Eyewear Lens Selection Guide
... infrared radiation generated when working with molten metal, and in welding, cutting, soldering and brazing. ...
... infrared radiation generated when working with molten metal, and in welding, cutting, soldering and brazing. ...
Following the path of light: recovering and
... Our didactic path is focused on image production and follows a route of increasing complexity from pinhole cameras to holography. The idea is to link the characteristics of the image to the selection operated on propagating light by optical systems. Further author information: (Send correspondence t ...
... Our didactic path is focused on image production and follows a route of increasing complexity from pinhole cameras to holography. The idea is to link the characteristics of the image to the selection operated on propagating light by optical systems. Further author information: (Send correspondence t ...
The Projecting Microscope
... you should take to avoid this risk. Remember: Never look into the beam! Always use a card held in the beam to see where it is. Be aware that the beam may be unexpectedly reflected off of shiny surfaces. 2. Learn how to handle and clean optical components so that they are not damaged. ...
... you should take to avoid this risk. Remember: Never look into the beam! Always use a card held in the beam to see where it is. Be aware that the beam may be unexpectedly reflected off of shiny surfaces. 2. Learn how to handle and clean optical components so that they are not damaged. ...
doc - University of Rochester
... is incident on a crystal that produces entangled photon pairs (biphotons). One of the photons, called the signal photon, scatters from the object and is detected by detector A. A point detector B in a CCD array located in the image plane detects the second photon, called the idler photon. The signal ...
... is incident on a crystal that produces entangled photon pairs (biphotons). One of the photons, called the signal photon, scatters from the object and is detected by detector A. A point detector B in a CCD array located in the image plane detects the second photon, called the idler photon. The signal ...
PHYS 1111 Mechanics, Waves, & Thermodynamics
... p = distance from object to surface (s or sO) q = distance from image to surface (s’ or sI) Extend the diverging light rays to a point where they meet to obtain the location of the image ...
... p = distance from object to surface (s or sO) q = distance from image to surface (s’ or sI) Extend the diverging light rays to a point where they meet to obtain the location of the image ...
Chapter 18 OPTICAL ELEMENTS - Doane College Physics Web
... incident wave energy. At other kinds of surfaces, the fraction of energy reflected depends on the angle of incidence and on the index of refraction of the two media defining the interface. The index of refraction of a material is defined in Equation 18.2. The index of refraction plays the analogous ...
... incident wave energy. At other kinds of surfaces, the fraction of energy reflected depends on the angle of incidence and on the index of refraction of the two media defining the interface. The index of refraction of a material is defined in Equation 18.2. The index of refraction plays the analogous ...
Experiments in Optics - Workspace
... turns out that an extremely high quality lens can be designed using the concept of rays (geometrical optics) and some knowledge of the wave model (physical optics). On the other hand, the basic principle of operation of a laser requires the quantum model - no amount of clever playing with rays or wa ...
... turns out that an extremely high quality lens can be designed using the concept of rays (geometrical optics) and some knowledge of the wave model (physical optics). On the other hand, the basic principle of operation of a laser requires the quantum model - no amount of clever playing with rays or wa ...
INDIAN SCHOOL DARSAIT
... explaining, with the help of a labeled diagram, the formation of a rainbow in the sky. List two essential conditions for observing a rainbow. a) Definition of Dispersion: Splitting of white light into seven constituent colors by a prism. Cause of dispersion − when white light passes through a glass ...
... explaining, with the help of a labeled diagram, the formation of a rainbow in the sky. List two essential conditions for observing a rainbow. a) Definition of Dispersion: Splitting of white light into seven constituent colors by a prism. Cause of dispersion − when white light passes through a glass ...
Ch30
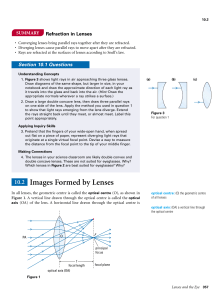
... When the object is beyond one focal length, a converging lens produces a real, inverted image. • If the object is close to (but slightly beyond) the focal point, the image is far away. • If the object is far from the focal point, the image is nearer. • In all cases where a real image is formed, the ...
... When the object is beyond one focal length, a converging lens produces a real, inverted image. • If the object is close to (but slightly beyond) the focal point, the image is far away. • If the object is far from the focal point, the image is nearer. • In all cases where a real image is formed, the ...
