Intro Physics Curriculum by Trimester
... how work can be expressed as a change in mechanical energy. 2.4 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively the concept of power as work done per unit time. 2.5 Provide and interpret examples showing that linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity, and is always conserved (law of conserv ...
... how work can be expressed as a change in mechanical energy. 2.4 Describe both qualitatively and quantitatively the concept of power as work done per unit time. 2.5 Provide and interpret examples showing that linear momentum is the product of mass and velocity, and is always conserved (law of conserv ...
Physics 201 - University of Virginia
... Engines must operate in cycles in order to be useful. A piston and cylinder must return to original position. The change in internal energy is zero. An engine operates between two thermal ...
... Engines must operate in cycles in order to be useful. A piston and cylinder must return to original position. The change in internal energy is zero. An engine operates between two thermal ...
Rankine cycle analysis 5
... Since there is not work done in the valve and heat transfer Q v can be neglected, last equation reduces to: ...
... Since there is not work done in the valve and heat transfer Q v can be neglected, last equation reduces to: ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics and Entropy
... Under certain conditions specified in the law, libraries and archives are authorized to furnish a photocopy or other reproduction. One of these specified conditions is that the photocopy or reproduction is not to be used for any purpose other than private study, scholarship, or research. If electron ...
... Under certain conditions specified in the law, libraries and archives are authorized to furnish a photocopy or other reproduction. One of these specified conditions is that the photocopy or reproduction is not to be used for any purpose other than private study, scholarship, or research. If electron ...
Course Home - Haldia Institute of Technology
... Thermodynamic processes; quasi-static, reversible & irreversible processes; Thermodynamic cycles. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Concept of empirical temperature. Heat and Work Definition & units of thermodynamic work. Examples of different forms of thermodynamic works; example of electricity flow as ...
... Thermodynamic processes; quasi-static, reversible & irreversible processes; Thermodynamic cycles. Zeroth law of thermodynamics. Concept of empirical temperature. Heat and Work Definition & units of thermodynamic work. Examples of different forms of thermodynamic works; example of electricity flow as ...
Chapter 4 Entropy and second law of thermodynamics
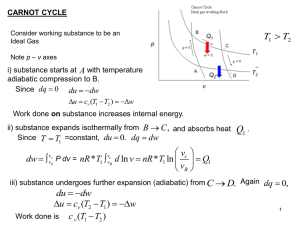
... Let us consider now the processes involved. A → B: isothermic compression. Work is performed on the gas and an amount of heat Q1 < 0 is given to the reservoir in a reversible process. As a result, ∆S = QT1 diminishes. B → C: adiabatic expansion. The gas performs work. Since δQ = 0, the entropy remai ...
... Let us consider now the processes involved. A → B: isothermic compression. Work is performed on the gas and an amount of heat Q1 < 0 is given to the reservoir in a reversible process. As a result, ∆S = QT1 diminishes. B → C: adiabatic expansion. The gas performs work. Since δQ = 0, the entropy remai ...
PPT
... For the irreversible case the work done is less than u T s since some of the heat added to the system can go into changing the ‘internal’ entropy of the system. ...
... For the irreversible case the work done is less than u T s since some of the heat added to the system can go into changing the ‘internal’ entropy of the system. ...
Chapter 5 – Energy
... Law of Conservation of Energy- another name for the First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics- any time energy is transferred, some of it will be lost as heat. Entropy- Symbol S, a quantitative measure of the amount of thermal energy not available to do work: or a measure of disorder ...
... Law of Conservation of Energy- another name for the First Law of Thermodynamics Second Law of Thermodynamics- any time energy is transferred, some of it will be lost as heat. Entropy- Symbol S, a quantitative measure of the amount of thermal energy not available to do work: or a measure of disorder ...
Document
... different conditions. In Figure part a the heat is supplied by a hot reservoir whose temperature is 650 K. In part b of the drawing, the heat flows irreversibly through a copper rod into a second reservoir whose temperature is 350 K and then enters the engine. In either case, a 150-K reservoir is us ...
... different conditions. In Figure part a the heat is supplied by a hot reservoir whose temperature is 650 K. In part b of the drawing, the heat flows irreversibly through a copper rod into a second reservoir whose temperature is 350 K and then enters the engine. In either case, a 150-K reservoir is us ...
Heat - Geography1000
... • As air rises the air cools, as the molecules spread out loosing heat • Compression: Adiabatic Warming • As air descends it is compressed, the molecules collide and create heat • Latent Heat • Storage or release of energy • Evaporation- liquid water changes to gases, energy is released, cooling hap ...
... • As air rises the air cools, as the molecules spread out loosing heat • Compression: Adiabatic Warming • As air descends it is compressed, the molecules collide and create heat • Latent Heat • Storage or release of energy • Evaporation- liquid water changes to gases, energy is released, cooling hap ...
Heat flow direction
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...
... then the direction of heat flow will be reversed. If a block of material (at 40C) is contact with surrounding at 80C then the ‘heat transfer’ with takes place is not reversible. Though the above example uses temperature differences to illustrate the point, the situation with other stimuli like ...