powerpoint ch 5 notes electrons in atoms
... • Neils Bohr (1913) explains… • When atoms absorb energy, electrons move into higher energy levels. • These electrons then lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. ...
... • Neils Bohr (1913) explains… • When atoms absorb energy, electrons move into higher energy levels. • These electrons then lose energy by emitting light when they return to lower energy levels. ...
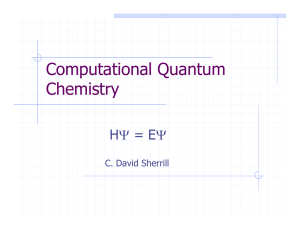
The Chiral Constituent Quark Model (cCQM)
... What is it? It is a very simple approximation that assumes that the quark movement is much faster than the relative movement between the baryons. We can integrate out quark degrees of freedom. ...
... What is it? It is a very simple approximation that assumes that the quark movement is much faster than the relative movement between the baryons. We can integrate out quark degrees of freedom. ...
Details
... Structure of the atom, the early atomic theories, theories of electromagnetic radiation, Plank theory, Bohr theory. Quantum theory, Schrodinger wave equation, quantum numbers, shapes of orbitals and electronic configuration. ...
... Structure of the atom, the early atomic theories, theories of electromagnetic radiation, Plank theory, Bohr theory. Quantum theory, Schrodinger wave equation, quantum numbers, shapes of orbitals and electronic configuration. ...
Atomic models: nuclear to quantum
... velocity would slow, and they would spiral into the nucleus and collapse the atom. But, in the subatomic quantum world, atoms are subject to quantum mechanics rather than the Newtonian laws of motion. • Electrons have quantum energy and that level of energy can only be changed transiently. • Uncerta ...
... velocity would slow, and they would spiral into the nucleus and collapse the atom. But, in the subatomic quantum world, atoms are subject to quantum mechanics rather than the Newtonian laws of motion. • Electrons have quantum energy and that level of energy can only be changed transiently. • Uncerta ...
The Atom
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical The atoms of a given element differ from those of other elements Atoms of one element can combine with those of other elements to form compounds, and a given compound always has the same relative numbers (rat ...
... Elements are made of tiny particles called atoms All atoms of a given element are identical The atoms of a given element differ from those of other elements Atoms of one element can combine with those of other elements to form compounds, and a given compound always has the same relative numbers (rat ...
Unit 2: Atoms and their Electrons
... The first ionization energy of magnesium is 738 kJ/mol and its second ionization energy is 1450 kJ/mol. For sodium the first ionization energy is 496 kJ/mol and its second ionization energy is 4560 kJ/mol. Explain why the second ionization energy for sodium is nearly 10 times the first while for mag ...
... The first ionization energy of magnesium is 738 kJ/mol and its second ionization energy is 1450 kJ/mol. For sodium the first ionization energy is 496 kJ/mol and its second ionization energy is 4560 kJ/mol. Explain why the second ionization energy for sodium is nearly 10 times the first while for mag ...
Chapter 7 - Gordon State College
... energy level. The farther away, the higher the Energy. Allowed electrons to jump from one shell to another. (ground state excited state) ...
... energy level. The farther away, the higher the Energy. Allowed electrons to jump from one shell to another. (ground state excited state) ...
ABCT1742
... property trends of elements and compounds; (b) understand the macroscopic properties and basic principles of liquids and solutions; (c) apply and incorporate the chemical principles and knowledge learned to solve chemical problems and to appreciate modern applications in real life; (d) demonstrate t ...
... property trends of elements and compounds; (b) understand the macroscopic properties and basic principles of liquids and solutions; (c) apply and incorporate the chemical principles and knowledge learned to solve chemical problems and to appreciate modern applications in real life; (d) demonstrate t ...
Quantum Theory of the Atom
... – Bohr – uses quantized energy of the atom (1913) – Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom (1926) ...
... – Bohr – uses quantized energy of the atom (1913) – Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom (1926) ...