The optical microscopy with virtual image breaks
... implies that the final images are not isotropic within the imaging plane. The other practical limit is that the SPP-superlenses must be excited with a specific laser source and configuration (wavelength, polarization, incident angle). It is hard to achieve SPP-superlens function with a standard whit ...
... implies that the final images are not isotropic within the imaging plane. The other practical limit is that the SPP-superlenses must be excited with a specific laser source and configuration (wavelength, polarization, incident angle). It is hard to achieve SPP-superlens function with a standard whit ...
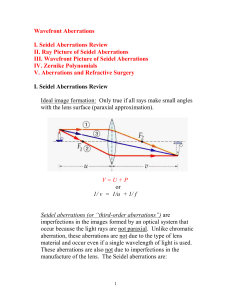
Wavefront Aberrations
... incident on a lens are NOT paraxial. So, ideal images are NOT formed. We can begin to see the effects of this if we expand the sine function in a power series expansion: sin = 3/3! + 5/5! .... In the paraxial approximation, we keep just the first term on the right hand side. Seidel aberratio ...
... incident on a lens are NOT paraxial. So, ideal images are NOT formed. We can begin to see the effects of this if we expand the sine function in a power series expansion: sin = 3/3! + 5/5! .... In the paraxial approximation, we keep just the first term on the right hand side. Seidel aberratio ...
Bright-Field Microscopy
... but then he would be in a quite different world from other people: nothing would appear the same to him and others: the visible ideas of everything would be different. So that I doubt, whether he and the rest of men could discourse concerning the objects of sight, or have any communication about col ...
... but then he would be in a quite different world from other people: nothing would appear the same to him and others: the visible ideas of everything would be different. So that I doubt, whether he and the rest of men could discourse concerning the objects of sight, or have any communication about col ...
Issues With Telescopes
... Adaptive optics measures the atmospheric distortions in the incoming light from a star or other object and sends electronic signals to a deformable mirror that can change its shape rapidly to correct for the distortions. In the system built for the 100-inch telescope, the light reflected from the te ...
... Adaptive optics measures the atmospheric distortions in the incoming light from a star or other object and sends electronic signals to a deformable mirror that can change its shape rapidly to correct for the distortions. In the system built for the 100-inch telescope, the light reflected from the te ...
optics - einstein classes
... light is incident and from which it emerges, If the faces of a prism on which light is incident and from which it emerges becomes parallel, angle of prism will be zero and as incident ray will emerge parallel to itself, deviation will also be zero i.e., the prism will act as a slab. ...
... light is incident and from which it emerges, If the faces of a prism on which light is incident and from which it emerges becomes parallel, angle of prism will be zero and as incident ray will emerge parallel to itself, deviation will also be zero i.e., the prism will act as a slab. ...
Document
... Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves when they meet an obstruction. It can occur with any type of wave… Diffraction also occurs when any group of waves of a finite size is propagating; for example… Diffraction is one particular type of wave interference, caused by the partial obstructio ...
... Diffraction is the bending and spreading of waves when they meet an obstruction. It can occur with any type of wave… Diffraction also occurs when any group of waves of a finite size is propagating; for example… Diffraction is one particular type of wave interference, caused by the partial obstructio ...
Diffracted Light Contrast: Improving the Resolution - Microscopy-UK
... and it does not require a second knife. With DLC, the coherent rays produced by the single edge will not interfere with rays from an opposing edge, as is the case when using a slit aperture. When using a convex edge to generate the diffracted light, each point along the edge serves as a point source ...
... and it does not require a second knife. With DLC, the coherent rays produced by the single edge will not interfere with rays from an opposing edge, as is the case when using a slit aperture. When using a convex edge to generate the diffracted light, each point along the edge serves as a point source ...
Chapter 3: Telescopes
... • Can observe 24 hours a day. • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere. • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information. ...
... • Can observe 24 hours a day. • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere. • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information. ...
Class 9
... What about rays aimed at the focus? (This is the previous rule, backwards) • Easy rule for rays aimed at focus: • An incoming ray aimed at F gets reflected back parallel (to the C-F axis). ...
... What about rays aimed at the focus? (This is the previous rule, backwards) • Easy rule for rays aimed at focus: • An incoming ray aimed at F gets reflected back parallel (to the C-F axis). ...
Transformation-designed optical elements
... and minimal reflection by judicious positioning of the mismatch discontinuity. The best position, for reasons described below, is at a focal plane. However, choosing the object or external image plane precludes having any free space working distance on the input or output side respectively. Fortunat ...
... and minimal reflection by judicious positioning of the mismatch discontinuity. The best position, for reasons described below, is at a focal plane. However, choosing the object or external image plane precludes having any free space working distance on the input or output side respectively. Fortunat ...
Physical Optics - Haverford College
... laser beam with one diameter and output a collimated beam with a larger diameter. Using lenses of your choice and using a ray optics diagram, show how to construct this device and compute its magnification (the factor by which the diameters have been expanded.) There are several designs possible! Ex ...
... laser beam with one diameter and output a collimated beam with a larger diameter. Using lenses of your choice and using a ray optics diagram, show how to construct this device and compute its magnification (the factor by which the diameters have been expanded.) There are several designs possible! Ex ...
Tidbits from the Hood (John Hood)
... The ocular lens is responsible for the magnifying power of the binocular. A ten power magnification allows the viewer to see an object ten times closer than with the unaided eye. This is wonderful, but the resulting field of view is more narrow thus creating difficulty when tracking a moving object. ...
... The ocular lens is responsible for the magnifying power of the binocular. A ten power magnification allows the viewer to see an object ten times closer than with the unaided eye. This is wonderful, but the resulting field of view is more narrow thus creating difficulty when tracking a moving object. ...
