Chapter 34 Geometric Optics
... light ray is a straight line in a uniform medium (i.e., when the index of refraction n is a constant.) The light rays change direction only when reflection and refraction are encountered. (1b) Each extended object can be thought of as a collection of points. Each such point can be considered as a po ...
... light ray is a straight line in a uniform medium (i.e., when the index of refraction n is a constant.) The light rays change direction only when reflection and refraction are encountered. (1b) Each extended object can be thought of as a collection of points. Each such point can be considered as a po ...
Lecture 27
... Current printers are at 4800 dpi, or about 5 microns, and produce binary images. Turning a printed image into a hologram requires reduction down to optical wavelengths (< 1 micron). e.g. Photograph with SLR camera with Fuji “minicopy” film. The negative is the hologram. ...
... Current printers are at 4800 dpi, or about 5 microns, and produce binary images. Turning a printed image into a hologram requires reduction down to optical wavelengths (< 1 micron). e.g. Photograph with SLR camera with Fuji “minicopy” film. The negative is the hologram. ...
University of Groningen CURVATURE MEASUREMENT
... practice. The measuring devices, called (optical) spherometers (lens surfaces commonly have a spherical shape), all are different types of reflected-light microscopes. Here, a simple spherometrical method is introduced, which can be executed with any standard microscope equipped with an epi-illumina ...
... practice. The measuring devices, called (optical) spherometers (lens surfaces commonly have a spherical shape), all are different types of reflected-light microscopes. Here, a simple spherometrical method is introduced, which can be executed with any standard microscope equipped with an epi-illumina ...
Geometric Optics
... Example 34.7 using Figure 34.26 at the left—how deep does the pool appear? Start with ...
... Example 34.7 using Figure 34.26 at the left—how deep does the pool appear? Start with ...
Handout Building the demonstration refractor tube
... that the negative eyepiece lens will focus. At most it moves out far enough so the positive eyepiece lens will come into focus. Both the negative and positive eyepieces are positioned relative to the focal length of the big objective lens. From the handouts on “How to make a Galilean Telescope” and ...
... that the negative eyepiece lens will focus. At most it moves out far enough so the positive eyepiece lens will come into focus. Both the negative and positive eyepieces are positioned relative to the focal length of the big objective lens. From the handouts on “How to make a Galilean Telescope” and ...
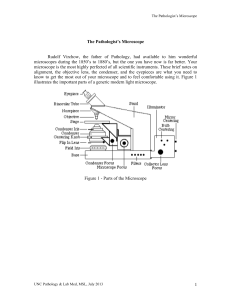
The Pathologist`s Microscope
... clean to function properly. Clean them and you will be amazed at the difference! Take them off the nosepiece and clean the end lens with a little glass cleaner on a cotton swab. In addition to magnification, objective lenses have other characteristics. The most important is numerical aperture (N.A.) ...
... clean to function properly. Clean them and you will be amazed at the difference! Take them off the nosepiece and clean the end lens with a little glass cleaner on a cotton swab. In addition to magnification, objective lenses have other characteristics. The most important is numerical aperture (N.A.) ...
Ultra–large field-of-view two-photon microscopy
... The design of the scan system begins with the selection of the objective. We seek a field-ofview that encompasses 10 mm, a numerical aperture (NA) to achieve 1-µm resolution, and a back aperture that does not exceed 25 mm. The singular choice is a 4-times magnification (f = 45 mm), 0.28 NA air-immer ...
... The design of the scan system begins with the selection of the objective. We seek a field-ofview that encompasses 10 mm, a numerical aperture (NA) to achieve 1-µm resolution, and a back aperture that does not exceed 25 mm. The singular choice is a 4-times magnification (f = 45 mm), 0.28 NA air-immer ...
laser optical disk set
... Now select five rays and repeat the observation. Note that the outer rays are brought to a focus a shorter distance from the lens than the inner rays (see Diagram 5.1). Measure f for the outer rays. The difference between the two focal points is due to spherical aberration, a geometric effect of l ...
... Now select five rays and repeat the observation. Note that the outer rays are brought to a focus a shorter distance from the lens than the inner rays (see Diagram 5.1). Measure f for the outer rays. The difference between the two focal points is due to spherical aberration, a geometric effect of l ...
