ray optics and optical instruments
... Property of partial reflection of light is yet another such example. Everyone who has looked into the water in a pond sees image of the face in it, but also sees the bottom of the pond. Newton argued that some of the corpuscles, which fall on the water, get reflected and some get transmitted. But wh ...
... Property of partial reflection of light is yet another such example. Everyone who has looked into the water in a pond sees image of the face in it, but also sees the bottom of the pond. Newton argued that some of the corpuscles, which fall on the water, get reflected and some get transmitted. But wh ...
Aberrations
... 1) “Aberrations” will be considered as small errors in an optical system that is already producing a reasonable image. This means that wavefronts will deviate from the ideal (usually spherical, for an imaging system) by only a few wavelengths. Ground glass, structural glass bricks and shower doors w ...
... 1) “Aberrations” will be considered as small errors in an optical system that is already producing a reasonable image. This means that wavefronts will deviate from the ideal (usually spherical, for an imaging system) by only a few wavelengths. Ground glass, structural glass bricks and shower doors w ...
Lens Films and Reflective Polarization Films
... film (BEF) of Sumitomo 3M will be described. A prism pattern is formed with optical precision on a polyester film having a high optical transparency. The film is attached to the front surface of a backlight unit and is capable of enhancing the brightness by recycling light which is normally wasted. ...
... film (BEF) of Sumitomo 3M will be described. A prism pattern is formed with optical precision on a polyester film having a high optical transparency. The film is attached to the front surface of a backlight unit and is capable of enhancing the brightness by recycling light which is normally wasted. ...
Introduction to Light Microscopy Introduction Light microscopes are
... objects are mixed phase-amplitude objects. The bright-field microscope is mainly suitable for examining amplitude objects. The phase contrast microscope was the first contrast generating system readily available for the study of phase objects. Many kinds of microscopes are now available for generati ...
... objects are mixed phase-amplitude objects. The bright-field microscope is mainly suitable for examining amplitude objects. The phase contrast microscope was the first contrast generating system readily available for the study of phase objects. Many kinds of microscopes are now available for generati ...
7.1 textbook answers - aiss-science-9
... 2 a A real image can be formed only with a convex lens and the object is greater than one focal length away. b A virtual image can be obtained only when the object is closer than one focal length to the convex lens. Concave lenses always form virtual images. c No image is obtained when the candle is ...
... 2 a A real image can be formed only with a convex lens and the object is greater than one focal length away. b A virtual image can be obtained only when the object is closer than one focal length to the convex lens. Concave lenses always form virtual images. c No image is obtained when the candle is ...
Measurement of the 4Pi-confocal point spread function proves 75
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
... by focusing elements. An objective lens focuses light by concentrating a segment of a spherical wave front into an object point. The intensity in the focal region is distributed around the focal point forming a focal volume, which is described by the point spread function (PSF). The extent of the PS ...
DYNAMICS OF THE CELL MEMBRANE OBSERVED UNDER THE
... fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM)'\ A disadvantage is that one has to use the lens in combination with specially selected oil and a coverslip of an optimized refractive index of 1.78. This 1.65NA lens collects a light with its acceptance angle larger than the so called critical angle. No possible opti ...
... fluorescence microscopy (TIRFM)'\ A disadvantage is that one has to use the lens in combination with specially selected oil and a coverslip of an optimized refractive index of 1.78. This 1.65NA lens collects a light with its acceptance angle larger than the so called critical angle. No possible opti ...
Introduction to Drawing Ray Diagrams Types of
... Types of Mirrors and Lenses Plane Mirror – a mirror with a flat, reflective surface Convex Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves outward Concave Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves inward Lens – a transparent device with at least 1 curved surface that changes the di ...
... Types of Mirrors and Lenses Plane Mirror – a mirror with a flat, reflective surface Convex Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves outward Concave Mirror – a mirror whose reflecting surface curves inward Lens – a transparent device with at least 1 curved surface that changes the di ...
Optical quality of the eye lens surfaces from
... The scattering halo of the third Purkinje image is obtained by microdensitometric measurement of the photographic recordings. The measurements (see Fig. 4) show that the third Purkinje image has a Lorentzian intensity distribution modulated by a random distribution (speckle) and that the specular co ...
