File
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
... a. deflection of alpha particles b. atomic absorption spectra c. atomic emission spectra d. the deflection of cathode rays by an electric field e. absorption of beta particles 3. Rutherford's gold foil experiment showed that the atom is mostly empty space because a. some alpha particles were reflect ...
Objective A - TuHS Physics Homepage
... Chapter 27: 14(1.1E-27 kgm/s), 37(2.9E-32 m), 38(6.1E-12 m), 39(26 V), 41(1.3E-24 kgm/s, 1.5E6 m/s, 6.0 V), 42(0.39 nm, 0.12 nm, 0.039 nm), 40(1840), 84(0.65 V, 4.8E5 m/s, 1.5 nm) Questions: 1. Why don’t we observe the wave behavior of a baseball? 2. Why do electrons have much bigger wavelengths tha ...
... Chapter 27: 14(1.1E-27 kgm/s), 37(2.9E-32 m), 38(6.1E-12 m), 39(26 V), 41(1.3E-24 kgm/s, 1.5E6 m/s, 6.0 V), 42(0.39 nm, 0.12 nm, 0.039 nm), 40(1840), 84(0.65 V, 4.8E5 m/s, 1.5 nm) Questions: 1. Why don’t we observe the wave behavior of a baseball? 2. Why do electrons have much bigger wavelengths tha ...
electron cloud - Wickliffe City School
... Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom ...
... Since the energy of an atom is never “in between” there must be a quantum leap in energy. Schrödinger derived an equation that described the energy and position of the electrons in an atom ...
Quantum Mechanical Model
... Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
... Directions: Complete the following notes and charts as you read through section 4.2 in your textbook. ...
Atomic Structure - Winona State University
... Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Orbitals Orbitals and Quantum Numbers • Schrödinger’s equation requires 3 quantum numbers: 1. Principal Quantum Number, n. This is the same as Bohr’s n. As n becomes larger, the atom becomes larger and the electron is further from the nucleus. ( n = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , …. ) ...
... Quantum Mechanics and Atomic Orbitals Orbitals and Quantum Numbers • Schrödinger’s equation requires 3 quantum numbers: 1. Principal Quantum Number, n. This is the same as Bohr’s n. As n becomes larger, the atom becomes larger and the electron is further from the nucleus. ( n = 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , …. ) ...
The Quantum Hypothesis slides
... Light can act as a wave or a particle The energy of light is directly proportional to its frequency ...
... Light can act as a wave or a particle The energy of light is directly proportional to its frequency ...
Introduction to Quantum Mechanics AEP3610 Professor Scott
... a uniform medium and the so-called free particle, to develop some calculational tools for describing matter waves, including the de Broglie wavelength for a moving particle, and the Born interpretion of the wave function • to ‘derive’ the Schrödinger equation(s) for said wave function for a particle ...
... a uniform medium and the so-called free particle, to develop some calculational tools for describing matter waves, including the de Broglie wavelength for a moving particle, and the Born interpretion of the wave function • to ‘derive’ the Schrödinger equation(s) for said wave function for a particle ...
Module code SP-2301 Module Title Concepts in Modern Physics
... relativity, matter waves, energy quantisation, x-ray and also laser generation, and the nuclear structure Middle order : 60% - evaluate the effects of special relativity on time and length measurements - explain and apply equations developed to the effects of relativity on momentum and energy ...
... relativity, matter waves, energy quantisation, x-ray and also laser generation, and the nuclear structure Middle order : 60% - evaluate the effects of special relativity on time and length measurements - explain and apply equations developed to the effects of relativity on momentum and energy ...
Tutorial 3 - answers • Complete the following table, giving either the
... Draw a graph showing the relationship between overall health and the level of copper in the body and identify the ‘healthy’ range. ...
... Draw a graph showing the relationship between overall health and the level of copper in the body and identify the ‘healthy’ range. ...
Problem-set10 32. Polarization of atomic hydrogen in the vicinity of a
... (a) Write down the Hamiltonian for the two electrons in the helium atom, neglecting the spin-orbit interaction. (b) Assume that the electron-electron interaction is small, we will treat this term by perturbation. Identify the H0 and H' where H' is the electron-electron interaction term. (c) For the ...
... (a) Write down the Hamiltonian for the two electrons in the helium atom, neglecting the spin-orbit interaction. (b) Assume that the electron-electron interaction is small, we will treat this term by perturbation. Identify the H0 and H' where H' is the electron-electron interaction term. (c) For the ...
Electrons in the Atom
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
Chapter 4
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
... Think of orbitals as sort of a "border” for spaces around the nucleus inside which electrons are allowed. No more than 2 electrons can ever be in 1 orbital. The orbital just defines an “area” where you can find an electron. ...
IB HL Physics More Problems on Quantum and Nuclear Physics_
... An -particle approaches a nucleus of palladium. The initial kinetic energy of the -particle is 3.8 MeV. The particle is brought to rest at point P, a distance d from the centre of the palladium nucleus. It then moves back along the path from which it came as shown in the diagram below. ...
... An -particle approaches a nucleus of palladium. The initial kinetic energy of the -particle is 3.8 MeV. The particle is brought to rest at point P, a distance d from the centre of the palladium nucleus. It then moves back along the path from which it came as shown in the diagram below. ...
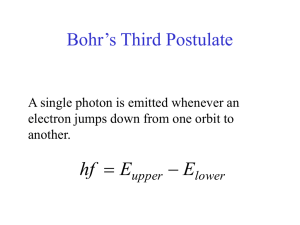
Bohr´s Third Postulate
... 2. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Zeta rays are charged particles or e/m waves? Could this experiment distinguish between neutral particles and an e/m wave? 3. If a metal surf ...
... 2. Suppose you were a nineteenth-century scientist who had just discovered a new phenomenon known as Zeta rays. What experiment could you perform to define if Zeta rays are charged particles or e/m waves? Could this experiment distinguish between neutral particles and an e/m wave? 3. If a metal surf ...