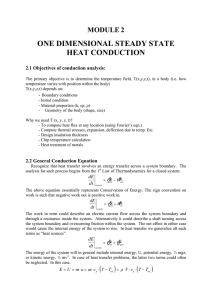
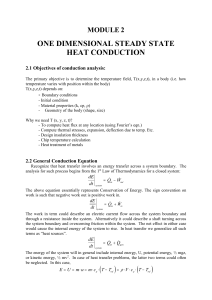
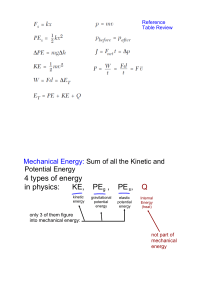
Heat flow direction
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...
Basics of Thermodynamics
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...
Energy Study Guide Key
... 2. Explain the transfer of energy. Give 3 examples. When one form of energy changes into another form of energy; gasoline in a lawn mower – chemical to mechanical; coal-power plants – chemical to electrical; light bulb – electrical to heat and light; toaster – electrical to heat; power drill – elect ...
... 2. Explain the transfer of energy. Give 3 examples. When one form of energy changes into another form of energy; gasoline in a lawn mower – chemical to mechanical; coal-power plants – chemical to electrical; light bulb – electrical to heat and light; toaster – electrical to heat; power drill – elect ...
Lecture Section 10
... First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy) • Change in internal energy = heat flowing in + work done on • dU = dQ + dR = TdS + dR • For thermally insulated body, dQ = TdS = 0 ...
... First Law of Thermodynamics (conservation of energy) • Change in internal energy = heat flowing in + work done on • dU = dQ + dR = TdS + dR • For thermally insulated body, dQ = TdS = 0 ...
Overview
... artificial ideal process that carries the system through the same beginning and ending state values as the real system. Adiabatic Expansion and Cooling As a simple illustration of the use of the fundamental equation (2), we consider the rapid expansion of an ideal gas. Consider n moles of helium ori ...
... artificial ideal process that carries the system through the same beginning and ending state values as the real system. Adiabatic Expansion and Cooling As a simple illustration of the use of the fundamental equation (2), we consider the rapid expansion of an ideal gas. Consider n moles of helium ori ...
Study Guide Energy
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
Slide 1
... A wide variety of compressor designs can be used on the separable unit including horizontal, vertical, semi-radial and Vtype. However, the most common design is the horizontal, balancedopposed compressor because of its stability and reduced ...
... A wide variety of compressor designs can be used on the separable unit including horizontal, vertical, semi-radial and Vtype. However, the most common design is the horizontal, balancedopposed compressor because of its stability and reduced ...
Class01 Intro Units
... Review of Thermodynamics • Extensive variables – depend on total mass of the system, e.g. M, E, S, V • Intensive variables – do not depend on total mass of the system, e.g. p, T, s, (1/v) • Equilibrium (state of maximum disorder) – bodies that are at the same temperature are called in thermal equ ...
... Review of Thermodynamics • Extensive variables – depend on total mass of the system, e.g. M, E, S, V • Intensive variables – do not depend on total mass of the system, e.g. p, T, s, (1/v) • Equilibrium (state of maximum disorder) – bodies that are at the same temperature are called in thermal equ ...
Chapter 18 - cloudfront.net
... held at –20.0°C and that the refrigerator exhausts energy into a room at 20.0°C. Ans 42. Review problem. This problem complements Problem 10.18 in Chapter 10. In the operation of a single-cylinder internal combustion piston engine, one charge of fuel explodes to drive the piston outward in the so-ca ...
... held at –20.0°C and that the refrigerator exhausts energy into a room at 20.0°C. Ans 42. Review problem. This problem complements Problem 10.18 in Chapter 10. In the operation of a single-cylinder internal combustion piston engine, one charge of fuel explodes to drive the piston outward in the so-ca ...