parallel to the axis A ray that strikes the center of the mirror reflects symmetrically A ray passing through the center of curvature c, returns on itself ...
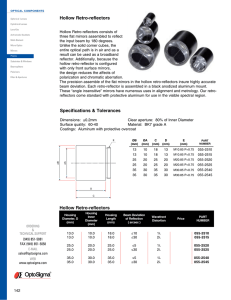
Convex Lenses and Mirrors
... before. Then you will form an image using a convex mirror and determine its radius of curvature. Place the lens on the optical bench near the object and move it away from the object until you have passed the first ‘faint’ image formation. Replace the plane mirror with the convex mirror and posit ...
... before. Then you will form an image using a convex mirror and determine its radius of curvature. Place the lens on the optical bench near the object and move it away from the object until you have passed the first ‘faint’ image formation. Replace the plane mirror with the convex mirror and posit ...
Chapter 4
... 2. Find the image of an object placed 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. What are the characteristics (location, size, direction, and nature) of the image? Location: 40 cm to left of mirror Size: Same as the object (M=1) ...
... 2. Find the image of an object placed 40 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 20 cm. What are the characteristics (location, size, direction, and nature) of the image? Location: 40 cm to left of mirror Size: Same as the object (M=1) ...
Key Words: Reflection: Light returning from a
... the wire the core becomes magnetic. Step up Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step up transformer increase the voltage. Step down Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step down transformer decrease the ...
... the wire the core becomes magnetic. Step up Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step up transformer increase the voltage. Step down Transformer: A device used to adjust the voltage. Step down transformer decrease the ...
Physics 44
... the lens opposite the bright object (that is, along the optical track). Find the position where an image of the bright object appears most clearly on the paper. The focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the position where the light from a distant object focuses. 3. You will be ...
... the lens opposite the bright object (that is, along the optical track). Find the position where an image of the bright object appears most clearly on the paper. The focal length is the distance from the center of the lens to the position where the light from a distant object focuses. 3. You will be ...
Microscope
... other tiny objects. Leeuwenhoek was the first person to describe bacteria, and he invented new methods for grinding and polishing microscope lenses that allowed for curvatures providing magnifications of up to 270 diameters, the best available lenses at that time. ...
... other tiny objects. Leeuwenhoek was the first person to describe bacteria, and he invented new methods for grinding and polishing microscope lenses that allowed for curvatures providing magnifications of up to 270 diameters, the best available lenses at that time. ...
Introduction to Mirrors and Lenses
... After passing through the lens, the three rays described above will appear to come from an enlarged and upright image. Any other ray leaving the tip of the object will appear to come from Three rays are included in the the tip of the image after passing illustration. Following are descriptions throu ...
... After passing through the lens, the three rays described above will appear to come from an enlarged and upright image. Any other ray leaving the tip of the object will appear to come from Three rays are included in the the tip of the image after passing illustration. Following are descriptions throu ...
[1] (similar to chapter 24, problem 3b). A cowboy, 7 feet tall with his
... A hiker is lost somewhere near Mt. Whitney, which she knows has an elevation of 4600 m. To determine her dis tance from the mountain, she uses her compact mirror, a small concave mirror with a focal length of 20 cm. She views an image of the mountain in her mirror, and notes that when the mirror is ...
... A hiker is lost somewhere near Mt. Whitney, which she knows has an elevation of 4600 m. To determine her dis tance from the mountain, she uses her compact mirror, a small concave mirror with a focal length of 20 cm. She views an image of the mountain in her mirror, and notes that when the mirror is ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.




















![[1] (similar to chapter 24, problem 3b). A cowboy, 7 feet tall with his](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/012836352_1-de06d5c02c2d314dd892be84f5d1f5aa-300x300.png)