Fourier Optics
... Locating the Transform Plane (this is a useful method for determining the focal length of a lens) ...
... Locating the Transform Plane (this is a useful method for determining the focal length of a lens) ...
LxxA, Overview of Microscopy methods, part a
... • Chemical composition of materials can be obtained using electron microprobes to produce characteristic X-ray emissions and electron energy losses. • Imaging (surface) can be characterized using secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, photo-electron, Auger electrons and ion scattering. • Crys ...
... • Chemical composition of materials can be obtained using electron microprobes to produce characteristic X-ray emissions and electron energy losses. • Imaging (surface) can be characterized using secondary electrons, backscattered electrons, photo-electron, Auger electrons and ion scattering. • Crys ...
Document
... converging at angle (θx, θy) has amplitude equal to the Fourier coefficient each output coordinate at frequency (θx/λ, θy /λ) of (x’,y’) receives amplitude gin(x,y) equal to that of the corresponding Fourier component ...
... converging at angle (θx, θy) has amplitude equal to the Fourier coefficient each output coordinate at frequency (θx/λ, θy /λ) of (x’,y’) receives amplitude gin(x,y) equal to that of the corresponding Fourier component ...
Active Aperture Control and Sensor Modulation for Flexible Imaging
... density filter in front of the camera to capture high dynamic range image. These two methods must be implemented on a panning camera in order to image every scene point with different exposures. [12] discussed three possible designs to achieve “adaptive” HDR using an SLM, where the SLM is placed adj ...
... density filter in front of the camera to capture high dynamic range image. These two methods must be implemented on a panning camera in order to image every scene point with different exposures. [12] discussed three possible designs to achieve “adaptive” HDR using an SLM, where the SLM is placed adj ...
Coupling to aeroGAIN-ROD fibers
... tested with respect to climate change, vibration, and drop testing, and is very robust against transport and storage conditions. The module can tolerate large temperature changes from -30°C to 60°C and large vibrations, shock tested up to 1G at frequencies from 30Hz to 500Hz, without affecting the o ...
... tested with respect to climate change, vibration, and drop testing, and is very robust against transport and storage conditions. The module can tolerate large temperature changes from -30°C to 60°C and large vibrations, shock tested up to 1G at frequencies from 30Hz to 500Hz, without affecting the o ...
22-Test Talk
... process of beam-size measurements along the beam path— a process that is not always intuitive. M2 determination requires mapping the beam propagation in space and taking beamwidth parameters along this path to determine the deviation from the theoretical. Some standards call for 10 or more measureme ...
... process of beam-size measurements along the beam path— a process that is not always intuitive. M2 determination requires mapping the beam propagation in space and taking beamwidth parameters along this path to determine the deviation from the theoretical. Some standards call for 10 or more measureme ...
Blind Optical Aberration Correction by Exploring
... Optical aberration widely exists in optical imaging systems, especially in consumer-level cameras. In contrast to previous solutions using hardware compensation or precalibration, we propose a computational approach for blind aberration removal from a single image, by exploring various geometric and ...
... Optical aberration widely exists in optical imaging systems, especially in consumer-level cameras. In contrast to previous solutions using hardware compensation or precalibration, we propose a computational approach for blind aberration removal from a single image, by exploring various geometric and ...
LM Ch 8: Bright Field
... many hours of observation. Here are a few suggestions: 1) Correct adjustment of the interpupillary distance and diopter correction of each eyepiece is very important. See Chapter 1 for details on adjusting the binocular tube. When observing a specimen you should feel as though your eyes are complete ...
... many hours of observation. Here are a few suggestions: 1) Correct adjustment of the interpupillary distance and diopter correction of each eyepiece is very important. See Chapter 1 for details on adjusting the binocular tube. When observing a specimen you should feel as though your eyes are complete ...
Design and construction of a refracting telescope
... lens and travel through a focal point on the opposite side of the lens Any incident ray travelling through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and travel parallel to the principal axis. An incident ray travelling through the center of the lens will continue in the sa ...
... lens and travel through a focal point on the opposite side of the lens Any incident ray travelling through the focal point on the way to the lens will refract through the lens and travel parallel to the principal axis. An incident ray travelling through the center of the lens will continue in the sa ...
Isotropic Diffraction-Limited Focusing Using a Single Objective Lens
... along the normal to the lens (the optical axis). Except for the evanescent spots that are bound to a surface [3], the axial extension is at least 3 times larger than the transverse ones ([7], p. 491). Since the three-dimensional resolution of any optical device using focused beams is dictated by the ...
... along the normal to the lens (the optical axis). Except for the evanescent spots that are bound to a surface [3], the axial extension is at least 3 times larger than the transverse ones ([7], p. 491). Since the three-dimensional resolution of any optical device using focused beams is dictated by the ...
Vision and Optical Instruments
... For an eye with this typical 2.00 cm lens-to-retina distance, the power of the eye ranges from 50.0 D (for distant totally relaxed vision) to 54.0 D (for close fully accommodated vision), which is an 8% increase. This increase in power for close vision is consistent with the preceding discussion and ...
... For an eye with this typical 2.00 cm lens-to-retina distance, the power of the eye ranges from 50.0 D (for distant totally relaxed vision) to 54.0 D (for close fully accommodated vision), which is an 8% increase. This increase in power for close vision is consistent with the preceding discussion and ...
MIRRORS reflect light and obey the law
... For a concave mirror, the focal length is __________________________. For a convex mirror the focal length is ____________________________. If the image is real, in front of the mirror, the distance to image is __________________________. If the image is virtual, behind the mirror, the distance to i ...
... For a concave mirror, the focal length is __________________________. For a convex mirror the focal length is ____________________________. If the image is real, in front of the mirror, the distance to image is __________________________. If the image is virtual, behind the mirror, the distance to i ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.