Chapter 25 Optical Instruments
... •F-stop controls the amount of light coming into the light-tight box, by controlling the size of the opening •F-stop=f/D ...
... •F-stop controls the amount of light coming into the light-tight box, by controlling the size of the opening •F-stop=f/D ...
Chapter 33E Worksheet - Rose
... bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid blinding the fish, which might swim into the focal point of the parallel rays from the sun. Is the focal point actually within the bowl? ...
... bowl to keep it out of direct sunlight to avoid blinding the fish, which might swim into the focal point of the parallel rays from the sun. Is the focal point actually within the bowl? ...
Fraunhofer diffraction from gratings In this exercise we use a two
... In this exercise we use a two-dimensional grating consisting of many straight and equidistant lines in a plane (a slide). We perform Fraunhofer diffraction which means a parallel incident beam entering the object, and we observe the diffraction pattern far away from the object. Depending on the scat ...
... In this exercise we use a two-dimensional grating consisting of many straight and equidistant lines in a plane (a slide). We perform Fraunhofer diffraction which means a parallel incident beam entering the object, and we observe the diffraction pattern far away from the object. Depending on the scat ...
OCR Document - mackenziekim
... the comparison of the experimental image with its corresponding ray diagram image characteristics and the thin lens equation results. Summarize image characteristics for a double convex lens. How does a concave mirror compare with a convex lens with respect to the images they produce? Do you think t ...
... the comparison of the experimental image with its corresponding ray diagram image characteristics and the thin lens equation results. Summarize image characteristics for a double convex lens. How does a concave mirror compare with a convex lens with respect to the images they produce? Do you think t ...
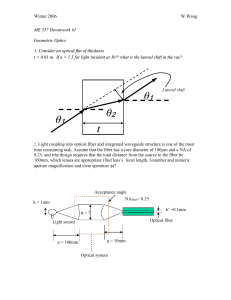
ME 557 Howmwork #1
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
... Light coupling into optical fiber and integrated waveguide structure is one of the most time consuming task. Assume that the fiber has a core diameter of 100m and a NA of 0.25, and trhe design requires that the total distance from the source to the fiber be 100mm, which lenses are appropriate (find ...
Here
... • A lens is made up of a some material with two curved surfaces, each with possibly different radii of curvature. To analyze this, consider refraction at a spherical surface. • Refraction at a spherical surface – Look at figure 5.6, p. 153 in the book. – C is the center of curvature of the spherical ...
... • A lens is made up of a some material with two curved surfaces, each with possibly different radii of curvature. To analyze this, consider refraction at a spherical surface. • Refraction at a spherical surface – Look at figure 5.6, p. 153 in the book. – C is the center of curvature of the spherical ...
How do eye glasses work? BUT first, let`s review!
... What is a longitudinal wave? The particles of the medium vibrate back and forth along the path that the wave ...
... What is a longitudinal wave? The particles of the medium vibrate back and forth along the path that the wave ...
Refraction, Lenses, Aberrations
... • Atmospheric refraction is a phenomenon that moves images of objects, seen through the air, due to a gradual change of the air density and temperature. • Thin lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments to enhance our vision. • Aberrations are distortions of images, predicte ...
... • Atmospheric refraction is a phenomenon that moves images of objects, seen through the air, due to a gradual change of the air density and temperature. • Thin lenses are used to form images by refraction in optical instruments to enhance our vision. • Aberrations are distortions of images, predicte ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... We find that two types of aberrations result from the use of spherical surfaces ...
... We find that two types of aberrations result from the use of spherical surfaces ...
LENSES and MIRRORS
... A convex lens is thicker in the center than on its edges. As light rays parallel to the optical axis pass through a convex lens, they are bent toward the center of the lens. Examples: Magnifying glass and corrective lenses for farsightedness. A concave lens is thinner in the center than on its edges ...
... A convex lens is thicker in the center than on its edges. As light rays parallel to the optical axis pass through a convex lens, they are bent toward the center of the lens. Examples: Magnifying glass and corrective lenses for farsightedness. A concave lens is thinner in the center than on its edges ...
Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics
... Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics ...
... Human Vision: Electrophysiology and Psychophysics ...
Microscopy - u.arizona.edu
... b. Robert Hooke, Late 1600s, English Scientist / Engineer A. Improved upon early compound microscopes B. Coined the word “cell” c. Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Also Late 1600s, Dutch Scientist A. Used simple “microscopes” but a premier lens maker B. First to describe bacteria, protists a.k.a. “animucules” ...
... b. Robert Hooke, Late 1600s, English Scientist / Engineer A. Improved upon early compound microscopes B. Coined the word “cell” c. Anton van Leeuwenhoek, Also Late 1600s, Dutch Scientist A. Used simple “microscopes” but a premier lens maker B. First to describe bacteria, protists a.k.a. “animucules” ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.