Organic chemistry is the study of carbon
... double bonds with two different oxygen atoms. The structural formula, O = C = O, shows that each atom has completed its valence shells. While CO2 can be classified as either organic or inorganic, its importance to the living world is clear. CO2 is the source for all organic molecules in organisms vi ...
... double bonds with two different oxygen atoms. The structural formula, O = C = O, shows that each atom has completed its valence shells. While CO2 can be classified as either organic or inorganic, its importance to the living world is clear. CO2 is the source for all organic molecules in organisms vi ...
136KB - NZQA
... B. cis 1,2-dibromoethene can form cis and trans isomers because it has a double bond. The double bond between two carbon atoms does not allow any rotation of atoms around it. As well as the double bond, the C atoms directly attached to it must have two different atoms or groups attached to them. For ...
... B. cis 1,2-dibromoethene can form cis and trans isomers because it has a double bond. The double bond between two carbon atoms does not allow any rotation of atoms around it. As well as the double bond, the C atoms directly attached to it must have two different atoms or groups attached to them. For ...
CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2OH CH3 - CH2-CH2
... Carbon has a valency of 4 (can form 4 bonds), and has 4 valence electrons (outermost energy level). Carbon has the ability to form long chains with other C atoms – called catenation. Carbon has the ability to form rings by joining with other C atoms ...
... Carbon has a valency of 4 (can form 4 bonds), and has 4 valence electrons (outermost energy level). Carbon has the ability to form long chains with other C atoms – called catenation. Carbon has the ability to form rings by joining with other C atoms ...
HYDROCARBONS HYDROCARBONS Types of Hydrocarbons
... • Aromatics are planar, ring structures with alternating single and double bonds: eg. C 6H6 Each C atom is trigonal planar with sp 2 hybridized orbitals. There is no rotation about the C=C bond in alkenes. ...
... • Aromatics are planar, ring structures with alternating single and double bonds: eg. C 6H6 Each C atom is trigonal planar with sp 2 hybridized orbitals. There is no rotation about the C=C bond in alkenes. ...
Products From Oil
... Biodegradable materials can be broken down by micro-organisms in the environment. Many polymers are not biodegradable, and can last for many years in land-fill. Others are, and will break down. Scientists have found ways to speed up this decomposition of polymers by adding starch which encourages mi ...
... Biodegradable materials can be broken down by micro-organisms in the environment. Many polymers are not biodegradable, and can last for many years in land-fill. Others are, and will break down. Scientists have found ways to speed up this decomposition of polymers by adding starch which encourages mi ...
Ch_4_Carbon - Bartlett High School
... When an oxygen atom is doublebonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group, the entire assembly of atoms is called a carboxyl group (— COOH). ...
... When an oxygen atom is doublebonded to a carbon atom that is also bonded to a hydroxyl group, the entire assembly of atoms is called a carboxyl group (— COOH). ...
91165 Organic Chemistry Cornell Notes.
... isomers (same molecular formula, different arrangement of carbon atoms) The C=C bond prevents rotation and so atoms / groups of atoms attached to either side of C=C are fixed in position. Alkenes with same molecular formula can be cis or trans. ...
... isomers (same molecular formula, different arrangement of carbon atoms) The C=C bond prevents rotation and so atoms / groups of atoms attached to either side of C=C are fixed in position. Alkenes with same molecular formula can be cis or trans. ...
Crazy Carbon - Cloudfront.net
... Carbon has 6 electrons, 2 in the first shell, 4 in the outer shell. So....Valence of Carbon is 4 (tetravalence) It can bond to four other molecules Carbon completes its valence by sharing electrons, forming covalent bonds (NOT ionic) Shape is a tetrahedron (109˚) Most frequent partners a ...
... Carbon has 6 electrons, 2 in the first shell, 4 in the outer shell. So....Valence of Carbon is 4 (tetravalence) It can bond to four other molecules Carbon completes its valence by sharing electrons, forming covalent bonds (NOT ionic) Shape is a tetrahedron (109˚) Most frequent partners a ...
