Chemistry Study Guide
... Dissolved Mixture Suspension Chemical property A liquid changes into a gas through evaporation When ingredients are evenly mixed a solution is formed. When iron turns to rust it is an example of a chemical property. When ingredients can easily be seen such as the ingredients in salad dressing it is ...
... Dissolved Mixture Suspension Chemical property A liquid changes into a gas through evaporation When ingredients are evenly mixed a solution is formed. When iron turns to rust it is an example of a chemical property. When ingredients can easily be seen such as the ingredients in salad dressing it is ...
CHM 2045C - State College of Florida
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A ...
... (5 Credit Hours) (A.A.) Three hours lecture, three hours laboratory per week. Prerequisites: Completion of MAC 1105. Completion of CHM 1025C with a grade of “C” or better or one year of high school college preparatory honors or AP chemistry within last three years. This course meets Area V for the A ...
Unit 5 Chemical Properties and Changes Video Notes A ______ is a
... ________________________ A change that alters the identity of a substance resulting in a new substance or substances with different properties ________________________ Those characteristics that can be observed when a chemical reaction changes the identity of the substance, such as potential to rus ...
... ________________________ A change that alters the identity of a substance resulting in a new substance or substances with different properties ________________________ Those characteristics that can be observed when a chemical reaction changes the identity of the substance, such as potential to rus ...
CHM 111: General Physical Chemistry 3 Units
... masses. Fundamental particles of the atom and atomic structure. Modern electronic theory of atoms; electronic configuration of the elements. Periodicity of the elements. Radioactivity: Stoichiometry: mole concept, chemical formulas, equations and calculations. States of matter: gas empirical gas law ...
... masses. Fundamental particles of the atom and atomic structure. Modern electronic theory of atoms; electronic configuration of the elements. Periodicity of the elements. Radioactivity: Stoichiometry: mole concept, chemical formulas, equations and calculations. States of matter: gas empirical gas law ...
ch_24_poss_elmo
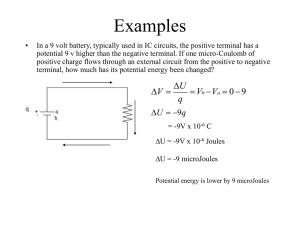
... • V = kq/r = 8.99*109 N m2//C2 *1.6*10-19 C/0.529*10-10m • V = 27. 2 J/C = 27. 2 Volts What is the electric potential energy of the electron at that point? U = qV= (-1.6 x 10-19 C) (27.2 V)= - 43.52 x 10-19 J or - 27.2 eV where eV stands for electron volts Total energy of the electron in the ground ...
... • V = kq/r = 8.99*109 N m2//C2 *1.6*10-19 C/0.529*10-10m • V = 27. 2 J/C = 27. 2 Volts What is the electric potential energy of the electron at that point? U = qV= (-1.6 x 10-19 C) (27.2 V)= - 43.52 x 10-19 J or - 27.2 eV where eV stands for electron volts Total energy of the electron in the ground ...
milli-extraction column for liquid-liquid phase separation
... LIQUID-LIQUID PHASE SEPARATION CHEMICAL PROCESS ENGINEERING Best Practice Example created by ...
... LIQUID-LIQUID PHASE SEPARATION CHEMICAL PROCESS ENGINEERING Best Practice Example created by ...