Report Liquid Lens
... Image formation by a lens depends upon the wave property called refraction. Refraction may be defined as the bending of waves when they enter a medium where their speed is different. Since the speed of light is slower in a glass lens than in air, a light ray will be bent upon entering and upon exiti ...
... Image formation by a lens depends upon the wave property called refraction. Refraction may be defined as the bending of waves when they enter a medium where their speed is different. Since the speed of light is slower in a glass lens than in air, a light ray will be bent upon entering and upon exiti ...
All-dielectric subwavelength metasurface focusing lens
... smooth radial dependence of phase increment on transmission, avoiding 2π phase steps. Quasi-parabolic radial gradients of phase along the surface were created by slow variation of geometric parameters of the fine pattern. The meta-surface thickness is approximately onethird of the free-space wavelen ...
... smooth radial dependence of phase increment on transmission, avoiding 2π phase steps. Quasi-parabolic radial gradients of phase along the surface were created by slow variation of geometric parameters of the fine pattern. The meta-surface thickness is approximately onethird of the free-space wavelen ...
Chapter 12 - GEOCITIES.ws
... • is the visual angle of the final image • is the visual angle of the object Note that the visual angles are usually small so tan sin and tan sin . ...
... • is the visual angle of the final image • is the visual angle of the object Note that the visual angles are usually small so tan sin and tan sin . ...
Full Article
... more specifically, for managing the amount and type of substituent group and filler, such as resin, that are often assimilated into a silicone system. Phenyl groups incorporated into the siloxane (Si-O) polymer backbone of a silicone can influence the silicone’s permeability as well as its refractiv ...
... more specifically, for managing the amount and type of substituent group and filler, such as resin, that are often assimilated into a silicone system. Phenyl groups incorporated into the siloxane (Si-O) polymer backbone of a silicone can influence the silicone’s permeability as well as its refractiv ...
Optics Studio Manual - Department of Physics
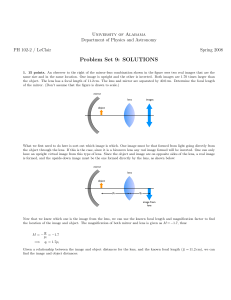
... object distances. Compare to the paraxial formula. Vary your object distances from much greater than the focal length f to twice the focal length (the “2f point,” an important point of symmetry) to f. Close than f, what happens? Draw a ray diagram and show consistency with both the calculation and t ...
... object distances. Compare to the paraxial formula. Vary your object distances from much greater than the focal length f to twice the focal length (the “2f point,” an important point of symmetry) to f. Close than f, what happens? Draw a ray diagram and show consistency with both the calculation and t ...
unit 9: imaging
... 2. A real, inverted, larger image is formed more than twice the objective lens’ focal length away on the other side of this lens. 3. The eyepiece lens is placed so that it acts as a simple magnifying glass, that is, so that the real image falls within its focal length. This lens then forms the final ...
... 2. A real, inverted, larger image is formed more than twice the objective lens’ focal length away on the other side of this lens. 3. The eyepiece lens is placed so that it acts as a simple magnifying glass, that is, so that the real image falls within its focal length. This lens then forms the final ...
Telescopes.
... large concave primary mirror and a smaller concave secondary mirror • 1666- Newton found that a prism breaks up white light into a rainbow of colours – Telescope lenses do the same ...
... large concave primary mirror and a smaller concave secondary mirror • 1666- Newton found that a prism breaks up white light into a rainbow of colours – Telescope lenses do the same ...
The Fresnel Biprism
... of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib was illuminated weakly and so it was difficult to determine where the centre of this area was. The alignment of the biprism may have caused some inaccuracies further on in the experiment. The light rays from the bipri ...
... of the illuminated area, this is fairly subjective as the area surrounding the rib was illuminated weakly and so it was difficult to determine where the centre of this area was. The alignment of the biprism may have caused some inaccuracies further on in the experiment. The light rays from the bipri ...
Dynamic pulsed-beam shaping using a TAG lens in the
... the dimensions and shapes of the patterns we can generate: the driving amplitude, the driving frequency, and the phase shift between the driving signal and the laser trigger. For this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is ca ...
... the dimensions and shapes of the patterns we can generate: the driving amplitude, the driving frequency, and the phase shift between the driving signal and the laser trigger. For this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is ca ...
Full text
... the dimensions and shapes of the patterns we can generate: the driving amplitude, the driving frequency, and the phase shift between the driving signal and the laser trigger. For this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is ca ...
... the dimensions and shapes of the patterns we can generate: the driving amplitude, the driving frequency, and the phase shift between the driving signal and the laser trigger. For this study, we have focused our attention on simple shapes including annuli and single spots, although the TAG lens is ca ...
Imaging and focusing of an atomic beam with a large period
... The focusing of atomic beams is a field of intense activity. One motivation for this activity is the use of a neutral atomic beam as a sensitive and high resolution microprobe. Neutral atoms as probing particles, because of their relatively high mass, have very low energy (for a given de Broglie wav ...
... The focusing of atomic beams is a field of intense activity. One motivation for this activity is the use of a neutral atomic beam as a sensitive and high resolution microprobe. Neutral atoms as probing particles, because of their relatively high mass, have very low energy (for a given de Broglie wav ...
Images in Lenses
... students understand each part, as various incident rays behave differently in other parts of the illustration. Ask students questions such as, Is this incident ray parallel or angled? Where is the light source now? What happens when it emerges and why? • As you work through the illustrations with st ...
