Solid-state physics
... mechanical (e.g. hardness and elasticity), thermal, electrical, magnetic and optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric pattern (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary wa ...
... mechanical (e.g. hardness and elasticity), thermal, electrical, magnetic and optical properties of solids. Depending on the material involved and the conditions in which it was formed, the atoms may be arranged in a regular, geometric pattern (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary wa ...
Energy and Matter - Hicksville Public Schools
... (momentum) and the location (position) of a particle at the same time. ...
... (momentum) and the location (position) of a particle at the same time. ...
Atomic Structure Notes
... 1. Planck’s constant (h) - the quantity of energy that can be absorbed or emitted. h = 6.626 x 10-34 J•s Now the energy of a system ∆E (as we learned last chapter) can be defined as E = nhν where n is an integer, h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed ...
... 1. Planck’s constant (h) - the quantity of energy that can be absorbed or emitted. h = 6.626 x 10-34 J•s Now the energy of a system ∆E (as we learned last chapter) can be defined as E = nhν where n is an integer, h is Planck’s constant and ν is the frequency of the electromagnetic radiation absorbed ...
Chapter 5 PPT/Notes B
... • If single objects approach a double slit, they pass through and slowly build up, one by one, the double slit pattern. Shut one slit off and they, one by one, create the ...
... • If single objects approach a double slit, they pass through and slowly build up, one by one, the double slit pattern. Shut one slit off and they, one by one, create the ...
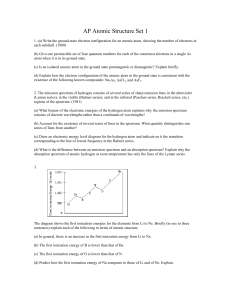
notes on Bohr and the hydrogen spectrum
... λ = R 42 − 32 = (1.097 10 ) m 9 − 16 → λ = 1.9 µm which is in the infrared. But the important thing is that each pair of integers gives an energy. n1 and n2 are whole numbers, so the spectrum has certain discrete values, rather than a continuum. By the way, when the electron 'jumps' from on ...
... λ = R 42 − 32 = (1.097 10 ) m 9 − 16 → λ = 1.9 µm which is in the infrared. But the important thing is that each pair of integers gives an energy. n1 and n2 are whole numbers, so the spectrum has certain discrete values, rather than a continuum. By the way, when the electron 'jumps' from on ...
Document
... Using ΔE = hf, calculate the frequency and wavelength of the spectral line emitted in (d). ...
... Using ΔE = hf, calculate the frequency and wavelength of the spectral line emitted in (d). ...
BINDING ENERGIES OF EXCITONS IN QUANTUM WELL
... a large number of variational parameters as well as the separation ansatz for the z-dependence of the exciton wave function. The only fitting parameters are the effective masses of the electron and the hole. Heavy-hole (RH) and light-hole (LH) excitons are treated separately by solving two sets of 2 ...
... a large number of variational parameters as well as the separation ansatz for the z-dependence of the exciton wave function. The only fitting parameters are the effective masses of the electron and the hole. Heavy-hole (RH) and light-hole (LH) excitons are treated separately by solving two sets of 2 ...
Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is
... Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is a vector, one quantum number is related to its length, the other to its direction, in bound states the angular momentum is quantized as well. Spin and associated magnetic momentum of an electron ‘The Stern-Gerlach Experiment’ atoms passin ...
... Azimuthal and magnetic quantum numbers As angular momentum is a vector, one quantum number is related to its length, the other to its direction, in bound states the angular momentum is quantized as well. Spin and associated magnetic momentum of an electron ‘The Stern-Gerlach Experiment’ atoms passin ...
Quantum Notes (Chapter 16)(Powerpoint document)
... Y2, however, represents the probability of finding an electron at a particular point around the H nucleus. A three dimensional plot of 2 vs. distance from the nucleus, r, represents a volume of space. ...
... Y2, however, represents the probability of finding an electron at a particular point around the H nucleus. A three dimensional plot of 2 vs. distance from the nucleus, r, represents a volume of space. ...
Finite T Dynamics of 1D Integrable Systems
... • At low T<< M order parameter type operators in integrable systems display universal dynamics which falls in two universality classes. • The physics at these T is controlled by multiple particle processes whose matrix elements are singular when in and out momenta ...
... • At low T<< M order parameter type operators in integrable systems display universal dynamics which falls in two universality classes. • The physics at these T is controlled by multiple particle processes whose matrix elements are singular when in and out momenta ...
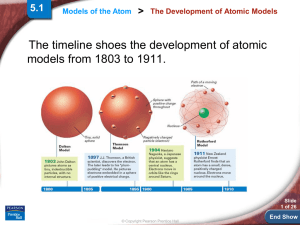
Sec 4-1 Chapter 4 Notes
... Investigations into Einstein’s idea of the Wave-Particle Duality led to a revolution of our basic idea of matter. In 1924, Louis de Broglie showed that the e- were waves by showing that they exhibited diffraction and interference. In 1927, Werner Heisenberg came up with his uncertainty principle. He ...
... Investigations into Einstein’s idea of the Wave-Particle Duality led to a revolution of our basic idea of matter. In 1924, Louis de Broglie showed that the e- were waves by showing that they exhibited diffraction and interference. In 1927, Werner Heisenberg came up with his uncertainty principle. He ...
End Show
... The Quantum Mechanical Model What does the quantum mechanical model determine about the electrons in an atom? The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations Slide around the nucleus. 6 of 26 © Copyright ...
... The Quantum Mechanical Model What does the quantum mechanical model determine about the electrons in an atom? The quantum mechanical model determines the allowed energies an electron can have and how likely it is to find the electron in various locations Slide around the nucleus. 6 of 26 © Copyright ...