Phys Chp 10
... lenses and objects in Figure 8. For each of the following cases, explain where the lens must be placed relative to the object: (a) a copy camera produces an image that is real and the same size (b) a hand magnifier produces an image that is virtual and larger (c) a slide projector produces an image ...
... lenses and objects in Figure 8. For each of the following cases, explain where the lens must be placed relative to the object: (a) a copy camera produces an image that is real and the same size (b) a hand magnifier produces an image that is virtual and larger (c) a slide projector produces an image ...
The pinhole camera
... – Pinhole camera – Lenses Basic properties of spherical surfaces Ray tracing Image formation Magnification Today: more optical elements, – Prisms – Mirrors ...
... – Pinhole camera – Lenses Basic properties of spherical surfaces Ray tracing Image formation Magnification Today: more optical elements, – Prisms – Mirrors ...
Physics 323 Lecture Notes Part I: Optics
... When light propagates in a transparent material medium, its speed is in general less than the speed in vacuum c. An interesting consequence of this is that a light ray will change direction when passing from one medium to another. Since the light ray appears to be “broken”, the phenomenon is known a ...
... When light propagates in a transparent material medium, its speed is in general less than the speed in vacuum c. An interesting consequence of this is that a light ray will change direction when passing from one medium to another. Since the light ray appears to be “broken”, the phenomenon is known a ...
Measurement of spectacle lenses: A review
... [3]. J. Schwiegerling, Field guide to Visual and Ophthalmic Optics, SPIE Press, Bellingham (2004). DOI [4]. The Vision Care Center: https://es.vsp.com/enes/cms/edc/glossary.html. [5]. D. Meister, “The Optics of Free-Form Progressive Lenses”, 20/20 Mag., 131-134 (2008). [6]. F. Z. Fang, X. D. Zhang, ...
... [3]. J. Schwiegerling, Field guide to Visual and Ophthalmic Optics, SPIE Press, Bellingham (2004). DOI [4]. The Vision Care Center: https://es.vsp.com/enes/cms/edc/glossary.html. [5]. D. Meister, “The Optics of Free-Form Progressive Lenses”, 20/20 Mag., 131-134 (2008). [6]. F. Z. Fang, X. D. Zhang, ...
Measuring the Real Point Spread Function of High Numerical
... computers. A bewildering array of techniques is described in Malacara’s classic reference book on the subject (Malacara, 1992). Several of these techniques, in particular the Twyman–Green interferometer and the star test, are applicable to testing of microscope objective lens. Characterizing high nu ...
... computers. A bewildering array of techniques is described in Malacara’s classic reference book on the subject (Malacara, 1992). Several of these techniques, in particular the Twyman–Green interferometer and the star test, are applicable to testing of microscope objective lens. Characterizing high nu ...
Get PDF - OSA Publishing
... wave from the air side to the focus Fm at the focal length fm in the metamaterial by given εx’ and εz’. The details of the PWC design follows similar principles described in literatures [23– 25]. Due to the hyperbolic dispersion of the metalens, a plane wave comes from the metamaterial side, instead ...
... wave from the air side to the focus Fm at the focal length fm in the metamaterial by given εx’ and εz’. The details of the PWC design follows similar principles described in literatures [23– 25]. Due to the hyperbolic dispersion of the metalens, a plane wave comes from the metamaterial side, instead ...
5.3.2 Processing Light
... The incoming beam is polarized at 45o relative to the principal polarization directions in the anisotropic medium. The two beams exciting the medium produce a circular polarization as shown in the animation (© Wikipedia) How is it done? Let's look at the "old" and slightly modified picture above to ...
... The incoming beam is polarized at 45o relative to the principal polarization directions in the anisotropic medium. The two beams exciting the medium produce a circular polarization as shown in the animation (© Wikipedia) How is it done? Let's look at the "old" and slightly modified picture above to ...
Microscope
... Bacteria is one of the small microorganisms that can’t be seen with the naked eyes, most bacteria range in size between 0.5-2.0 micrometers (μm) so, there is a need to magnify the bacteria several times by using a microscope in order to see it. ...
