PHYS 202 Notes, Week 10
... This week we learn about optical instruments, interference, and thin ...
... This week we learn about optical instruments, interference, and thin ...
Lens 101 review
... ED etc.) improve contrast and sharpness by reducing chromatic aberration (color defects) that usually occur in tele lenses. These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expensive and usually not used for cheaper l ...
... ED etc.) improve contrast and sharpness by reducing chromatic aberration (color defects) that usually occur in tele lenses. These elements are able to focus different wave lengths of one light ray in one point (see picture below). These elements are quite expensive and usually not used for cheaper l ...
Desert Island themed project - science
... ■ long sight, caused by the eyeball being too short, or the eye lens being unable to focus ■ short sight, caused by the eyeball being too long, or the eye lens being unable to focus. c) Range of vision. The eye can focus on objects between the near point and the far point. e) The power of a lens is ...
... ■ long sight, caused by the eyeball being too short, or the eye lens being unable to focus ■ short sight, caused by the eyeball being too long, or the eye lens being unable to focus. c) Range of vision. The eye can focus on objects between the near point and the far point. e) The power of a lens is ...
Newtons Ring
... In the Newton’s ring experiment, how does interference occur? Where have the fringes formed? Why are the fringes circular? Are all rings equispaced? Why is an extended source used in this experiment? What will happen if a point source or an illuminated slit is used instead of the extended source? In ...
... In the Newton’s ring experiment, how does interference occur? Where have the fringes formed? Why are the fringes circular? Are all rings equispaced? Why is an extended source used in this experiment? What will happen if a point source or an illuminated slit is used instead of the extended source? In ...
FRESNEL LENSES BASED ON NANO SHELL
... Abstract—Fresnel lenses are low-cost optical elements used for focusing sunlight to solar panels to ensure operation under highflux density. However, the conventional Fresnel lens has a relatively high material usage and hence contributes to additional efficiency degradation. Moreover, traditional d ...
... Abstract—Fresnel lenses are low-cost optical elements used for focusing sunlight to solar panels to ensure operation under highflux density. However, the conventional Fresnel lens has a relatively high material usage and hence contributes to additional efficiency degradation. Moreover, traditional d ...
Geometric Optics
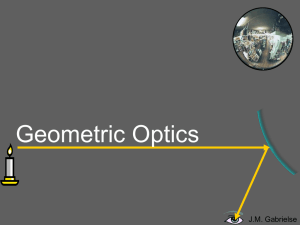
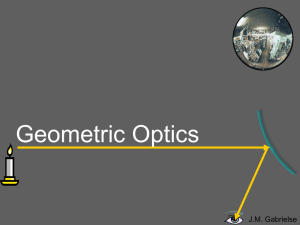
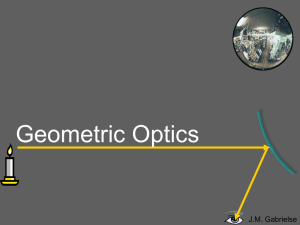
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics - Mr. Gabrielse's Physics
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The image forms where the rays converge. But they don’t seem to converge. J.M. Gabrielse ...
Geometric Optics
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
... The first ray comes in parallel to the optical axis and reflects through the focal point. The second ray comes through the focal point and reflects parallel to the optical axis. The light rays don’t converge, but the sight lines do. A virtual image forms where the sight lines converge. ...
Waves - Morgan Science
... Virtual – Light appears to be at that location Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
... Virtual – Light appears to be at that location Upright – image is right side up compared to object Inverted – image is upside down as compared to object ...
Slide 1
... Interference effects and diffraction result in “ringing” and spreading outside the aperture. Edges of image rise gradually (not abrupt) from zero. Intensity of image oscillates about the expected intensity. Oscillations decay as one approaches the center of the image. The oscillations are due to con ...
... Interference effects and diffraction result in “ringing” and spreading outside the aperture. Edges of image rise gradually (not abrupt) from zero. Intensity of image oscillates about the expected intensity. Oscillations decay as one approaches the center of the image. The oscillations are due to con ...
lenses - Van Buren Public Schools
... you only have to know the paths of two rays from a point on the object, represented by the vertical arrow. Any point except for the point on the principal axis will work, but it is customary to choose a point at the tip of the arrow. The path of one refracted ray is known from the definition of the ...
... you only have to know the paths of two rays from a point on the object, represented by the vertical arrow. Any point except for the point on the principal axis will work, but it is customary to choose a point at the tip of the arrow. The path of one refracted ray is known from the definition of the ...
Optical and Electron Microscopy
... Another solution is to use a different type of radiation altogether to "illuminate" the object. Quantum physics describes how sub-atomic particles, such as electrons, protons and neutrons, can be treated as waveforms (just as visible light may also be considered to be particulate in nature). This so ...
... Another solution is to use a different type of radiation altogether to "illuminate" the object. Quantum physics describes how sub-atomic particles, such as electrons, protons and neutrons, can be treated as waveforms (just as visible light may also be considered to be particulate in nature). This so ...
Lecture 18 - Purdue Physics
... Case 1: The object is located beyond the center of curvature (C) Case 2: The object is located at the center of curvature (C) Case 3: The object is located between the center of curvature and the focal point (F) Case 4: The object is located at the focal point (F) Case 5: The object is located betwe ...
