Direct detection of ligand–protein interaction using AFM
... information about such properties as the presence of binding sites and the presence of other cells, elasticity of substrates, and strength of forces acting on cells. Cell adhesion plays crucial role in many events governing the maintenance of various tissue structures and integrity where the interac ...
... information about such properties as the presence of binding sites and the presence of other cells, elasticity of substrates, and strength of forces acting on cells. Cell adhesion plays crucial role in many events governing the maintenance of various tissue structures and integrity where the interac ...
View/Open - VUW research archive - Victoria University of Wellington
... Conditions for extraction and two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins were established. One hundred and seventy nine proteins were identified by MALDI mass spectrometry of tryptic digests of protein spots excised from Coomassie stained gels. All of the enzymes for conversion of glucose to ethano ...
... Conditions for extraction and two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins were established. One hundred and seventy nine proteins were identified by MALDI mass spectrometry of tryptic digests of protein spots excised from Coomassie stained gels. All of the enzymes for conversion of glucose to ethano ...
A role for FKBP52 in Tau protein function
... drugs have already been described as evoking a possible mechanism via immunophilins (4, 5). Another remarkable feature of FKBPs is their rotamase (peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase) activity (6), which links them to the parvulin family of isomerases such as Pin1 (7). Among the FKBP family members, ...
... drugs have already been described as evoking a possible mechanism via immunophilins (4, 5). Another remarkable feature of FKBPs is their rotamase (peptidyl prolyl cis-trans isomerase) activity (6), which links them to the parvulin family of isomerases such as Pin1 (7). Among the FKBP family members, ...
Therapeutic approaches to Lysosomal Storage Disorders
... required for membrane fusion. SNARE proteins are classified as vesicle SNAREs (vSNAREs), located on the vesicles membrane, and target SNAREs (t-SNAREs), located on the membranes of target compartments. SNAREs may vary in size and composition, but they all share a 60-70 amino acid cytosolic domain ( ...
... required for membrane fusion. SNARE proteins are classified as vesicle SNAREs (vSNAREs), located on the vesicles membrane, and target SNAREs (t-SNAREs), located on the membranes of target compartments. SNAREs may vary in size and composition, but they all share a 60-70 amino acid cytosolic domain ( ...
Extensive tissue-specific transcriptomic plasticity in maize primary
... potential gradient towards the environment is maintained; that is, a more negative water potential than in the outside medium, enabling water influx. Maintenance of root elongation further depends on an increase of longitudinal cell wall extensibility (reviewed in Yamaguchi and Sharp, 2010). Other d ...
... potential gradient towards the environment is maintained; that is, a more negative water potential than in the outside medium, enabling water influx. Maintenance of root elongation further depends on an increase of longitudinal cell wall extensibility (reviewed in Yamaguchi and Sharp, 2010). Other d ...
Free Article - Crop Functional Genomics
... potential gradient towards the environment is maintained; that is, a more negative water potential than in the outside medium, enabling water influx. Maintenance of root elongation further depends on an increase of longitudinal cell wall extensibility (reviewed in Yamaguchi and Sharp, 2010). Other d ...
... potential gradient towards the environment is maintained; that is, a more negative water potential than in the outside medium, enabling water influx. Maintenance of root elongation further depends on an increase of longitudinal cell wall extensibility (reviewed in Yamaguchi and Sharp, 2010). Other d ...
Thermodynamic analysis of the unfolding and stability of the dimeric
... complexes and is also involved in a variety of DNA metabolic events, such as replication, transcription and transposition [11,12]. Its ability to repair DNA [13,14] and to prevent DNA duplex melting [7] has also been described. HU proteins from several species of bacillus growing in environments of ...
... complexes and is also involved in a variety of DNA metabolic events, such as replication, transcription and transposition [11,12]. Its ability to repair DNA [13,14] and to prevent DNA duplex melting [7] has also been described. HU proteins from several species of bacillus growing in environments of ...
A Dominant Negative Mutant of Cyclin-Dependent
... the way it occurs in yeast and animal cells. The endoreduplication cell cycle is a variant of the standard mitotic cell cycle in which there are recurrent S- and G-phases without M-phase (Edgar and Orr-Weaver, 2001). The mechanisms that enable cells to sequentially replicate chromosomes without prog ...
... the way it occurs in yeast and animal cells. The endoreduplication cell cycle is a variant of the standard mitotic cell cycle in which there are recurrent S- and G-phases without M-phase (Edgar and Orr-Weaver, 2001). The mechanisms that enable cells to sequentially replicate chromosomes without prog ...