... The scattering halo of the third Purkinje image is obtained by microdensitometric measurement of the photographic recordings. The measurements (see Fig. 4) show that the third Purkinje image has a Lorentzian intensity distribution modulated by a random distribution (speckle) and that the specular co ...
Light Microscopy Excerpt from Chapter 1
... In the microscope, objects are enlarged or magnified with a convex lens that bends light rays by refraction. Diverging rays from points within the object (object points) are made to converge behind the convex lens and cross over each other to form image points (i.e., a focused image). The distance o ...
... In the microscope, objects are enlarged or magnified with a convex lens that bends light rays by refraction. Diverging rays from points within the object (object points) are made to converge behind the convex lens and cross over each other to form image points (i.e., a focused image). The distance o ...
Reflection
... depend on the wavelength of light, so mirrors produce perfect color images (no chromatic aberration) If the curvature of the mirror is large, the point becomes spread out. This is called spherical aberration. ...
... depend on the wavelength of light, so mirrors produce perfect color images (no chromatic aberration) If the curvature of the mirror is large, the point becomes spread out. This is called spherical aberration. ...
Microscopy
... In the third lab, we learned about the basic configuration of the compound microscope. In general, an object you wish to image is 3-dimensional. Although you may wish to image one plane of a specimen, out-of-plane light will cause distortion of your image and make it look blurry. The confocal micros ...
... In the third lab, we learned about the basic configuration of the compound microscope. In general, an object you wish to image is 3-dimensional. Although you may wish to image one plane of a specimen, out-of-plane light will cause distortion of your image and make it look blurry. The confocal micros ...
Fourier Optics
... place where they cut the +1 and -1 diffraction orders of the grating formed by the lines of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison ...
... place where they cut the +1 and -1 diffraction orders of the grating formed by the lines of the screen. In this way, the picture is passed unchanged and the lines are eliminated. 4. Image correlation. More complicated filters can be made by photography. One interesting application is the comparison ...
The Optics of the Compound Eye of the Honeybee
... was taken for each structural element. Glycerin was used as the mounting medium only in the measurement of the refractive index of the corneal elements. Other preparations were made using the Smith and Farquhar tissue sectioner (Sorvall TC-2). Heads were embedded in agar at about 35°C, and 10-20 pus ...
... was taken for each structural element. Glycerin was used as the mounting medium only in the measurement of the refractive index of the corneal elements. Other preparations were made using the Smith and Farquhar tissue sectioner (Sorvall TC-2). Heads were embedded in agar at about 35°C, and 10-20 pus ...
Devil`s lens optical tweezers
... Optical tweezers [1] are well-established as a powerful and versatile tool for the study of matter on the micron and sub-micron scale [2, 3, 4]. In the most common implementation an optical tweezers uses a strongly focused gaussian beam as a three-dimensional trap which can hold, move, guide and exe ...
... Optical tweezers [1] are well-established as a powerful and versatile tool for the study of matter on the micron and sub-micron scale [2, 3, 4]. In the most common implementation an optical tweezers uses a strongly focused gaussian beam as a three-dimensional trap which can hold, move, guide and exe ...
biology 163 laboratory use of the compound light microscope
... 100X) that can be rotated into position. Combined with a 10X ocular lens (standard on our microscopes), this gives the user the option of 40X, 100X, 400X and 1000X magnification. Magnification, however, is only part of the equation. The real purpose of a microscope lies in its ability to allow the u ...
... 100X) that can be rotated into position. Combined with a 10X ocular lens (standard on our microscopes), this gives the user the option of 40X, 100X, 400X and 1000X magnification. Magnification, however, is only part of the equation. The real purpose of a microscope lies in its ability to allow the u ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2014 Semester Lecture 39 – Review
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
... (b) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is unpolarized (c) Calculate the intensity of transmitted light if the incident light is left circular polarized (d) Is the system symmetric? That is, is the intensity of transmitted light the same if the paths of all light rays ...
System for observing interference phenomenon: In the previous
... In Michelson interferometer the two coherent sources are derived from the principle of division of amplitude. The parallel light rays from a monochromatic source are incident on beams splitter (glass plate) G1 which is semi silvered on its back surface and mounted at 45° to the axis. Light ray incid ...
