
Chapter 5 auxiliary functions
... such process can only spontaneously If The Gibbs Free Energy decrease since in any spontaneously process dsirr > 0 * As the condition for the thermodynamic equilibrium is that d sirr = 0 then with respect to isothermal and isobanic processes , equilibrium is defined by the coordination that : dG=0 ...
... such process can only spontaneously If The Gibbs Free Energy decrease since in any spontaneously process dsirr > 0 * As the condition for the thermodynamic equilibrium is that d sirr = 0 then with respect to isothermal and isobanic processes , equilibrium is defined by the coordination that : dG=0 ...
Basic Thermodynamics - CERN Accelerator School
... A thermodynamic system is in thermodynamic equilibrium when all its state variables remain constant with time: there is no net flow of matter or energy, no phase changes, and no unbalanced potentials (or driving forces) within the system. A system that is in thermodynamic equilibrium experiences no ...
... A thermodynamic system is in thermodynamic equilibrium when all its state variables remain constant with time: there is no net flow of matter or energy, no phase changes, and no unbalanced potentials (or driving forces) within the system. A system that is in thermodynamic equilibrium experiences no ...
1 Problem T4 (Unified Thermodynamics): SOLUTIONS a) Describe
... External work is done on the upper chamber by the weight. The potential energy of the weight is reduced and the internal energy of the gas in the upper chamber is increased. The process is not quasi-static. Then heat is gradually transferred from the upper chamber to the lower chamber. During this p ...
... External work is done on the upper chamber by the weight. The potential energy of the weight is reduced and the internal energy of the gas in the upper chamber is increased. The process is not quasi-static. Then heat is gradually transferred from the upper chamber to the lower chamber. During this p ...
1 Introduction - Wiley-VCH
... Engineering can be defined as “the science or art of practical applications of the knowledge of pure sciences such as physics, chemistry, and biology.” Compared with civil, mechanical, and other forms of engineering, chemical engineering is a relatively young branch of the subject that has been devel ...
... Engineering can be defined as “the science or art of practical applications of the knowledge of pure sciences such as physics, chemistry, and biology.” Compared with civil, mechanical, and other forms of engineering, chemical engineering is a relatively young branch of the subject that has been devel ...
chapter20
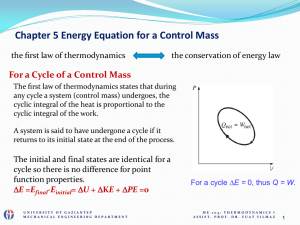
... The internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...
... The internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...
Introduction to Physical Chemistry
... The pressure (P) of a gas depends on its temperature (T) and volume (V), so P=f(T,V). Write the general differential for P. dP = Assuming that the gas is ideal (that is, there are not intermolecular forces and the individual gas particles occupy no volume), the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) can be used to ...
... The pressure (P) of a gas depends on its temperature (T) and volume (V), so P=f(T,V). Write the general differential for P. dP = Assuming that the gas is ideal (that is, there are not intermolecular forces and the individual gas particles occupy no volume), the ideal gas law (PV=nRT) can be used to ...
The basic concepts For the purposes of physical chemistry, the
... electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1 V; the relation between electronvolts and joules is 1 eV = 1.6x10-19 J. Many processes in chemistry have an energy of several electronvolts. Thus, the energy to remove an electron from a sodium atom is close to 5 eV. Calories (cal ...
... electron is accelerated from rest through a potential difference of 1 V; the relation between electronvolts and joules is 1 eV = 1.6x10-19 J. Many processes in chemistry have an energy of several electronvolts. Thus, the energy to remove an electron from a sodium atom is close to 5 eV. Calories (cal ...
Study Guide for QCA4 ans. key
... in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 6. Give an example of Newton’s First Law and explain it. You are driving in a car, without your seatbelt, and the car hits a wall. The car stops because of the unbalanced force (wall), but you keep moving through the windshield ...
... in motion will stay in motion unless acted upon by an unbalanced force. 6. Give an example of Newton’s First Law and explain it. You are driving in a car, without your seatbelt, and the car hits a wall. The car stops because of the unbalanced force (wall), but you keep moving through the windshield ...
Energy Vocabulary I
... 15. ____________ Something that is good at allowing energy to flow. 16. ____________ Potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. 17. ____________ Potential energy where energy is stored in the bonds of atoms. 18. ____________ the rubbing of the surface of one object on another object (creates ...
... 15. ____________ Something that is good at allowing energy to flow. 16. ____________ Potential energy stored in the nucleus of an atom. 17. ____________ Potential energy where energy is stored in the bonds of atoms. 18. ____________ the rubbing of the surface of one object on another object (creates ...
Thermal Cycles - Rankine Cycle with Reheat - plaza
... FLORIDA equilibrium state to another without experiencing a change in the amount of energy contained in the material, in the amount of material, or in the external forces placed on the material. d. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to accept from a heat interaction with ...
... FLORIDA equilibrium state to another without experiencing a change in the amount of energy contained in the material, in the amount of material, or in the external forces placed on the material. d. A cyclic machine that will experience no other interaction than to accept from a heat interaction with ...
Chapter 20 - UCF College of Sciences
... The change in internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...
... The change in internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...
Chapter 20 - UCF Physics
... The change in internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...
... The change in internal energy must be zero since it is a state variable If DEint = 0, Q = -W In a cyclic process, the net work done on the system per cycle equals the area enclosed by the path representing the process on a PV diagram ...




















![BTD QUESTION BANK[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/009330461_1-f5de3108f7a7a17ebe3a8cbd391865db-300x300.png)

