Atomic Orbitals and quantum numbers
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
... •Therefore, on any given energy level, there can be up to 1s orbital, 3p orbitals, 5d orbitals, and 7f orbitals. ...
explo3
... Atomic and molecular physics: 2012 EXPLORATIONS –3 1) Sketch the energy level diagram of hydrogen atom, including the fine structure up to n=3. Show the possible transitions. How many different lines are there? ...
... Atomic and molecular physics: 2012 EXPLORATIONS –3 1) Sketch the energy level diagram of hydrogen atom, including the fine structure up to n=3. Show the possible transitions. How many different lines are there? ...
Energy Sublevels
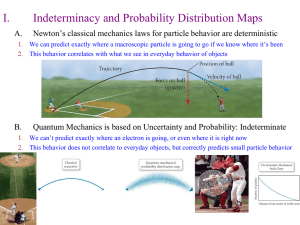
... A photon striking an electron causes the electron To change both position and velocity. So an electrons Position can not be specified with precision . ...
... A photon striking an electron causes the electron To change both position and velocity. So an electrons Position can not be specified with precision . ...
The Atom Board - ETC Montessori
... the theoretical description with physical observations. The first atom board that we used was a two dimensional board, where in the strictest sense it portrayed the atomic structure as a planetary system. The new model adds a third dimension, electrons orbiting in energy clouds. It visually differen ...
... the theoretical description with physical observations. The first atom board that we used was a two dimensional board, where in the strictest sense it portrayed the atomic structure as a planetary system. The new model adds a third dimension, electrons orbiting in energy clouds. It visually differen ...
Quantum/Nuclear - Issaquah Connect
... Calculate wavelengths of spectral lines from energy level differences and vice versa ...
... Calculate wavelengths of spectral lines from energy level differences and vice versa ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE NOTES n hcZ E ℜ
... through the nucleus. Therefore, it is more shielded from the nucleus by the electrons of the core. We can conclude that a 2s electron has lower energy (more bound) than a 2p, so for Lithium the ground state configuration must be 1s22s1. It usually follows that: ns > np > nd > nf ...
... through the nucleus. Therefore, it is more shielded from the nucleus by the electrons of the core. We can conclude that a 2s electron has lower energy (more bound) than a 2p, so for Lithium the ground state configuration must be 1s22s1. It usually follows that: ns > np > nd > nf ...
Theory of Chemical Bonds
... Figure 5.2 uses the radial dependency ψ ≈ exp(−r/a0) with a0 ≈ 53 pm, cf. chapter 4.1.1, for the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orb ...
... Figure 5.2 uses the radial dependency ψ ≈ exp(−r/a0) with a0 ≈ 53 pm, cf. chapter 4.1.1, for the wave function of the atomic orbitals. During the calculation of the eigenvalues of the Schrödinger equation with equ. 4.15, we get integrals which contain the square of the wave function of an atomic orb ...
Document
... Equation gives rise to ‘Orbitals.’ These orbitals provide the electron density distributed about the nucleus. Orbitals are described by quantum numbers. ...
... Equation gives rise to ‘Orbitals.’ These orbitals provide the electron density distributed about the nucleus. Orbitals are described by quantum numbers. ...
ELECTRONIC STRUCTURE OF ATOMS
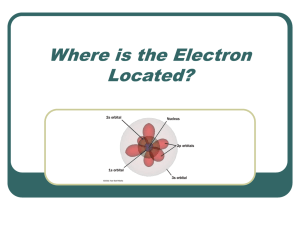
... particles as they apply to low mass(electron), high speed objects. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but i ...
... particles as they apply to low mass(electron), high speed objects. The Heisenberg uncertainty principle states that it is impossible to determine the position and momentum of an electron at a particular instant. That means that electron orbitals do not represent specific orbits(i.e. planets) but i ...
Module code SP-2306 Module Title Condensed Matter Physics
... sound foundation for research and innovation in the field of condensed matter. Learning Outcomes On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order : 30% - Identify crystal structures of solids, and explain electronic band structures. - Understand th ...
... sound foundation for research and innovation in the field of condensed matter. Learning Outcomes On successful completion of this module, a student will be expected to be able to: Lower order : 30% - Identify crystal structures of solids, and explain electronic band structures. - Understand th ...
Bonding 1 - Department of Chemistry
... The eight orbitals can be classified by symmetry into two sets: 4 s and 4 orbitals. The four orbitals from one doubly degenerate pair of bonding orbitals and one doubly degenerate pair of antibonding orbitals. The four s orbitals span a range of energies, one being strongly bonding and another s ...
... The eight orbitals can be classified by symmetry into two sets: 4 s and 4 orbitals. The four orbitals from one doubly degenerate pair of bonding orbitals and one doubly degenerate pair of antibonding orbitals. The four s orbitals span a range of energies, one being strongly bonding and another s ...