... In Michelson interferometer the two coherent sources are derived from the principle of division of amplitude. The parallel light rays from a monochromatic source are incident on beams splitter (glass plate) G1 which is semi silvered on its back surface and mounted at 45° to the axis. Light ray incid ...
On the chromatic aberration of microlenses
... The refractive index of any transparent material is function of the wavelength. Therefore, a lens made in one single material shows different positions of focus at each wavelength. The difference in position of these focal points is known as the longitudinal primary chromatic aberration [1]. To corr ...
... The refractive index of any transparent material is function of the wavelength. Therefore, a lens made in one single material shows different positions of focus at each wavelength. The difference in position of these focal points is known as the longitudinal primary chromatic aberration [1]. To corr ...
Tutor 4
... errors, resulting in image degradation. If, however, the angle of illumination were chosen such that, for a given feature, the zero order and one of the first diffraction orders are spaced evenly about the center of the objective lens (Fig. 2), the phase change due to defocus will be the same for b ...
... errors, resulting in image degradation. If, however, the angle of illumination were chosen such that, for a given feature, the zero order and one of the first diffraction orders are spaced evenly about the center of the objective lens (Fig. 2), the phase change due to defocus will be the same for b ...
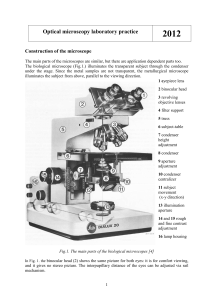
Optical microscopy laboratory practice 2012
... 4. Nose Piece: This connects the objective lens to the microscope body. With a turret, or rotating nose piece as many as five objectives can be attached to create different powers of magnification when rotated into position and used with the existing eyepiece. 5. Objective: The lens closest to the o ...
... 4. Nose Piece: This connects the objective lens to the microscope body. With a turret, or rotating nose piece as many as five objectives can be attached to create different powers of magnification when rotated into position and used with the existing eyepiece. 5. Objective: The lens closest to the o ...
Orbital Dynamics of the Laser Interferometer Space Antenna
... Next, the beam is expanded and collimated from the initial 5mm diameter to 12.4mm by the use of an expanding lens (3) with a 100mm focal length and a collimating lens (5) with a focal length of 250nm. The two lenses are positioned 350mm apart and an iris (4) is placed at the focal point between the ...
... Next, the beam is expanded and collimated from the initial 5mm diameter to 12.4mm by the use of an expanding lens (3) with a 100mm focal length and a collimating lens (5) with a focal length of 250nm. The two lenses are positioned 350mm apart and an iris (4) is placed at the focal point between the ...
univ. physics
... the lateral magnification m is positive. The y and y' have both the same magnitude and the same sign; the lateral magnification of a plane mirror is always m = + 1. Later we will encounter situations in which the image is inverted; that is, the image arrow points in the direction opposite to that of ...
... the lateral magnification m is positive. The y and y' have both the same magnitude and the same sign; the lateral magnification of a plane mirror is always m = + 1. Later we will encounter situations in which the image is inverted; that is, the image arrow points in the direction opposite to that of ...
Microscopy corrected
... cells are out of focus, rotate the left ocular until the cells are in focus. Do not touch the fine adjustment knob. Now the image should be in focus for both eyes. If your cells were already in focus for your left eye, you can skip this step too. 10. Now that you have focused on the cells using the ...
... cells are out of focus, rotate the left ocular until the cells are in focus. Do not touch the fine adjustment knob. Now the image should be in focus for both eyes. If your cells were already in focus for your left eye, you can skip this step too. 10. Now that you have focused on the cells using the ...
L/f 1
... nearsightedness (myopia) In case of nearsightedness, the far-point is much smaller than infinity for example because the eyeball is elongated. on object placed at infinity is focused in front of the retina. this can be corrected using a diverging lens… ...
... nearsightedness (myopia) In case of nearsightedness, the far-point is much smaller than infinity for example because the eyeball is elongated. on object placed at infinity is focused in front of the retina. this can be corrected using a diverging lens… ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.