... Case 1: The object is located beyond the center of curvature (C) Case 2: The object is located at the center of curvature (C) Case 3: The object is located between the center of curvature and the focal point (F) Case 4: The object is located at the focal point (F) Case 5: The object is located betwe ...
Two-dimensional array of diffractive microlenses
... 2 k discrete levels, only k repetitive steps are required. This is achieved by a binary decomposition of the final phase pattern as visualized in Figure 7. The thickness of the first layer h is chosen such that it yields a phase shift of r. The thickness of the remaining deposited layers then gets s ...
... 2 k discrete levels, only k repetitive steps are required. This is achieved by a binary decomposition of the final phase pattern as visualized in Figure 7. The thickness of the first layer h is chosen such that it yields a phase shift of r. The thickness of the remaining deposited layers then gets s ...
Summary Notes- EM spectrum and Light
... Large doses of UV can damage the retina in your eyes, so it's important to check that your sunglasses will block UV light. Cheap sunglasses can be dangerous because they may not block UV light as effectively as the more expensive ones. The pupil of your eye opens up more because some of the sunlight ...
... Large doses of UV can damage the retina in your eyes, so it's important to check that your sunglasses will block UV light. Cheap sunglasses can be dangerous because they may not block UV light as effectively as the more expensive ones. The pupil of your eye opens up more because some of the sunlight ...
RAY OPTICS notes
... Let θ be the angle of incidence, and MD be the perpendicular from M on the principal axis. ...
... Let θ be the angle of incidence, and MD be the perpendicular from M on the principal axis. ...
ppt document
... screwing the lens closer or further from the film or slide. But what about the eye? How do we focus on objects that are close and then further away with our eyes? Do we screw our eyes in and out like the lens on a camera or ...
... screwing the lens closer or further from the film or slide. But what about the eye? How do we focus on objects that are close and then further away with our eyes? Do we screw our eyes in and out like the lens on a camera or ...
Mindfiesta Page 1 CHAPTER – 10 WAVE OPTICS EXPERTS TIPS
... Sometimes, refractive indices of the materials of prisms for blue, mean and red light i.e. b, and r are represented by F, D and C respectively. (51) When two prisms (of different materials and angles of prism) are combined so as to produce dispersion without deviation, the condition for no de ...
... Sometimes, refractive indices of the materials of prisms for blue, mean and red light i.e. b, and r are represented by F, D and C respectively. (51) When two prisms (of different materials and angles of prism) are combined so as to produce dispersion without deviation, the condition for no de ...
Chapter 23 Ray Optics
... Calculate angles of reflection and refraction Understand the color and dispersion Use ray tracing to analyze lens and mirror systems Use refraction theory to calculate the properties of lens ...
... Calculate angles of reflection and refraction Understand the color and dispersion Use ray tracing to analyze lens and mirror systems Use refraction theory to calculate the properties of lens ...
W11Physics1CLec26Afkw
... Mirrors and Lenses For both mirrors and lenses: The object distance, p, is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens. The image distance, q, is the distance from the image to the mirror or lens. The lateral magnification, M, of the mirror or lens is the ratio of the image height to the obj ...
... Mirrors and Lenses For both mirrors and lenses: The object distance, p, is the distance from the object to the mirror or lens. The image distance, q, is the distance from the image to the mirror or lens. The lateral magnification, M, of the mirror or lens is the ratio of the image height to the obj ...
Strategies for the compensation of specimen
... medium such as skin, index matching is more difficult because each layer has different optical properties. If however, one were able to choose any refractive index for the immersion medium, it would be possible, for a given focusing situation, to find the optimum value. If the immersion medium is no ...
... medium such as skin, index matching is more difficult because each layer has different optical properties. If however, one were able to choose any refractive index for the immersion medium, it would be possible, for a given focusing situation, to find the optimum value. If the immersion medium is no ...
2 Fabry-Perot resonator
... The peaks have a finite width of 2φ1/2 (FWHM) since energy is lost from the resonator (R < 1). ...
... The peaks have a finite width of 2φ1/2 (FWHM) since energy is lost from the resonator (R < 1). ...
Optics - Jnoodle
... source at the bottom of a pool, from which light can be refracted into the air only for angles of incidence smaller than the critical angle as they hit the water surface from below. If light was sent in the opposite direction, it should follow the same path back (it can be shown by swapping 1 and ...
... source at the bottom of a pool, from which light can be refracted into the air only for angles of incidence smaller than the critical angle as they hit the water surface from below. If light was sent in the opposite direction, it should follow the same path back (it can be shown by swapping 1 and ...
Relating axial motion of optical elements to focal shift
... When designing and tolerancing an optical system, typically a full computer model of the system is created and a complete tolerance analysis is done. It is good practice to understand what the expected outcome of a simulation is before dedicating time to the endeavor. First order calculations, estim ...
... When designing and tolerancing an optical system, typically a full computer model of the system is created and a complete tolerance analysis is done. It is good practice to understand what the expected outcome of a simulation is before dedicating time to the endeavor. First order calculations, estim ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.