Wanganui High School
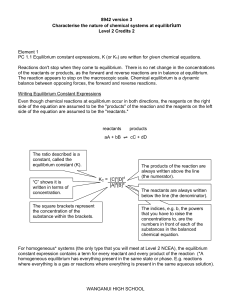
... (the numerator). The reactants are always written below the line (the denominator). ...
... (the numerator). The reactants are always written below the line (the denominator). ...
Understanding temperature and chemical potential using computer
... We can easily demonstrate the nature of the equipartition theorem by applying the demon algorithm to the ideal gas for which the kinetic energy of a particle is given by ǫ(p) = p2 /2m. In this case the trial moves are changes in the momentum p of a particle. Figure 1 shows the demon probability dist ...
... We can easily demonstrate the nature of the equipartition theorem by applying the demon algorithm to the ideal gas for which the kinetic energy of a particle is given by ǫ(p) = p2 /2m. In this case the trial moves are changes in the momentum p of a particle. Figure 1 shows the demon probability dist ...
Dipole Moment
... Polarities of X-H bonds increase upon hydrogen-bond formation, often leading to complexes whose dipole moments are larger than those expected from vectorial addition. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance (NMR) chemical shifts of protons in hydrogen bonds are substantially smaller than those observed in the co ...
... Polarities of X-H bonds increase upon hydrogen-bond formation, often leading to complexes whose dipole moments are larger than those expected from vectorial addition. Nuclear-magnetic-resonance (NMR) chemical shifts of protons in hydrogen bonds are substantially smaller than those observed in the co ...
Phy 211: General Physics I
... Conservation of Mass: The total quantity of mass is never created nor destroyed during a chemical process ...
... Conservation of Mass: The total quantity of mass is never created nor destroyed during a chemical process ...
Balancing a Chemical Equation
... 2. Write the skeleton equation by to be 1. Begin by balancing placing the formulas for the elements that appear only once on reactants on the left and the each side of the equation. Never formulas for the products on the balance an equation by changing right with a yields sign (→) in the subscripts ...
... 2. Write the skeleton equation by to be 1. Begin by balancing placing the formulas for the elements that appear only once on reactants on the left and the each side of the equation. Never formulas for the products on the balance an equation by changing right with a yields sign (→) in the subscripts ...
Matter - cloudfront.net
... 2. Can be reversible, or irreversible. 3. Chemical change - a change where a new form of matter is formed. – Rust, burn, decompose, ferment ...
... 2. Can be reversible, or irreversible. 3. Chemical change - a change where a new form of matter is formed. – Rust, burn, decompose, ferment ...
lecture chapter 23
... is the topographical map – the lines connect points of equal gravitational potential (altitude). ...
... is the topographical map – the lines connect points of equal gravitational potential (altitude). ...
Theories in the Evolution of Chemical Equilibrium: Impli
... out on a large scale. He faced the problem of the variability of affinities when trying to obtain pure KNO3 because the process required some recrystallizations and Berthollet noted that as the concentration of nitrate increased, the capacity of the ...
... out on a large scale. He faced the problem of the variability of affinities when trying to obtain pure KNO3 because the process required some recrystallizations and Berthollet noted that as the concentration of nitrate increased, the capacity of the ...
Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potential
... We’ve seen that a charge creates an electric field in all the space surrounding it. This field exists whether or not a test charge is placed in the field. The electric field is what “communicates” the electric force: q1 creates a field E, and q2 interacts with this field, experiencing a force of ma ...
... We’ve seen that a charge creates an electric field in all the space surrounding it. This field exists whether or not a test charge is placed in the field. The electric field is what “communicates” the electric force: q1 creates a field E, and q2 interacts with this field, experiencing a force of ma ...
Chemical changes
... are: melting, freezing, condensing, breaking, crushing, cutting, and bending. ...
... are: melting, freezing, condensing, breaking, crushing, cutting, and bending. ...
WRL1834.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... classical context). Equilibrium states do not change with time (in contrast to microstates, which are perennially hustling about), and in practice such states are often metastable, meaning they change on a very long timescale, and can ‘therefore’ be viewed to be equilibrium states. It does not seem ...
... classical context). Equilibrium states do not change with time (in contrast to microstates, which are perennially hustling about), and in practice such states are often metastable, meaning they change on a very long timescale, and can ‘therefore’ be viewed to be equilibrium states. It does not seem ...
Pages from PS 11 Textbook for Lab
... term is small compared with the change in enthalpy, ∆H, of a reaction, and thus the thermal energy (heat) produced in a chemical reaction at constant pressure is approximately equal to that produced at constant volume. To summarize ∆H = qp ...
... term is small compared with the change in enthalpy, ∆H, of a reaction, and thus the thermal energy (heat) produced in a chemical reaction at constant pressure is approximately equal to that produced at constant volume. To summarize ∆H = qp ...























