VSEPR Molecular Geometry VSEPR Molecular Geometry
... Add total # of valence electrons Determine central atom, eletropositive element Determine terminal/ peripheral atoms Connect central and terminal atoms Fulfill octet rule for terminal atoms Add electron to the central atom Determine the possibility of multiple bonds ...
... Add total # of valence electrons Determine central atom, eletropositive element Determine terminal/ peripheral atoms Connect central and terminal atoms Fulfill octet rule for terminal atoms Add electron to the central atom Determine the possibility of multiple bonds ...
The Quantum Model of the Atom
... -the # of orbital shapes possible is equal to n -values are zero and positive integers less than or equal to n-1 (0 = s, 1 = p, 2 = d, 3 = f) -s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell shaped; d and f orbitals are more complex -value of n = # of sublevels. Ex: nth main energy level is n subl ...
... -the # of orbital shapes possible is equal to n -values are zero and positive integers less than or equal to n-1 (0 = s, 1 = p, 2 = d, 3 = f) -s orbitals are spherical; p orbitals are dumbbell shaped; d and f orbitals are more complex -value of n = # of sublevels. Ex: nth main energy level is n subl ...
PHY4604–Introduction to Quantum Mechanics Fall 2004 Practice
... ground state of 3 He. You may need ψ100 = (2/ 4πa30 ) exp −r/a0 , with a0 = h̄2 /(mZe2 ), where Z is the nuclear charge. Z, the nuclear charge or number of protons, is 1 for tritium and 2 for 3 He. Thus the Bohr radius for 3 He is twice as small as for tritium or hydrogen, ...
... ground state of 3 He. You may need ψ100 = (2/ 4πa30 ) exp −r/a0 , with a0 = h̄2 /(mZe2 ), where Z is the nuclear charge. Z, the nuclear charge or number of protons, is 1 for tritium and 2 for 3 He. Thus the Bohr radius for 3 He is twice as small as for tritium or hydrogen, ...
Inorganic Chemistry A Self-study exercises Chapters 1,2 and 3 1
... 27.In which of the following molecules is the octet rule apparently violated by the central atom: (a) H2S; (b) HCN; (c) SO2; (d) CO2; (e) SO3? 28.Within the series of fluorides IF, IF3 and IF5, show that the octet rule appears to be obeyed in only one instance for iodine. 29.Predict the structures o ...
... 27.In which of the following molecules is the octet rule apparently violated by the central atom: (a) H2S; (b) HCN; (c) SO2; (d) CO2; (e) SO3? 28.Within the series of fluorides IF, IF3 and IF5, show that the octet rule appears to be obeyed in only one instance for iodine. 29.Predict the structures o ...
Class 39 1
... the same set of four quantum numbers. The consequence of the Pauli Exclusion Principle is that when we fill the energy levels of an atom with electrons (where there are Z of them), we can only fill one electron in each distinguishable slot (i.e., sub-orbital and spin state) available in a energy lev ...
... the same set of four quantum numbers. The consequence of the Pauli Exclusion Principle is that when we fill the energy levels of an atom with electrons (where there are Z of them), we can only fill one electron in each distinguishable slot (i.e., sub-orbital and spin state) available in a energy lev ...
uncertainty, atom
... You cannot know position and momentum both very precisely at the same time If you measure momentum, you disturb the position, so you no longer know the position accurately -- and vice versa This disturbance is random, indeterminate ...
... You cannot know position and momentum both very precisely at the same time If you measure momentum, you disturb the position, so you no longer know the position accurately -- and vice versa This disturbance is random, indeterminate ...
Chemistry Chapter 4 - Harding Charter Preparatory High School
... • Atomic orbitals (wave functions) are often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron – Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called quantum numbers, which describe various properties of the orbital: • Energy levels of electrons in th ...
... • Atomic orbitals (wave functions) are often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron – Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called quantum numbers, which describe various properties of the orbital: • Energy levels of electrons in th ...
Atomic Orbitals - Harding Charter Preparatory High School
... • Atomic orbitals (wave functions) are often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron – Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called quantum numbers, which describe various properties of the orbital: • Energy levels of electrons in th ...
... • Atomic orbitals (wave functions) are often thought of as a region of space in which there is a high probability of finding an electron – Each orbital is characterized by a series of numbers called quantum numbers, which describe various properties of the orbital: • Energy levels of electrons in th ...
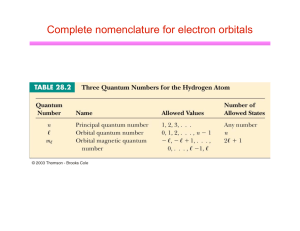
Complete nomenclature for electron orbitals
... incident on the atom l Incoming photon of this energy increases the probability of the atom returning to the ground state emitting a photon of the same energy hf as the incident photon and in phase with the incident photon l These photons can then stimulate other atoms to emit photons l The end resu ...
... incident on the atom l Incoming photon of this energy increases the probability of the atom returning to the ground state emitting a photon of the same energy hf as the incident photon and in phase with the incident photon l These photons can then stimulate other atoms to emit photons l The end resu ...
KS-DFT formalism
... Our choice of wave functions is very limited; we only know how to use independent particle wave functions. The degree to which this limitation has invaded our thinking is marked by our constant use of concepts which have meaning only in terms of independent particle wave functions: shell structure, ...
... Our choice of wave functions is very limited; we only know how to use independent particle wave functions. The degree to which this limitation has invaded our thinking is marked by our constant use of concepts which have meaning only in terms of independent particle wave functions: shell structure, ...
Advanced Physical Chemistry
... What is the crucial complication in all electronic structure calculations, remember in HF this is treated in an average way. Essentially the HF method used the variation theory to calculate the correction to the core hamiltonian (no electron repulsion included). What does it mean to be self consiste ...
... What is the crucial complication in all electronic structure calculations, remember in HF this is treated in an average way. Essentially the HF method used the variation theory to calculate the correction to the core hamiltonian (no electron repulsion included). What does it mean to be self consiste ...