Chap-3
... • In thermodynamics, a reversible process, or reversible cycle if the process is cyclic, is a process that can be "reversed" by means of infinitesimal changes in some property of the system without loss or dissipation of energy. Due to these infinitesimal changes, the system is at rest during the wh ...
... • In thermodynamics, a reversible process, or reversible cycle if the process is cyclic, is a process that can be "reversed" by means of infinitesimal changes in some property of the system without loss or dissipation of energy. Due to these infinitesimal changes, the system is at rest during the wh ...
Lecture 4: Heat transfer
... Thermal Radiation (or sometimes Blackbody Radiation ). The hotter an object is, the more light it emits. And, as the temperature of the object increase, it emits most of its light at higher and higher energies. (Higher energy light means shorter wavelength light.) The relationship between the amount ...
... Thermal Radiation (or sometimes Blackbody Radiation ). The hotter an object is, the more light it emits. And, as the temperature of the object increase, it emits most of its light at higher and higher energies. (Higher energy light means shorter wavelength light.) The relationship between the amount ...
Heat Transfer, Greenhouse Effect, Ozone Layer Notes
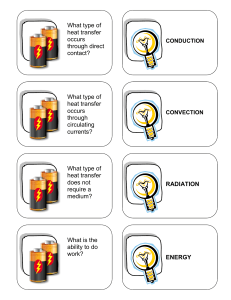
... The atmosphere moves energy • Energy moves by heat transfer • There are 3 types of heat transfer – Conduction – Convection – Radiation ...
... The atmosphere moves energy • Energy moves by heat transfer • There are 3 types of heat transfer – Conduction – Convection – Radiation ...
Chapter 8
... The leakage must therefore be positioned beneath the hot layer at all times (only cold air flowing out) or be positioned in the hot layer at all times (only hot smoke flowing out). ...
... The leakage must therefore be positioned beneath the hot layer at all times (only cold air flowing out) or be positioned in the hot layer at all times (only hot smoke flowing out). ...
Chapter 10 – States of Matter
... o Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that are far apart relative to their size. o Collisions between gas particles and between particles and container walls are elastic collisions. There is no net loss of total _____________________. o Gas particles are in continuous, rapid, random ___ ...
... o Gases consist of large numbers of tiny particles that are far apart relative to their size. o Collisions between gas particles and between particles and container walls are elastic collisions. There is no net loss of total _____________________. o Gas particles are in continuous, rapid, random ___ ...
Maxwell Relations
... This result helps to show that the internal energy of an ideal gas does not depend upon specific volume. This is known as Joule’s Law. For Vander Waal’s / real gases ...
... This result helps to show that the internal energy of an ideal gas does not depend upon specific volume. This is known as Joule’s Law. For Vander Waal’s / real gases ...
PSS 17.1: The Bermuda Triangle
... amount of work done on the system. Note the italicized words "to" and "on." These words are short, yet important: They contain, in effect, the sign convention; that is, they help you choose a positive or negative sign for the quantities that enter your calculations. For instance, a positive value of ...
... amount of work done on the system. Note the italicized words "to" and "on." These words are short, yet important: They contain, in effect, the sign convention; that is, they help you choose a positive or negative sign for the quantities that enter your calculations. For instance, a positive value of ...
Momentum Heat Mass Transfer
... and molecular forces could not be included into the internal energy. This view reduces the internal energy only to the thermal energy (kinetic energy of random molecular motion). Example: Consider exothermic chemical reaction proceeding inside a closed and thermally insulated vessel. Chemical energy ...
... and molecular forces could not be included into the internal energy. This view reduces the internal energy only to the thermal energy (kinetic energy of random molecular motion). Example: Consider exothermic chemical reaction proceeding inside a closed and thermally insulated vessel. Chemical energy ...
First law of thermodynamics
... Before look at the second law of thermodynamics, let us discuss where first law of thermodynamics fails. According to the first law of thermodynamics, whenever any process occurs, there may be either heat interaction or work interaction. But we cannot exactly tell by first law that in which directio ...
... Before look at the second law of thermodynamics, let us discuss where first law of thermodynamics fails. According to the first law of thermodynamics, whenever any process occurs, there may be either heat interaction or work interaction. But we cannot exactly tell by first law that in which directio ...
GCE Physics - Thermodynamics Notes Word Document
... We could equally well write this as Work done by band = – Fx To see the point of this, suppose we allow the band to contract, exerting a pull F. In this case x is negative so the work done by the band is positive, which makes sense. If we stretch the band a lot, then F will change significantly du ...
... We could equally well write this as Work done by band = – Fx To see the point of this, suppose we allow the band to contract, exerting a pull F. In this case x is negative so the work done by the band is positive, which makes sense. If we stretch the band a lot, then F will change significantly du ...
Session 15 Thermodynamics
... The total energy of the gas is also a state variable. That is, it depends on one or more of P, V and T. In fact, for a fixed quantity of an ideal gas the total energy depends just on the temperature. We can change the state of the gas in various ways: by some combination of heating it or doing work ...
... The total energy of the gas is also a state variable. That is, it depends on one or more of P, V and T. In fact, for a fixed quantity of an ideal gas the total energy depends just on the temperature. We can change the state of the gas in various ways: by some combination of heating it or doing work ...
Study Guide
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
... 4. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the slowest? ____________ 5. In which substance (solids, liquids, gases) do particles move the fastest? ____________ 6. As a substance is cooled the molecules/particles move (faster/slower)? _____________ 7. By increasing the _________ ...
Lecture 1 Objectives: Students will be able to: 1. Describe the terms
... Physics outside Physics Departments. Engineers, Chemists, and Material Scientists do not study relatively or particle physics, but thermodynamics is an integral, and very important, part of their degree courses. Many people are drawn to Physics because they want to understand why the world around us ...
... Physics outside Physics Departments. Engineers, Chemists, and Material Scientists do not study relatively or particle physics, but thermodynamics is an integral, and very important, part of their degree courses. Many people are drawn to Physics because they want to understand why the world around us ...
Internal Energy, Heat, Enthalpy, and Calorimetry
... Non-examples Work Heat Distance travelled (nonscientific analogy) ...
... Non-examples Work Heat Distance travelled (nonscientific analogy) ...
Thermodynamics Day I: UU
... is no such thing as a perfectly efficient engine or a perfectly efficient refrigerator. Also, gases will spontaneously expand into empty space but never spontaneously contract to create empty space. Doubtless, there are many others. ...
... is no such thing as a perfectly efficient engine or a perfectly efficient refrigerator. Also, gases will spontaneously expand into empty space but never spontaneously contract to create empty space. Doubtless, there are many others. ...
Energy
... What does Conservation of Energy mean? • Energy can flow from one object to another. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. • It is converted from one form to another. • Energy in an isolated system is conserved. • This is also known as the first law of thermodynamics ...
... What does Conservation of Energy mean? • Energy can flow from one object to another. • Energy cannot be created or destroyed. • It is converted from one form to another. • Energy in an isolated system is conserved. • This is also known as the first law of thermodynamics ...
worth 50 points!!- Due when you take your midterm!!!
... Wind, water going over a dam, person kicking a ball Heat from a fire, heat from friction, your body temperature Electrons flowing from atom to atom to make a light bulb light up ...
... Wind, water going over a dam, person kicking a ball Heat from a fire, heat from friction, your body temperature Electrons flowing from atom to atom to make a light bulb light up ...