Thermodynamics: Notes
... equilibrium. So we require a quasistatic process. Thus, every process involving heat flow is to be quasistatic. Further, we have banned dissipative forces from the system. Therefore, these processes are reversible. A process involving heat flow is made reversible by making the process isothermal. Th ...
... equilibrium. So we require a quasistatic process. Thus, every process involving heat flow is to be quasistatic. Further, we have banned dissipative forces from the system. Therefore, these processes are reversible. A process involving heat flow is made reversible by making the process isothermal. Th ...
biomolecules and bioenergetics
... To see more clearly how the First Law operates, internal energy and work have to be defined As with heat, both internal energy and work are measured in units of joules (or calories) The internal energy, U, is the energy within a system It represents only those kinds of energy that can be modified by ...
... To see more clearly how the First Law operates, internal energy and work have to be defined As with heat, both internal energy and work are measured in units of joules (or calories) The internal energy, U, is the energy within a system It represents only those kinds of energy that can be modified by ...
The Helmholtz Function
... Suppose W (other) 0 If we have a reversible process Q = TS and G = -W(other), so W(other) (Gi Gf ) Gf - Gi = -W (other) or The change in the Gibbs function gives the maximum energy that can be freed in an isothermal, isobaric process and made available for non-mechanical work. For this reas ...
... Suppose W (other) 0 If we have a reversible process Q = TS and G = -W(other), so W(other) (Gi Gf ) Gf - Gi = -W (other) or The change in the Gibbs function gives the maximum energy that can be freed in an isothermal, isobaric process and made available for non-mechanical work. For this reas ...
Section 3 Entropy and Classical Thermodynamics
... 3.3 The Carnot cycle 3.3.1 Introduction to Carnot cycles — Thermodynamic temperature The Carnot cycle is an important example of a cyclic process. In such a process the state of the working substance is varied but returns to the original state. So at the end of the cycle the functions of state of t ...
... 3.3 The Carnot cycle 3.3.1 Introduction to Carnot cycles — Thermodynamic temperature The Carnot cycle is an important example of a cyclic process. In such a process the state of the working substance is varied but returns to the original state. So at the end of the cycle the functions of state of t ...
ENERGY
... • Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes form • Energy in = energy out • Heat, light and sound are common forms of energy transfer ...
... • Energy cannot be created or destroyed; it only changes form • Energy in = energy out • Heat, light and sound are common forms of energy transfer ...
Thermodynamics and Irreversibility
... consider a transformation of this cycle, the isothermal transformation. See Figure 4. An isothermal transformation is a transformation that takes place at constant temperature, in contact with a thermostat. Take for example a piston air-filled at 20˚ Celsius, in an external medium like water also at ...
... consider a transformation of this cycle, the isothermal transformation. See Figure 4. An isothermal transformation is a transformation that takes place at constant temperature, in contact with a thermostat. Take for example a piston air-filled at 20˚ Celsius, in an external medium like water also at ...
PHYS2LessonsContinued
... Thermodynamics is the study of relationship involving heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer. Or, the field of physics that describes and correlates the physical properties of macroscopic systems of matter and energy. An example of thermodynamic process is the liquefa ...
... Thermodynamics is the study of relationship involving heat, mechanical work, and other aspects of energy and energy transfer. Or, the field of physics that describes and correlates the physical properties of macroscopic systems of matter and energy. An example of thermodynamic process is the liquefa ...
First Law of Thermodynamics - Erwin Sitompul
... Heats of Transformation When energy is absorbed as heat by a solid or liquid, the temperature of the sample does not necessarily rise. Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferr ...
... Heats of Transformation When energy is absorbed as heat by a solid or liquid, the temperature of the sample does not necessarily rise. Instead, the sample may change from one phase, or state, to another, with no change in temperature. The amount of energy per unit mass that must be transferr ...
Chapter 4
... enough energy to escape into the gas phase. • Once these particles escape another batch will take their place with enough kinetic energy to escape and eventually they will all evaporate. ...
... enough energy to escape into the gas phase. • Once these particles escape another batch will take their place with enough kinetic energy to escape and eventually they will all evaporate. ...
15. Thermodynamics
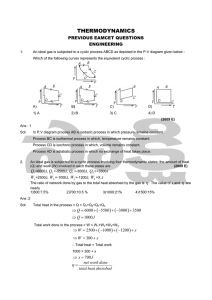
... 11. Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume2V. The changes in the pressure ...
... 11. Two identical containers A and B with frictionless pistons contain the same ideal gas at the same temperature and same volume V. The mass of the gas in A is mA and that in B is mB . The gas in each cylinder is now allowed to expand isothermally to the final volume2V. The changes in the pressure ...
Powerpoint
... • Heat flows from hot to cold (thermodynamics) and is proportional to the temperature gradient • Here k is the thermal conductivity (W m-1 K-1) and units of F are W m-2 (heat flux is power per unit area) • Typical values for k are 2-4 Wm-1K-1 (rock, ice) and 3060 Wm-1K-1 (metal) • Solar heat flux at ...
... • Heat flows from hot to cold (thermodynamics) and is proportional to the temperature gradient • Here k is the thermal conductivity (W m-1 K-1) and units of F are W m-2 (heat flux is power per unit area) • Typical values for k are 2-4 Wm-1K-1 (rock, ice) and 3060 Wm-1K-1 (metal) • Solar heat flux at ...