1 Light Microscopy
... in general cannot be observed. The first commercial development of the Environmental SEM (ESEM) in the late 1980s allowed samples to be observed in low-pressure gaseous environments (e.g. 1-50 Torr) and high relative humidity (up to 100%). The first commercial ESEMs were produced by the ElectroScan ...
... in general cannot be observed. The first commercial development of the Environmental SEM (ESEM) in the late 1980s allowed samples to be observed in low-pressure gaseous environments (e.g. 1-50 Torr) and high relative humidity (up to 100%). The first commercial ESEMs were produced by the ElectroScan ...
6,
... theoretical and experimental treatment for the diffraction efficiencies of transmission HOEs and three- and two-element cascades when subject to broad spectral and field angle detuning. C. Shakher and S . Sirohi [4] have shown that a pair of thick phase holograms can be used to image extended object ...
... theoretical and experimental treatment for the diffraction efficiencies of transmission HOEs and three- and two-element cascades when subject to broad spectral and field angle detuning. C. Shakher and S . Sirohi [4] have shown that a pair of thick phase holograms can be used to image extended object ...
The Resolving Power Of a Microscope and Telescope
... Let the diameter of the lens used is D and the distance of the two non-luminous point objects A and B is h and the distance between their respective image is A’B’ =h’. Also let the refractive index of the two media before lens and after lens are n1 and n2, respectively. Assuming the absence of any s ...
... Let the diameter of the lens used is D and the distance of the two non-luminous point objects A and B is h and the distance between their respective image is A’B’ =h’. Also let the refractive index of the two media before lens and after lens are n1 and n2, respectively. Assuming the absence of any s ...
Is the Magnetosphere a Lens to MHD Waves?
... which is the product of the lensing effect of the solenoid represented by Ms and the subsequent rectilinearpropagation in a medium of constantrefractive index % for the distance (x- L/2) represented by Ml(x -- L/2). The focal length of the optical systemrepresentingthe magnetosphere can be computedf ...
... which is the product of the lensing effect of the solenoid represented by Ms and the subsequent rectilinearpropagation in a medium of constantrefractive index % for the distance (x- L/2) represented by Ml(x -- L/2). The focal length of the optical systemrepresentingthe magnetosphere can be computedf ...
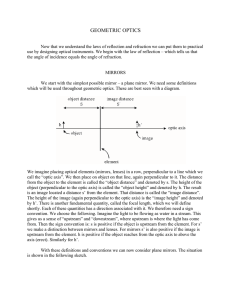
GEOMETRIC OPTICS
... We now introduce a new concept to distinguish between situations where light actually comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Sum ...
... We now introduce a new concept to distinguish between situations where light actually comes from the image and those where it merely appears to. The first case we call “real images” and the second “virtual images”. In our case, there is no light behind the mirror, and hence the image is virtual. Sum ...
Leaving Cert Physics Notes by Mary Singleton
... Total internal reflection has several applications. It can be used with a prism to turn light through 900 or through 1800. It is also used in optical fibres. Optical fibres – are thin glass rods which can bend easily and so be used to carry light around corners. The light always hits the inside of t ...
... Total internal reflection has several applications. It can be used with a prism to turn light through 900 or through 1800. It is also used in optical fibres. Optical fibres – are thin glass rods which can bend easily and so be used to carry light around corners. The light always hits the inside of t ...
Aberration Correction in Electron Microscopy
... the first lens and the other at the back focal plane of the second lens, as shown in figure 3. These focal planes represent the nodal planes N1 and N 2 of the transfer doublet, which images the first sextupole with magnification M = −1 onto the second sextupole. As a result all second-order path dev ...
... the first lens and the other at the back focal plane of the second lens, as shown in figure 3. These focal planes represent the nodal planes N1 and N 2 of the transfer doublet, which images the first sextupole with magnification M = −1 onto the second sextupole. As a result all second-order path dev ...
Word Doc - Imagineering Ezine
... Types of Lenses Most of the lenses used in through-the-air communications have one or two outwardly curved surfaces. Such lenses are called "convex" lenses. Small glass or plastic lenses are great for shortrange applications. However, glass lenses larger than about 3 inches become too heavy and expe ...
... Types of Lenses Most of the lenses used in through-the-air communications have one or two outwardly curved surfaces. Such lenses are called "convex" lenses. Small glass or plastic lenses are great for shortrange applications. However, glass lenses larger than about 3 inches become too heavy and expe ...