... students understand each part, as various incident rays behave differently in other parts of the illustration. Ask students questions such as, Is this incident ray parallel or angled? Where is the light source now? What happens when it emerges and why? • As you work through the illustrations with st ...
Lecture 21 Wave Optics
... The Hubble space telescope has a diameter 2.4 meters. It is used to photograph objects 30000 light years away ( 1 light year is 9.46x1015 meters). Assume that it uses red light with 650 nm wavelength. What is the distance between two stars that can be resolved? ...
... The Hubble space telescope has a diameter 2.4 meters. It is used to photograph objects 30000 light years away ( 1 light year is 9.46x1015 meters). Assume that it uses red light with 650 nm wavelength. What is the distance between two stars that can be resolved? ...
Chromatic and Monochromatic Aberrations
... (reference material: Keating 20.9-20.11, 20.15,20.16) Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from ...
... (reference material: Keating 20.9-20.11, 20.15,20.16) Everything you have learned about object and image formation is an approximation. When light is refracted by spherical surfaces the rays do not all converge to a point, even if they are of one wavelength. Monochromatic aberrations can arise from ...
A high numerical aperture (NA = 0.92)
... 0.92. Tailored to the requirements of optical lattice experiments, the objective lens features a relatively long working distance of 150 µm. Our two-lens design is remarkably insensitive to mechanical tolerances in spite of the large NA. Additionally, we demonstrate the application of a tapered opti ...
... 0.92. Tailored to the requirements of optical lattice experiments, the objective lens features a relatively long working distance of 150 µm. Our two-lens design is remarkably insensitive to mechanical tolerances in spite of the large NA. Additionally, we demonstrate the application of a tapered opti ...
focusing of light by corneal lenses in a reflecting superposition eye
... The back focal distance (B.F.D.) of individual corneal facet lenses (the distance between the back of the lens and the back focal point) was determined by focusing consecutively on the back surface of a lens and on the image of a distant object formed by the lens (object distance 50 mm, effectively ...
... The back focal distance (B.F.D.) of individual corneal facet lenses (the distance between the back of the lens and the back focal point) was determined by focusing consecutively on the back surface of a lens and on the image of a distant object formed by the lens (object distance 50 mm, effectively ...
Fraunhofer Diffraction
... d being the grating period. Secondary wavelets, produced by these coherent sources, will interfere with each other, producing an image of the grating in plane P2. Suppose now that we place a diaphragm into the F plane, so some of these diffraction maxima are blocked and do not participate in the for ...
... d being the grating period. Secondary wavelets, produced by these coherent sources, will interfere with each other, producing an image of the grating in plane P2. Suppose now that we place a diaphragm into the F plane, so some of these diffraction maxima are blocked and do not participate in the for ...
Lasers and lenses - University of Toronto
... Gaussian optics, in order to obtain the smallest spot size (focus of the laser) the largest possible lens with the shortest possible focal length should be used [6]. However, due to aberrations introduced by real lenses this is not always the case. A good choice of lens for the ODT are the achromati ...
... Gaussian optics, in order to obtain the smallest spot size (focus of the laser) the largest possible lens with the shortest possible focal length should be used [6]. However, due to aberrations introduced by real lenses this is not always the case. A good choice of lens for the ODT are the achromati ...
Problem Set 9: SOLUTIONS
... the atmosphere is n = 1.000293. The day appears to be slightly longer because we see the sun even after it has gone through an extra angle of rotation δθ due to atmospheric refraction. To set up the geometry, we first draw a radial line from point B to the center of the earth. This line, BC, will in ...
... the atmosphere is n = 1.000293. The day appears to be slightly longer because we see the sun even after it has gone through an extra angle of rotation δθ due to atmospheric refraction. To set up the geometry, we first draw a radial line from point B to the center of the earth. This line, BC, will in ...
test
... You are asked to design a pinhole camera with Gaussian amplitude apodization in the pinhole. So, rather than a perfectly clear circular “hole” for a pinhole, the “hole” is a piece of material which has increasing attenuation (less than unity amplitude transmission) as the distance from the center of ...
... You are asked to design a pinhole camera with Gaussian amplitude apodization in the pinhole. So, rather than a perfectly clear circular “hole” for a pinhole, the “hole” is a piece of material which has increasing attenuation (less than unity amplitude transmission) as the distance from the center of ...
CE-PHY II - OPTICS
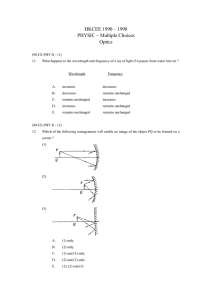
... A beam consisting of read and violet light travels in a glass block with an air cavity. The cavity is in the shape of a prism as shown above. Which of the following diagrams best shows the subsequent path of the beam ? A. ...
... A beam consisting of read and violet light travels in a glass block with an air cavity. The cavity is in the shape of a prism as shown above. Which of the following diagrams best shows the subsequent path of the beam ? A. ...
Learning material
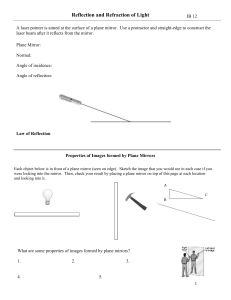
... The section shows a small bundle of rays that enter the eye that originate form the object at B, but are traced back apparently from the image at B’. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence the triangles BQP and B’QP are similar, and since QP is a common side, they are congruent. ...
... The section shows a small bundle of rays that enter the eye that originate form the object at B, but are traced back apparently from the image at B’. Since the angle of reflection equals the angle of incidence the triangles BQP and B’QP are similar, and since QP is a common side, they are congruent. ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.