Insulin hormone: Mechanism and effects on the body and
... 2 domains. IRS-1 in particular is phosphorylated on several tyrosine residues by the insulin receptor’s intracellular catalytic part and these phosphorylated tyrosine residues in turn employee other proteins with src homology 2 domains, one of which is phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Phosphatidylinos ...
... 2 domains. IRS-1 in particular is phosphorylated on several tyrosine residues by the insulin receptor’s intracellular catalytic part and these phosphorylated tyrosine residues in turn employee other proteins with src homology 2 domains, one of which is phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Phosphatidylinos ...
A Comprehensive Mutational Analysis of the
... showed that compared with the functional RPW8.2 allele from accession Ms-0 (designated R82Ms-0), Thr-64 to Ser (T64S), Asp-116 to Gly (D116G), and Thr-161 to Lys (T161K) substitutions are present in alleles from most accessions that are susceptible to powdery mildew (Figure 5 in Orgil et al., 2007). ...
... showed that compared with the functional RPW8.2 allele from accession Ms-0 (designated R82Ms-0), Thr-64 to Ser (T64S), Asp-116 to Gly (D116G), and Thr-161 to Lys (T161K) substitutions are present in alleles from most accessions that are susceptible to powdery mildew (Figure 5 in Orgil et al., 2007). ...
Vertebrate somitogenesis: a novel paradigm for animal segmentation?
... coding for the basic helix loop helix (b-HLH) transcription factor chairy1, a vertebrate homologue of the protein encoded by the fly pair-rule gene hairy (Palmeirim, et al., 1997). This periodic expression of c-hairy1 provided evidence for the existence of an oscillator acting in PSM cells, which wa ...
... coding for the basic helix loop helix (b-HLH) transcription factor chairy1, a vertebrate homologue of the protein encoded by the fly pair-rule gene hairy (Palmeirim, et al., 1997). This periodic expression of c-hairy1 provided evidence for the existence of an oscillator acting in PSM cells, which wa ...
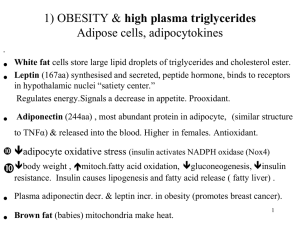
No Slide Title
... F) Drug therapy to decrease plasma cholesterol i) The STATINS inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol and cut the risk of heart attacks and strokes by at least 33% even in people with normal cholesterol. Several million Canadians are taking statins. HMG CoA reductase inh ...
... F) Drug therapy to decrease plasma cholesterol i) The STATINS inhibit cholesterol biosynthesis to decrease plasma LDL cholesterol and cut the risk of heart attacks and strokes by at least 33% even in people with normal cholesterol. Several million Canadians are taking statins. HMG CoA reductase inh ...
Session 241 Ganglion Cells: Development, axotomy, trauma
... leading to visual impairment, seems to be mediated by programed cell death. Therefore, activation of survival pathways, such as that of PI3K/Akt, is a potential therapeutical target to delay retinal degeneration. The aim of this study is to test in retinal explants the effect of PTD4-PI3KAc, a synth ...
... leading to visual impairment, seems to be mediated by programed cell death. Therefore, activation of survival pathways, such as that of PI3K/Akt, is a potential therapeutical target to delay retinal degeneration. The aim of this study is to test in retinal explants the effect of PTD4-PI3KAc, a synth ...
Large Intercalated Neurons of Amygdala Relay Noxious Sensory
... U138197109), the Austrian Science Fund (F.F.): I252-B18, P22969-B11 and W12060-10 to F.F., T.C.M.B. was funded by an MRC DPhil studentship, and is a fellow of the Ecole de l’Inserm Liliane Bettencourt MD-PhD Program, France. D.B. was also supported by a NENS studentship. We thank R. Hauer and G. Sch ...
... U138197109), the Austrian Science Fund (F.F.): I252-B18, P22969-B11 and W12060-10 to F.F., T.C.M.B. was funded by an MRC DPhil studentship, and is a fellow of the Ecole de l’Inserm Liliane Bettencourt MD-PhD Program, France. D.B. was also supported by a NENS studentship. We thank R. Hauer and G. Sch ...
G1 Phase-Dependent Expression of Bcl
... We investigated levels of Bcl-2 family proteins during the cell cycle progression. Human Jurkat T cells were synchronized at the G1/S boundary by using aphidicolin, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase ␣ (Huberman, 1981), followed by removal of the drug and further incubation of the cells in fresh growth ...
