Variation of Chemical Potential Oscillations of a
... itself as magnetic field changes, (ii) the chemical potential remains fixed while the electron concentration varies to adopt to the existing conditions as magnetic field changes, and (iii) both the electron concentration and chemical potential varies as a function of magnetic field. We assume that t ...
... itself as magnetic field changes, (ii) the chemical potential remains fixed while the electron concentration varies to adopt to the existing conditions as magnetic field changes, and (iii) both the electron concentration and chemical potential varies as a function of magnetic field. We assume that t ...
CHM 110 - Equation Interpretation (r14)
... 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 In fact, the chemical equation is easier, since it's more consistent! We don't have to worry about things like what exactly a "package" or a "cup" is. Interpretation From balancing equations, we already know one way to interpret the chemical formula, the "molecular" interpretation ...
... 4Fe + 3O2 → 2Fe2O3 In fact, the chemical equation is easier, since it's more consistent! We don't have to worry about things like what exactly a "package" or a "cup" is. Interpretation From balancing equations, we already know one way to interpret the chemical formula, the "molecular" interpretation ...
Chapter 8 Chemical Thermodynamics Study Guide and Test Review
... physical process. A calorimeter is a device in which an experiment is carried out to determine the energy change of a process. Measuring the temperature change of a known amount of substance with a known specific heat. The change in temperature is caused by the release or absorption of heat by the ...
... physical process. A calorimeter is a device in which an experiment is carried out to determine the energy change of a process. Measuring the temperature change of a known amount of substance with a known specific heat. The change in temperature is caused by the release or absorption of heat by the ...
Writing Chemical Formulas and Chemical Reactions
... An oxy acid derivative may be formed during a chemical reaction when oxygen atom(s) are added to or removed from an oxy acid. (Note: Although you can write the chemical formulas and names of all oxy acid derivatives using the system described below, some may not be able to be produced naturally or s ...
... An oxy acid derivative may be formed during a chemical reaction when oxygen atom(s) are added to or removed from an oxy acid. (Note: Although you can write the chemical formulas and names of all oxy acid derivatives using the system described below, some may not be able to be produced naturally or s ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... Formula equation- qualitatively represents the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas Notice that the formula equation does not give information about the amounts of reactants and products. A formula equation meets two of the three requirements for a correct c ...
... Formula equation- qualitatively represents the reactants and products of a chemical reaction by their symbols or formulas Notice that the formula equation does not give information about the amounts of reactants and products. A formula equation meets two of the three requirements for a correct c ...
Miami-Dade College
... substances to physical properties such as vapor pressure, melting point, boiling point, and viscosity. ...
... substances to physical properties such as vapor pressure, melting point, boiling point, and viscosity. ...
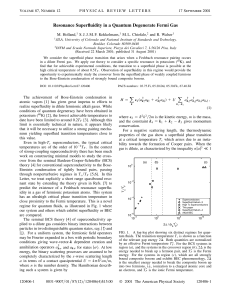
Resonance Superfluidity in a Quantum Degenerate Fermi Gas
... As an example of the application of this theory, we study the experimentally relevant system of fermionic 40 K atoms equally distributed between the two hyperfine states which have the lowest internal energy in the presence of a magnetic field. The values of our interaction parameters abg 苷 176a0 an ...
... As an example of the application of this theory, we study the experimentally relevant system of fermionic 40 K atoms equally distributed between the two hyperfine states which have the lowest internal energy in the presence of a magnetic field. The values of our interaction parameters abg 苷 176a0 an ...
Physical and Chemical Change
... through careful observation. Physical properties include color, odor, density, solubility and the state of matter. Chemical properties describe the changes that take place when new substances are formed during a chemical reaction. When matter undergoes a change, it is classified as either a physical ...
... through careful observation. Physical properties include color, odor, density, solubility and the state of matter. Chemical properties describe the changes that take place when new substances are formed during a chemical reaction. When matter undergoes a change, it is classified as either a physical ...
EE3 2007 Hannes Jónsson Transition state theory A very important
... rate theory’ (ART) and, derived from a slightly different point of view, as ’activated complex theory’ (ACT). This is one of the most important topics in physical chemistry. Despite its importance, the presentation of TST is often misleading. In 1974 Prof. Bruce Mahan published an article in the Jou ...
... rate theory’ (ART) and, derived from a slightly different point of view, as ’activated complex theory’ (ACT). This is one of the most important topics in physical chemistry. Despite its importance, the presentation of TST is often misleading. In 1974 Prof. Bruce Mahan published an article in the Jou ...
16 3.0 Chapter Contents 3.1 The Entropy and Internal Energy
... which the physical properties change discontinuously (see Chapter 19), and of reactive systems, i.e., to systems in which changes in composition occur as a result of chemical reactions (see Chapter 20). 3.9 The Gibbs Equation The differential forms of the fundamental equation, Eqs.(3.5h and (3.5)3, ...
... which the physical properties change discontinuously (see Chapter 19), and of reactive systems, i.e., to systems in which changes in composition occur as a result of chemical reactions (see Chapter 20). 3.9 The Gibbs Equation The differential forms of the fundamental equation, Eqs.(3.5h and (3.5)3, ...