TOPS Optical Bench Finding Focal Length of Lenses and
... Optical Bench Finding focal lengths of lenses and mirrors In this activity you will find focal lengths using the basic lens equation: ...
... Optical Bench Finding focal lengths of lenses and mirrors In this activity you will find focal lengths using the basic lens equation: ...
PHYS 1112 In-Class Exam #1A Thu. Feb. 5, 2009, 11:00am-12:15pm
... d > 0 (real object) if object on ”incoming” side; else d < 0 (virtual object). d" > 0 (real image) if image on ”outgoing” side; else d" < 0 (virtual image). If m > 0 then image erect (upright) rel. to object; else, if m < 0 then image inverted (upside-down) rel. to object. If f > 0 then F on ”incomi ...
... d > 0 (real object) if object on ”incoming” side; else d < 0 (virtual object). d" > 0 (real image) if image on ”outgoing” side; else d" < 0 (virtual image). If m > 0 then image erect (upright) rel. to object; else, if m < 0 then image inverted (upside-down) rel. to object. If f > 0 then F on ”incomi ...
ChE 393 Course Notes
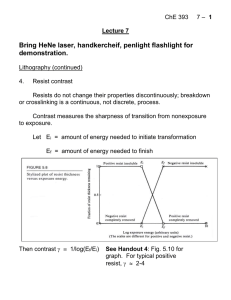
... System produces a distorted image. For optical lenses (or mirrors), we can get the following problems (and others): ...
... System produces a distorted image. For optical lenses (or mirrors), we can get the following problems (and others): ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
... Exercise 6: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
Scope Definitions
... No multi-coating is 100% efficient. Since each extra lens introduces more lightreflecting surfaces, simpler fixed-power scopes are often brighter and sharper than variables with more lenses. Chromatic Abberation n. When light passes through a lens, light of different colors are bent (refracted) to a ...
... No multi-coating is 100% efficient. Since each extra lens introduces more lightreflecting surfaces, simpler fixed-power scopes are often brighter and sharper than variables with more lenses. Chromatic Abberation n. When light passes through a lens, light of different colors are bent (refracted) to a ...
the P3 `bus stop`
... Concave lenses are called diverging lenses as they spread light out. Convex lenses are called converging lenses as they bring light rays together. Converging lenses are used as magnifying glasses. Concave lens ...
... Concave lenses are called diverging lenses as they spread light out. Convex lenses are called converging lenses as they bring light rays together. Converging lenses are used as magnifying glasses. Concave lens ...
Astronomy 100 Name(s):
... Exercise 5: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
... Exercise 5: Optics of telescopes Optics is the field of physics involved in the study of light. No less a luminary than Isaac Newton is credited with originating the field, though of course humans have been interested in the properties of light since antiquity. Newton, in his book Opticks (1704), sy ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... Notice the distance between the penguin and the lens in the illustration on page 122. The distance is measured in terms of a focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the ima ...
... Notice the distance between the penguin and the lens in the illustration on page 122. The distance is measured in terms of a focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the ima ...
Lenses form images by refracting light.
... Notice the distance between the penguin and the lens in the illustration on page 602. The distance is measured in terms of a focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the ima ...
... Notice the distance between the penguin and the lens in the illustration on page 602. The distance is measured in terms of a focal length, which is the distance from the center of the lens to the lens’s focal point. The penguin is more than two focal lengths from the camera lens, which means the ima ...
Chapter 5: Geometrical Optics
... Finding an image using ray diagrams: Three key rays in locating an image point: 1) Ray through the optical center: a straight line. 2) Ray parallel to the optical axis: emerging passing through the focal point. 3) Ray passing through the focal point: emerging parallel to the optical axis. ...
... Finding an image using ray diagrams: Three key rays in locating an image point: 1) Ray through the optical center: a straight line. 2) Ray parallel to the optical axis: emerging passing through the focal point. 3) Ray passing through the focal point: emerging parallel to the optical axis. ...
f - Uplift Education
... The hole through which light passes (the pupil) is black because no light is reflected from it (it’s a hole), and very little light is reflected back out from the interior of eye. The retina, which plays the role of the film in a camera is on the curved rear surface. It consists of array of nerves a ...
... The hole through which light passes (the pupil) is black because no light is reflected from it (it’s a hole), and very little light is reflected back out from the interior of eye. The retina, which plays the role of the film in a camera is on the curved rear surface. It consists of array of nerves a ...