Document
... es with g C M.P affected by how close the molecules can pack together Branchg may mp Though less efficient id-id forces, isomer able to pack into regular arrays ...
... es with g C M.P affected by how close the molecules can pack together Branchg may mp Though less efficient id-id forces, isomer able to pack into regular arrays ...
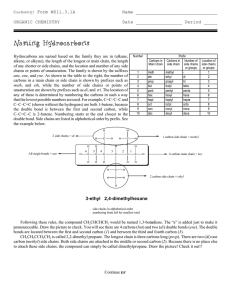
Naming Hydrocarbons
... Hydrocarbons are named based on the family they are in (alkane, alkene, or alkyne), the length of the longest or main chain, the length of any shorter or side chains, and the location and number of any side chains or points of unsaturation. The family is shown by the suffixes ane, ene, and yne. As s ...
... Hydrocarbons are named based on the family they are in (alkane, alkene, or alkyne), the length of the longest or main chain, the length of any shorter or side chains, and the location and number of any side chains or points of unsaturation. The family is shown by the suffixes ane, ene, and yne. As s ...
Regents Unit 15b: Halides, Alcohols, & Ethers
... • General formula is ROR where R may or may not be the same as R. • R and R are hydrocarbon branches. • O is an oxygen bridge. • Ethers are not linear. They are bent, like ...
... • General formula is ROR where R may or may not be the same as R. • R and R are hydrocarbon branches. • O is an oxygen bridge. • Ethers are not linear. They are bent, like ...
Name of alkane Chemical formula Displayed formula Methane CH4
... Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have single covalent bond ONLY; you can work out how many carbon atoms there should be in an alkane if you know how many hydrogen atoms there are and vice-versa using this formula: CnH 2n+2 (The number of hydrogen atoms is twice the number of carbon atoms plus 2) ...
... Alkanes are hydrocarbons that have single covalent bond ONLY; you can work out how many carbon atoms there should be in an alkane if you know how many hydrogen atoms there are and vice-versa using this formula: CnH 2n+2 (The number of hydrogen atoms is twice the number of carbon atoms plus 2) ...
PowerPoint - Name Hydrocarbons
... • To give each isomer a name you need to use a # to indicate which C atom the double bond starts (lowest possible number is given to carbon closest to double bond) ...
... • To give each isomer a name you need to use a # to indicate which C atom the double bond starts (lowest possible number is given to carbon closest to double bond) ...
Organic Compound - TangHua2012-2013
... carbon atom. 3. Finally, we add enough hydrogen atoms to give each carbon atom four bonds. ...
... carbon atom. 3. Finally, we add enough hydrogen atoms to give each carbon atom four bonds. ...
Carbon Compounds
... Hydrocarbons with double or triple bonds have fewer hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom than a saturated hydrocarbon does. They are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. Notice that the names of methane, ethane, propane, and butane end in the suffix - ane. Any hydrocarbon with a name that ends in ...
... Hydrocarbons with double or triple bonds have fewer hydrogen atoms for each carbon atom than a saturated hydrocarbon does. They are called unsaturated hydrocarbons. Notice that the names of methane, ethane, propane, and butane end in the suffix - ane. Any hydrocarbon with a name that ends in ...
Alkanes CH4 + Cl2 → CH3Cl + HCl CH3CH3 + Cl2 → CH3CH2Cl +
... CH4 CH3CH3 CH3CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH2CH3 ...
... CH4 CH3CH3 CH3CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2CH3 CH3CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2 CH2CH2CH2CH3 ...
04 Carbon
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
... – Carbon has little tendency to form ionic bonds by loosing or gaining 4 electrons. – Instead, carbon usually completes its valence shell by sharing electrons with other atoms in four covalent bonds. – This tetravalence by carbon makes large, complex molecules possible. ...
Evaporation and Intermolecular Attractions
... In this demonstration, temperature probes are placed in various liquids. Evaporation occurs when the probe is removed from the liquid’s container. This evaporation is an endothermic process that results in a temperature decrease. The magnitude of a temperature decrease is, like viscosity and boiling ...