... We investigated levels of Bcl-2 family proteins during the cell cycle progression. Human Jurkat T cells were synchronized at the G1/S boundary by using aphidicolin, an inhibitor of DNA polymerase ␣ (Huberman, 1981), followed by removal of the drug and further incubation of the cells in fresh growth ...
System approaches to study root hairs as a single cell plant model
... they serve as a model to study this distinctive growth process (Campanoni and Blatt, 2007). However, in legumes, root hairs are also the primary site for rhizobial infection and, therefore, several studies have sought to define the early events in this infection process. Libault et al. (2010b) studi ...
... they serve as a model to study this distinctive growth process (Campanoni and Blatt, 2007). However, in legumes, root hairs are also the primary site for rhizobial infection and, therefore, several studies have sought to define the early events in this infection process. Libault et al. (2010b) studi ...
Polar auxin transport and patterning
... most conspicuous “rules” were to allow a cell to position PIN proteins toward neighboring cells with higher auxin levels (Jonsson et al. 2006) and to make PIN1 levels auxin dependent (Smith et al. 2006). While several additional rules were needed to make the different phyllotaxis models run, these t ...
... most conspicuous “rules” were to allow a cell to position PIN proteins toward neighboring cells with higher auxin levels (Jonsson et al. 2006) and to make PIN1 levels auxin dependent (Smith et al. 2006). While several additional rules were needed to make the different phyllotaxis models run, these t ...
High-Performance Exosome Purification
... sample preparation indicate that density gradient is an impor tant step in isolating exosomes. When ultracentrifugation and pelleting are used alone, without a density gradient, larger species and cellular debris are removed from the exosome sample. However, protein and small macromolecule impuritie ...
... sample preparation indicate that density gradient is an impor tant step in isolating exosomes. When ultracentrifugation and pelleting are used alone, without a density gradient, larger species and cellular debris are removed from the exosome sample. However, protein and small macromolecule impuritie ...
Novel Ubiquitin Fusion Proteins: Ribosomal Protein
... present in B. natans polyubiquitin genes and to the ubiquitin moieties of the S27a and L40 fusion proteins. In contrast, the ubiquitin extension encoded by actin-3 was more divergent at the protein level than is typical of ubiquitin (the cDNA encoding this gene was slightly truncated at its 50 end). ...
... present in B. natans polyubiquitin genes and to the ubiquitin moieties of the S27a and L40 fusion proteins. In contrast, the ubiquitin extension encoded by actin-3 was more divergent at the protein level than is typical of ubiquitin (the cDNA encoding this gene was slightly truncated at its 50 end). ...
Chapter 4 Calsequestrin - Department of Molecular Physiology and
... able to draw Ca 2+ away from the sarcoplasmic Ca 2+ -binding proteins which have Kd values for Ca2+ binding of about 1-5 µM (Greaser et al., 1972b; Kretsinger. 1976). The contest for Ca2+ is, therefore, unequal and Ca 2+ finds itself in the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum There it encounters ano ...
... able to draw Ca 2+ away from the sarcoplasmic Ca 2+ -binding proteins which have Kd values for Ca2+ binding of about 1-5 µM (Greaser et al., 1972b; Kretsinger. 1976). The contest for Ca2+ is, therefore, unequal and Ca 2+ finds itself in the lumen of the sarcoplasmic reticulum There it encounters ano ...
University of Groningen Cross-linking of dimeric CitS and GltS
... and includes the Ion Transporter (IT) superfamily ...
... and includes the Ion Transporter (IT) superfamily ...
Document
... growth conditions) and becomes the NMR-visible component. The other protein is expressed in an unlabeled form, after switching the medium to non-labeled growth conditions and thus remains NMR-invisible. Once the two proteins encounter each other in the cytoplasm of the expression host, the resulting ...
... growth conditions) and becomes the NMR-visible component. The other protein is expressed in an unlabeled form, after switching the medium to non-labeled growth conditions and thus remains NMR-invisible. Once the two proteins encounter each other in the cytoplasm of the expression host, the resulting ...
Signal transduction
Signal transduction occurs when an extracellular signaling molecule activates a specific receptor located on the cell surface or inside the cell. In turn, this receptor triggers a biochemical chain of events inside the cell, creating a response. Depending on the cell, the response alters the cell's metabolism, shape, gene expression, or ability to divide. The signal can be amplified at any step. Thus, one signaling molecule can cause many responses.