Microscopes - OpenStax CNX
... negative, consistent with Figure 2, where the image is seen to be large and inverted. In this case, the image is virtual and inverted, which cannot happen for a single element (case 2 and case 3 images for single elements are virtual and upright). The nal image is 367 mm (0.367 m) to the left of th ...
... negative, consistent with Figure 2, where the image is seen to be large and inverted. In this case, the image is virtual and inverted, which cannot happen for a single element (case 2 and case 3 images for single elements are virtual and upright). The nal image is 367 mm (0.367 m) to the left of th ...
Non-invasive ophthalmic imaging of adult zebrafish eye using
... resolutions of the set-up were estimated to be ~ 11 and 17 µm respectively. Images of whole eye, cornea and retina acquired with the set-up have been used to estimate several ocular parameters, viz. corneal thickness, mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Key ...
... resolutions of the set-up were estimated to be ~ 11 and 17 µm respectively. Images of whole eye, cornea and retina acquired with the set-up have been used to estimate several ocular parameters, viz. corneal thickness, mean retinal thickness and effective refractive index of the crystalline lens. Key ...
Negative Refraction Makes a Perfect Lens
... A moments thought will show that the figure obeys Snell’s laws of refraction at the surface as light inside the medium makes a negative angle with the surface normal. The other characteristic of the system is the double focusing effect revealed by a simple ray diagram. Light transmitted through a sl ...
... A moments thought will show that the figure obeys Snell’s laws of refraction at the surface as light inside the medium makes a negative angle with the surface normal. The other characteristic of the system is the double focusing effect revealed by a simple ray diagram. Light transmitted through a sl ...
Negative Refraction Makes a Perfect Lens
... A moments thought will show that the figure obeys Snell’s laws of refraction at the surface as light inside the medium makes a negative angle with the surface normal. The other characteristic of the system is the double focusing effect revealed by a simple ray diagram. Light transmitted through a sl ...
... A moments thought will show that the figure obeys Snell’s laws of refraction at the surface as light inside the medium makes a negative angle with the surface normal. The other characteristic of the system is the double focusing effect revealed by a simple ray diagram. Light transmitted through a sl ...
© NCERT not to be republished
... known then rough value of its focal length (f L ) should be estimated first to ensure that its focal length is less than that of the concave lens. ...
... known then rough value of its focal length (f L ) should be estimated first to ensure that its focal length is less than that of the concave lens. ...
Atchison Eye Models For Correction
... Early Greek descriptions of the eye were based more on philosophy than on observation Democritus described the eye as three concentric spheres containing the various humours required by the visual sense The innermost sphere (the crystalline humour) produces the visual impression when it receives vis ...
... Early Greek descriptions of the eye were based more on philosophy than on observation Democritus described the eye as three concentric spheres containing the various humours required by the visual sense The innermost sphere (the crystalline humour) produces the visual impression when it receives vis ...
Optics-Light Lab - University of Michigan SharePoint Portal
... A concave lens or mirror is thinner at the center than at its edges. You will find diagrams illustrating convex and concave lenses and mirrors at the end of this worksheet. 1. Plug in the ray box and insert the slit screen into the front of it so that only one narrow beam is emitted. Place a piece o ...
... A concave lens or mirror is thinner at the center than at its edges. You will find diagrams illustrating convex and concave lenses and mirrors at the end of this worksheet. 1. Plug in the ray box and insert the slit screen into the front of it so that only one narrow beam is emitted. Place a piece o ...
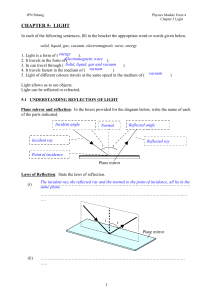
CHAPTER 5: LIGHT
... 1. Magnifying glass (simple microscope ): A lens acts as a magnifying glass when the object is placed as in case 5 on page 23. i) A magnifying glass consists of a (converging / diverging) lens. ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / mo ...
... 1. Magnifying glass (simple microscope ): A lens acts as a magnifying glass when the object is placed as in case 5 on page 23. i) A magnifying glass consists of a (converging / diverging) lens. ii) The object must be placed at a distance (more than f / same as f / less than f / between f and 2f / mo ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.