... In this demonstration, temperature probes are placed in various liquids. Evaporation occurs when the probe is removed from the liquid’s container. This evaporation is an endothermic process that results in a temperature decrease. The magnitude of a temperature decrease is, like viscosity and boiling ...
Carbon Compounds
... Draw their structural formulae and write their IUPAC name. Why do alkenes and alkynes burn with sooty flame in air but alkanes burn without soot? State whether alkanes can also burn with sooty flame. If yes, under what conditions? Which of the following will burn with smoke in air: ethane, ethene, p ...
... Draw their structural formulae and write their IUPAC name. Why do alkenes and alkynes burn with sooty flame in air but alkanes burn without soot? State whether alkanes can also burn with sooty flame. If yes, under what conditions? Which of the following will burn with smoke in air: ethane, ethene, p ...
Islamic University of Gaza Biochemistry School of Nursing Midterm
... 8. If two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond, those two carbon atoms but not the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has t ...
... 8. If two carbon atoms are connected by a double bond, those two carbon atoms but not the four groups attached to them, lie in a single plane (incorrect) All four groups and the 2 carbon atoms lie in a single plane 9. A tertiary alcohol is one in which the –OH is attached to a carbon atom that has t ...
PowerPoint 簡報 - Solon City Schools
... The Functional Groups The properties of different biological molecules depend on certain characteristic groupings of atoms called functional groups. The names of the six most important functional groups are: – Hydroxyl – Carbonyl –Aldehydes – Ketones – Carboxyl – Amino – Sulfhydryl – Phosphate ...
... The Functional Groups The properties of different biological molecules depend on certain characteristic groupings of atoms called functional groups. The names of the six most important functional groups are: – Hydroxyl – Carbonyl –Aldehydes – Ketones – Carboxyl – Amino – Sulfhydryl – Phosphate ...
Organic Chemistry Nomenclature
... each type of organic compound only simple hydrocarbon chains and alcohols will be instructed below. When naming straight chains of hydrocarbons a prefix is added indicating the number of carbons to the suffix matching the type (e.g. ethyne H─C≡C─H or C2H2). The following prefixes are used to indicat ...
... each type of organic compound only simple hydrocarbon chains and alcohols will be instructed below. When naming straight chains of hydrocarbons a prefix is added indicating the number of carbons to the suffix matching the type (e.g. ethyne H─C≡C─H or C2H2). The following prefixes are used to indicat ...
Alkane
In organic chemistry, an alkane, or paraffin (a historical name that also has other meanings), is a saturated hydrocarbon. Alkanes consist only of hydrogen and carbon atoms and all bonds are single bonds. Alkanes (technically, always acyclic or open-chain compounds) have the general chemical formula CnH2n+2. For example, Methane is CH4, in which n=1 (n being the number of Carbon atoms). Alkanes belong to a homologous series of organic compounds in which the members differ by a molecular mass of 14.03u (mass of a methanediyl group, —CH2—, one carbon atom of mass 12.01u, and two hydrogen atoms of mass ≈1.01u each). There are two main commercial sources: petroleum (crude oil) and natural gas.Each carbon atom has 4 bonds (either C-H or C-C bonds), and each hydrogen atom is joined to a carbon atom (H-C bonds). A series of linked carbon atoms is known as the carbon skeleton or carbon backbone. The number of carbon atoms is used to define the size of the alkane e.g., C2-alkane.An alkyl group, generally abbreviated with the symbol R, is a functional group or side-chain that, like an alkane, consists solely of single-bonded carbon and hydrogen atoms, for example a methyl or ethyl group.The simplest possible alkane (the parent molecule) is methane, CH4. There is no limit to the number of carbon atoms that can be linked together, the only limitation being that the molecule is acyclic, is saturated, and is a hydrocarbon. Waxes include examples of larger alkanes where the number of carbons in the carbon backbone is greater than about 17, above which the compounds are solids at standard ambient temperature and pressure (SATP).Alkanes are not very reactive and have little biological activity. All alkanes are colourless and odourless. Alkanes can be viewed as a molecular tree upon which can be hung the more biologically active/reactive portions (functional groups) of the molecule.