Light and Optics - Mayfield City Schools
... • A camera works by collecting the rays from an object so they form an image on the film. • Many rays can be focused to a single point by a camera lens, forming the image of that part of the ...
... • A camera works by collecting the rays from an object so they form an image on the film. • Many rays can be focused to a single point by a camera lens, forming the image of that part of the ...
Three Lasers Converging at a Focal Point : A Demonstration
... 3. Now replace the glass block with the positive lens. Two things to note here: The center laser beam needs to go through the center of the lens, and the set up should have the screen placed at a distance away from the laser such that the three spots are similar in appearance as they were for the gl ...
... 3. Now replace the glass block with the positive lens. Two things to note here: The center laser beam needs to go through the center of the lens, and the set up should have the screen placed at a distance away from the laser such that the three spots are similar in appearance as they were for the gl ...
Class10 CBSE Test paper Chapter: Reflection and Refraction of Light -...
... Solution: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is known as the principal focus of the concave mirror Question 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. W ...
... Solution: Light rays that are parallel to the principal axis of a concave mirror converge at a specific point on its principal axis after reflecting from the mirror. This point is known as the principal focus of the concave mirror Question 2: The radius of curvature of a spherical mirror is 20 cm. W ...
Lens Webquest and Virtual Lab File
... Read the box on the left and fill in the blanks below as you read along: How are lenses used to correct vision? A _____________ is a type of transparent material that bends light. Most manufactured lenses are made of glass or plastic. The bending of light is called __________________. As parallel ra ...
... Read the box on the left and fill in the blanks below as you read along: How are lenses used to correct vision? A _____________ is a type of transparent material that bends light. Most manufactured lenses are made of glass or plastic. The bending of light is called __________________. As parallel ra ...
“Beam Paths” to the “Microscope”
... 3) Light rays that enter the lens from the focal point exit parallel to the optical axis. f ...
... 3) Light rays that enter the lens from the focal point exit parallel to the optical axis. f ...
Light Rays
... direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. The principal focus is the point that rays parallel to the principal axis converge to (f ...
... direction. The principal axis is the line passing through the optical centre and perpendicular to the lens. Rays parallel to the principal axis converge to or diverge from the focus or focal point of a lens. The principal focus is the point that rays parallel to the principal axis converge to (f ...
What is a Fresnel Lens?
... middle and tapers down to nothing at the edges. In other words, it is shaped like a lentil, which is where the word lens comes from. It would not be very easy to make a big magnifying glass lens for your monitor or TFT screen because it would be thick, heavy and hard to mount. A Fresnel lens overcom ...
... middle and tapers down to nothing at the edges. In other words, it is shaped like a lentil, which is where the word lens comes from. It would not be very easy to make a big magnifying glass lens for your monitor or TFT screen because it would be thick, heavy and hard to mount. A Fresnel lens overcom ...
SIMG-733-20092 Optics for Imaging Solutions to Final Exam
... 5. A lens with f = +500 mm is sawn into two pieces through a plane cutting through the optical axis (i.e., the cut is along a diameter). A point source of monochromatic light with λ0 = 500 nm is placed on the optical axis at a distance z1 = 1000 mm from the lens. The half lenses are gradually moved ...
... 5. A lens with f = +500 mm is sawn into two pieces through a plane cutting through the optical axis (i.e., the cut is along a diameter). A point source of monochromatic light with λ0 = 500 nm is placed on the optical axis at a distance z1 = 1000 mm from the lens. The half lenses are gradually moved ...
Paraxial Formulas - CVI Laser Optics
... point of the system exits the system from the second principal point parallel to its original direction (i.e., its ...
... point of the system exits the system from the second principal point parallel to its original direction (i.e., its ...
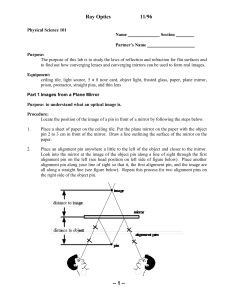
Lab #8 Ray Optics
... Real images are formed when the rays of light really come together on the screen and virtual images are where the light appears to come from. Is the image formed by a plane mirror real or virtual? ...
... Real images are formed when the rays of light really come together on the screen and virtual images are where the light appears to come from. Is the image formed by a plane mirror real or virtual? ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.