Quantum Mechanics Problem Set
... of ∆E are allowed. These are represented by the lines on the emission spectra of excited atoms. 3. Is energy emitted or absorbed when the following electronic transitions occur in hydrogen (circle): (a) from n = 4 to n = 2. ...
... of ∆E are allowed. These are represented by the lines on the emission spectra of excited atoms. 3. Is energy emitted or absorbed when the following electronic transitions occur in hydrogen (circle): (a) from n = 4 to n = 2. ...
n 1
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE If an electron has wave-like properties, it becomes impossible to know both the momentum and position of the electron at the same instant in time. To overcome this problem, we use the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space and this is determined from ...
... THE UNCERTAINTY PRINCIPLE If an electron has wave-like properties, it becomes impossible to know both the momentum and position of the electron at the same instant in time. To overcome this problem, we use the probability of finding the electron in a given volume of space and this is determined from ...
BAND THEORY OF SOLIDS
... of the solid to be isolated from one another, they would have completely coinciding schemes of their energy levels. Let us study what happens to the energy levels of an isolated atom, as they are brought closer and closer together to form a solid. If the atoms are brought in close proximity, the val ...
... of the solid to be isolated from one another, they would have completely coinciding schemes of their energy levels. Let us study what happens to the energy levels of an isolated atom, as they are brought closer and closer together to form a solid. If the atoms are brought in close proximity, the val ...
Atomic Structure and Electron Configurations Multiple Choice PSI
... A. proposes that electrons occupy specific energy levels. B. explains the emission spectra of hydrogen atoms. C. predicts the energy levels of multi-electron atoms. D. Both a and b 5. The quantum-mechanical model of the atom A. describes an electron probability distribution that determines the most ...
... A. proposes that electrons occupy specific energy levels. B. explains the emission spectra of hydrogen atoms. C. predicts the energy levels of multi-electron atoms. D. Both a and b 5. The quantum-mechanical model of the atom A. describes an electron probability distribution that determines the most ...
Lecture Notes, Feb 24, 2016
... in terms of de Broglie waves. The lead player in the equation is a quantity called Ψ ( pronounced ”sigh” ) which is called the wave function. • Instead of describing particle by its position and velocity, in Schr”odinger’s equation, the particle is described by wave function Ψ. • Even in classical p ...
... in terms of de Broglie waves. The lead player in the equation is a quantity called Ψ ( pronounced ”sigh” ) which is called the wave function. • Instead of describing particle by its position and velocity, in Schr”odinger’s equation, the particle is described by wave function Ψ. • Even in classical p ...
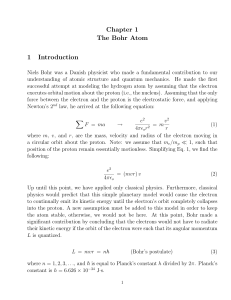
Chapter 1 The Bohr Atom 1 Introduction
... h = 6.626 × 10−34 J·s, show that: a) me c2 ' 511, 000 eV, and b) ~c ' 197 eV·nm c) hc ' 1240 eV·nm ...
... h = 6.626 × 10−34 J·s, show that: a) me c2 ' 511, 000 eV, and b) ~c ' 197 eV·nm c) hc ' 1240 eV·nm ...
Chapter 2
... (a) n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0 (b) n = 2, l = 1, ml = –1 (c) n = 4, l = 3, ml = –2 (d) n = 4, l = 2, ml = 0 10. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have each of the following sets of quantum numbers or sublevel designations? ...
... (a) n = 3, l = 0, ml = 0 (b) n = 2, l = 1, ml = –1 (c) n = 4, l = 3, ml = –2 (d) n = 4, l = 2, ml = 0 10. What is the maximum number of electrons in an atom that can have each of the following sets of quantum numbers or sublevel designations? ...
Van der Waals Forces Between Atoms
... The perfect gas equation of state PV = NkT is manifestly incapable of describing actual gases at low temperatures, since they undergo a discontinuous change of volume and become liquids. In the 1870’s, the Dutch physicist Van der Waals came up with an improvement: a gas law that recognized the m ...
... The perfect gas equation of state PV = NkT is manifestly incapable of describing actual gases at low temperatures, since they undergo a discontinuous change of volume and become liquids. In the 1870’s, the Dutch physicist Van der Waals came up with an improvement: a gas law that recognized the m ...
Atomic Structure MC Review_ corrected
... A. proposes that electrons occupy specific energy levels. B. explains the emission spectra of hydrogen atoms. C. predicts the energy levels of multi-electron atoms. D. Both a and b 5. The quantum-mechanical model of the atom A. describes an electron probability distribution that determines the most ...
... A. proposes that electrons occupy specific energy levels. B. explains the emission spectra of hydrogen atoms. C. predicts the energy levels of multi-electron atoms. D. Both a and b 5. The quantum-mechanical model of the atom A. describes an electron probability distribution that determines the most ...
CHM1045 - Michael Blaber
... E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, and the orbit number of the electron) Elevel = RH * (1/ni2 - 1/nf2) or En = B * (1/ni2 - 1/n ...
... E = h * (the relationship between energy and frequency for electromagnetic radiation En = -RH / n2 or En = -B / n2 (the relationship between the energy of an electron in Bohr's model of the hydrogen atom, and the orbit number of the electron) Elevel = RH * (1/ni2 - 1/nf2) or En = B * (1/ni2 - 1/n ...
(1)
... With a group of elements, the atomic radius increases with increasing atomic number. For a given group, ionization energy increases with increasing atomic number. Cation is always smaller than atom from which it is formed Metals have relatively low ionization energies compared to nonmetals. ...
... With a group of elements, the atomic radius increases with increasing atomic number. For a given group, ionization energy increases with increasing atomic number. Cation is always smaller than atom from which it is formed Metals have relatively low ionization energies compared to nonmetals. ...
Electron wavepackets and microscopic Ohm`s law
... • Each atomic state a band of states in the crystal These are the “allowed” states for electrons in the crystal Fill according to Pauli Exclusion Principle • There may be gaps between the bands These are “forbidden”energies where there are no states for electrons What do you expect to be a metal ...
... • Each atomic state a band of states in the crystal These are the “allowed” states for electrons in the crystal Fill according to Pauli Exclusion Principle • There may be gaps between the bands These are “forbidden”energies where there are no states for electrons What do you expect to be a metal ...
Lecture : 4 Quantum Numbers : Using wave mechanics, every
... 1-The smaller the principal QN , the lower the energy level. 2- Within each shell, the energy of a subshell level increases with the value of the l QN. 3 -There may be overlap in energy of a state in one shell with states in an adjacent shell, which is especially true of d and f states. 4- The first ...
... 1-The smaller the principal QN , the lower the energy level. 2- Within each shell, the energy of a subshell level increases with the value of the l QN. 3 -There may be overlap in energy of a state in one shell with states in an adjacent shell, which is especially true of d and f states. 4- The first ...
Electron configuration of atoms
... Bunsen and Kirchhoff further developed the spectroscope by incorporating the Bunsen burner as a source to heat the elements. In 1861, experiments by Kirchhoff and Bunsen demonstrated that each element, when heated to incandescence, gave off a characteristic color of light. When the light was separat ...
... Bunsen and Kirchhoff further developed the spectroscope by incorporating the Bunsen burner as a source to heat the elements. In 1861, experiments by Kirchhoff and Bunsen demonstrated that each element, when heated to incandescence, gave off a characteristic color of light. When the light was separat ...