WRL1738.tmp - Symposium on Chemical Physics
... thermodynamics only refers to the properties of equilibrium states, and does not immediately apply to the non-equilibrium processes that connect various equilibrium states. 3. It is possible to connect the equilibrium states A(U A ,V , n) B(U B ,V , n) , by transforming either A to B or B to A usi ...
... thermodynamics only refers to the properties of equilibrium states, and does not immediately apply to the non-equilibrium processes that connect various equilibrium states. 3. It is possible to connect the equilibrium states A(U A ,V , n) B(U B ,V , n) , by transforming either A to B or B to A usi ...
Turn in Homework to the front! 9/7 Warm Up
... • When of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) break down, 7 grams nitrogen and 4 grams of oxygen form. How many grams of water are formed? • X = 20 - 7- 4 = 9 ...
... • When of ammonium nitrate (NH4NO3) break down, 7 grams nitrogen and 4 grams of oxygen form. How many grams of water are formed? • X = 20 - 7- 4 = 9 ...
Quantum Mechanics Gibbs free energy
... History See also: Thermodynamic free energy The quantity called "free energy" is a more advanced and accurate replacement for the outdated term affinity, which was used by chemists in previous years to describe the force that caused chemical reactions. In 1873, Willard Gibbs published A Method of Ge ...
... History See also: Thermodynamic free energy The quantity called "free energy" is a more advanced and accurate replacement for the outdated term affinity, which was used by chemists in previous years to describe the force that caused chemical reactions. In 1873, Willard Gibbs published A Method of Ge ...
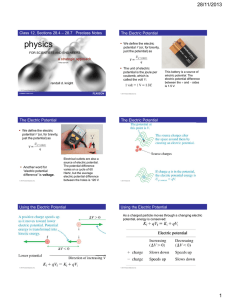
Electric Potential - Little Shop of Physics
... 1. What is the potential difference between the two spheres? This is “the voltage of the Van de Graaf generator”. 2. A typical charge on the sphere is 10 µC. If we could transfer this charge without changing the potential difference, what would be the change in potential energy? ...
... 1. What is the potential difference between the two spheres? This is “the voltage of the Van de Graaf generator”. 2. A typical charge on the sphere is 10 µC. If we could transfer this charge without changing the potential difference, what would be the change in potential energy? ...
solid metal
... Referring to Figures 4.5 and 4.6, we observe the following: (a) Barium (Ba) is on the left side of the periodic table; it is a solid metal under normal conditions. (b) Boron (B) is in the middle of the periodic table; it is a solid semimetal. (c) Bismuth (Bi) is to the right, but below the semimetal ...
... Referring to Figures 4.5 and 4.6, we observe the following: (a) Barium (Ba) is on the left side of the periodic table; it is a solid metal under normal conditions. (b) Boron (B) is in the middle of the periodic table; it is a solid semimetal. (c) Bismuth (Bi) is to the right, but below the semimetal ...
Topic/Objective - cloudfront.net
... Title: Molecular mass of a volatile liquid (exp3) Objective: A small amount of a volatile liquid inside a small test tube and then heated in boiling water until all the liquid vaporizes and fills the tube as excess water escapes. After the gas is cooled, the mass, volume, and pressure is measured to ...
... Title: Molecular mass of a volatile liquid (exp3) Objective: A small amount of a volatile liquid inside a small test tube and then heated in boiling water until all the liquid vaporizes and fills the tube as excess water escapes. After the gas is cooled, the mass, volume, and pressure is measured to ...
Chemical Reactions and Equations
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
... What is a ‘Reaction’? Reaction is a term used for depicting a change or transformation in which a substance decomposes, combines with other substances, or interchanges constituents with other substances. What is a ‘Chemical Reaction’? A chemical change is always accompanied by a chemical reaction. a ...
Chemical Equations and Reactions
... the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction ...
... the claim that atoms, and therefore mass, are conserved during a chemical reaction ...
Influence of the chemical potential
... magnetotransport11 because it leads to unconventional Landau level quantization as compared to the case of parabolic bands. One essential difference is that a zeroth order Landau level is pinned at zero energy for any field strength. With increasing impurity scattering, the pseudogap is therefore gr ...
... magnetotransport11 because it leads to unconventional Landau level quantization as compared to the case of parabolic bands. One essential difference is that a zeroth order Landau level is pinned at zero energy for any field strength. With increasing impurity scattering, the pseudogap is therefore gr ...
VCAA Study Design - Chemistry Education Association
... • lack of awareness of the differences between discharging and recharging in terms of the direction of electron flow, and that electrons always move from the site of oxidation (anode) to the site of reduction (cathode) • inability to correctly explain the changes in the rates of the forward and reve ...
... • lack of awareness of the differences between discharging and recharging in terms of the direction of electron flow, and that electrons always move from the site of oxidation (anode) to the site of reduction (cathode) • inability to correctly explain the changes in the rates of the forward and reve ...