... Bacteria is one of the small microorganisms that can’t be seen with the naked eyes, most bacteria range in size between 0.5-2.0 micrometers (μm) so, there is a need to magnify the bacteria several times by using a microscope in order to see it. ...
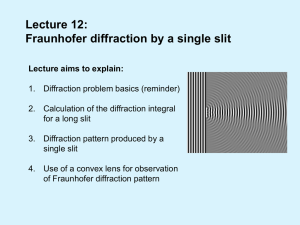
Lecture 12: Fraunhofer diffraction by a single slit
... blue and (ii) red light. To see how diffraction on a slit works visit: http://surendranath.tripod.com/Applets/Optics/Slits/SingleSlit/SS.html ...
... blue and (ii) red light. To see how diffraction on a slit works visit: http://surendranath.tripod.com/Applets/Optics/Slits/SingleSlit/SS.html ...
Cylindrical adaptive lenses - Durham University Community
... 2. Investigation of cylindrical modal LC lens control modes We have investigated the optical performance of cylindrical modal LC lenses using a Michelson interferometer. The optical setup is shown in fig. 4. We placed the adaptive lens in one arm of the interferometer so that the axis of the LC's ex ...
... 2. Investigation of cylindrical modal LC lens control modes We have investigated the optical performance of cylindrical modal LC lenses using a Michelson interferometer. The optical setup is shown in fig. 4. We placed the adaptive lens in one arm of the interferometer so that the axis of the LC's ex ...
Lecture_22
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
... light under water. We said that color depends on wavelength. For example, for an object emitting 650 nm light in air, we see red. But this is true only in air. If we observe this same object when under water, it still looks red. But the wavelength in water λn is 650 nm/1.33 = 489 nm. Light with wave ...
Optical Instruments
... the photographic plate should be large. Thus a magnified image requires a long camera which may be unmanageable and inconvenient. To avoid this difficulty a telephoto lens is used. It consists of two lenses mounted in a tube. The tube is fixed in the camera in place of a single lens. One of the lens ...
... the photographic plate should be large. Thus a magnified image requires a long camera which may be unmanageable and inconvenient. To avoid this difficulty a telephoto lens is used. It consists of two lenses mounted in a tube. The tube is fixed in the camera in place of a single lens. One of the lens ...
Structure and Imaging of a Transmission Electron Microscope (TEM)
... lens, an intermediate lens, and a projector lens. The condenser lens works for illuminating specimens with slightly focusing electrons from the source. In TEM, particularly, the “Koeller illumination mode” is used, where the lens works for making a parallel beam along the optical axis for a specimen ...
... lens, an intermediate lens, and a projector lens. The condenser lens works for illuminating specimens with slightly focusing electrons from the source. In TEM, particularly, the “Koeller illumination mode” is used, where the lens works for making a parallel beam along the optical axis for a specimen ...
AY 105 Lab Experiment #3: Optical aberrations
... • Skim the lab but don’t worry too much about understanding the software instructions as these technical parts are better appreciated when you see them in operation. • Skim the additional material on the CodeV ray tracing software so that you have an idea of what optical design is all about. This ch ...
... • Skim the lab but don’t worry too much about understanding the software instructions as these technical parts are better appreciated when you see them in operation. • Skim the additional material on the CodeV ray tracing software so that you have an idea of what optical design is all about. This ch ...
startest
... visible, the diameter of the central core is approximately equal to the f# in microns. The central core contains approximately 84% of the total amount of light, while the total amount of light contained within the first, second, and third rings is approximately 91%, 94%, and 95%, respectively. If th ...
... visible, the diameter of the central core is approximately equal to the f# in microns. The central core contains approximately 84% of the total amount of light, while the total amount of light contained within the first, second, and third rings is approximately 91%, 94%, and 95%, respectively. If th ...
A high resolution ion microscope for cold atoms
... tract the ions generated in the MOT. Four consecutive einzel lenses image the ions onto a microchannel plate detector with 40 mm diameter. Starting with einzel lens 1, each lens produces a magnified image in the image plane behind the lens, which is further magnified by the next lens and finally ima ...
... tract the ions generated in the MOT. Four consecutive einzel lenses image the ions onto a microchannel plate detector with 40 mm diameter. Starting with einzel lens 1, each lens produces a magnified image in the image plane behind the lens, which is further magnified by the next lens and finally ima ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.