Electrochemical Cell – Basic Analysis
... • During discharge, the cell transforms chemical energy into electric energy. The voltage then drops below OCV due to losses in the cell. These losses are caused by various types of polarisation or overpotential and occur as a load current i passes through the cell. a) activation polarisation origin ...
... • During discharge, the cell transforms chemical energy into electric energy. The voltage then drops below OCV due to losses in the cell. These losses are caused by various types of polarisation or overpotential and occur as a load current i passes through the cell. a) activation polarisation origin ...
the properties and structure of matter
... its state (phase change), but does not change its chemical composition – E.g. Grinding, cutting ...
... its state (phase change), but does not change its chemical composition – E.g. Grinding, cutting ...
Water Chemistry 3
... Thermodynamics tells us where the system should go at equilibrium, and kinetics tells us how fast. • Definition of Equilibrium 1) A system at equilibrium has none of its properties changing with time, no matter how long it is observed 2) A system at equilibrium will return to that state after being ...
... Thermodynamics tells us where the system should go at equilibrium, and kinetics tells us how fast. • Definition of Equilibrium 1) A system at equilibrium has none of its properties changing with time, no matter how long it is observed 2) A system at equilibrium will return to that state after being ...
The Helmholtz Function
... The quantity G is tabulated for a variety of chemical reactions and other processes. G = H - TS In most work we do not need to choose a reference point as, usually, only changes in the quantities are of interest. {One source of tabulations of thermodynamic properties is the CRC Handbook of Chem ...
... The quantity G is tabulated for a variety of chemical reactions and other processes. G = H - TS In most work we do not need to choose a reference point as, usually, only changes in the quantities are of interest. {One source of tabulations of thermodynamic properties is the CRC Handbook of Chem ...
Chapter 21: Electric potential
... A parallel-plate capacitor is held at a potential difference of 250 V. A proton is fired toward a small hole in the negative plate with a speed of 3.0 x 105 m/s. What is its speed when it emerges through the hole in the positive plate? (Hint: The electric potential outside of a parallel-plate capaci ...
... A parallel-plate capacitor is held at a potential difference of 250 V. A proton is fired toward a small hole in the negative plate with a speed of 3.0 x 105 m/s. What is its speed when it emerges through the hole in the positive plate? (Hint: The electric potential outside of a parallel-plate capaci ...
CHAPTER 23 ELECTRIC POTENTIAL • Potential difference and
... For a small displacement dr in the radial direction ( ˆr ), the change in potential is: ...
... For a small displacement dr in the radial direction ( ˆr ), the change in potential is: ...
TDDFT as a tool in chemistry
... Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of the interactions between atoms, small molecules, and light (or electromagnetic radiation). […] Photochemistry may also be introduced to laymen as a reaction that proceeds with the absorption of light. Normally a reaction (not just a phot ...
... Photochemistry, a sub-discipline of chemistry, is the study of the interactions between atoms, small molecules, and light (or electromagnetic radiation). […] Photochemistry may also be introduced to laymen as a reaction that proceeds with the absorption of light. Normally a reaction (not just a phot ...
V. Diffusion
... fluctuating hydrodynamics. In this theoretical framework, diffusion is due to fluctuations whose dimensions range from the molecular scale to the macroscopic scale. Chemical diffusion increases the entropy of a system, i.e. diffusion is a spontaneous and irreversible process. Particles can spread ou ...
... fluctuating hydrodynamics. In this theoretical framework, diffusion is due to fluctuations whose dimensions range from the molecular scale to the macroscopic scale. Chemical diffusion increases the entropy of a system, i.e. diffusion is a spontaneous and irreversible process. Particles can spread ou ...
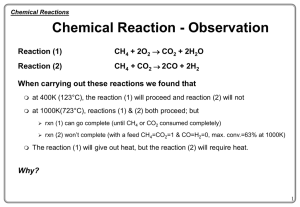
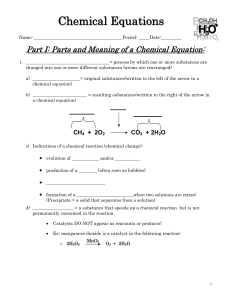
Chemical Equations
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
... “yields”; indicates result of a reaction Indicates a reversible reaction A reactant or product in the solid state Alternative to (s); used only for a precipitate (solid) falling out of solution A reactant or product in the liquid state A reactant or product in aqueous solution (dissolved in water) A ...
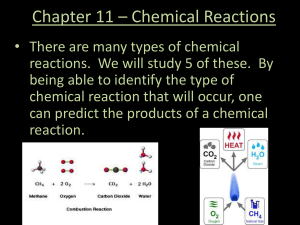
Chapter 11 * Chemical Reactions
... reactions. We will study 5 of these. By being able to identify the type of chemical reaction that will occur, one can predict the products of a chemical reaction. ...
... reactions. We will study 5 of these. By being able to identify the type of chemical reaction that will occur, one can predict the products of a chemical reaction. ...