LAB 1 - SIMPLE DIFFRACTION, FOURIER OPTICS AND ACOUSTO
... Locating the Transform Plane (this is a useful method for determining the focal length of a lens) ...
... Locating the Transform Plane (this is a useful method for determining the focal length of a lens) ...
The Optics of the Spherical Fish Lens
... derived. Maxwell’s infinite lens did not consider refraction at the fish lens boundary. Also, an infinitely distant object would have been imaged infinitesimally small, as the rule of image formation of the Maxwell lens differs from that of more conventional lenses. The Luneburg lens also does not a ...
... derived. Maxwell’s infinite lens did not consider refraction at the fish lens boundary. Also, an infinitely distant object would have been imaged infinitesimally small, as the rule of image formation of the Maxwell lens differs from that of more conventional lenses. The Luneburg lens also does not a ...
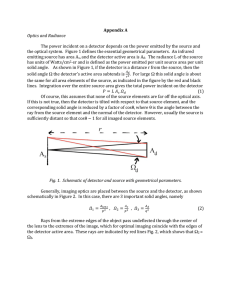
Appendix A Optics and Radiance The power incident on a
... corresponding solid angle is reduced by a factor of cosθ, where θ is the angle between the ray from the source element and the normal of the detector. However, usually the source is sufficiently ...
... corresponding solid angle is reduced by a factor of cosθ, where θ is the angle between the ray from the source element and the normal of the detector. However, usually the source is sufficiently ...
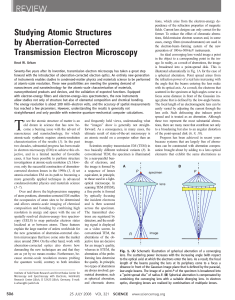
Urban - TEM aberration correction review
... technique (15, 16). A series of typ- atoms have no effect on the intensity measured in a given atomic position. from neighboring atoms. ically 20 images are recorded by a This provides the basis for the quantitative site-occupation measurements. The The described quantitative techcharge-coupled devi ...
... technique (15, 16). A series of typ- atoms have no effect on the intensity measured in a given atomic position. from neighboring atoms. ically 20 images are recorded by a This provides the basis for the quantitative site-occupation measurements. The The described quantitative techcharge-coupled devi ...
Document
... for a simple geometrical object e.g. a point or line of light - PSF (point spread function): distribution of light in the image plane for a point - LSF (line spread function): distribution for a line ...
... for a simple geometrical object e.g. a point or line of light - PSF (point spread function): distribution of light in the image plane for a point - LSF (line spread function): distribution for a line ...
12. confocal microscopy.
... Most commonly, confocal microscopy is used with fluorescence, which provides significantly higher contrast. Theoretically, the contrast in a fluorescence image is infinite, i.e. untagged structures (background) give zero signal. However, practical issues related to dark signals in the detector, limi ...
... Most commonly, confocal microscopy is used with fluorescence, which provides significantly higher contrast. Theoretically, the contrast in a fluorescence image is infinite, i.e. untagged structures (background) give zero signal. However, practical issues related to dark signals in the detector, limi ...
Mirrors - Purdue Physics
... such that its extrapolation crosses the optical axis a distance from the surface of the mirror equal to the focal length of the mirror • The third ray begins at the top of the object and is directed so that its extrapolation would intersect the center of the sphere • This ray is reflected back on it ...
... such that its extrapolation crosses the optical axis a distance from the surface of the mirror equal to the focal length of the mirror • The third ray begins at the top of the object and is directed so that its extrapolation would intersect the center of the sphere • This ray is reflected back on it ...
Nikonorov_Fresnel_Le.. - The Computer Vision Foundation
... As a result, Fresnel lenses are typically used as optical collimators or concentrators and not as imaging lens [3]. Other common applications include chromatic aberration compensation using doublets with refractive lenses [4], and as an element in X-Ray microscopes [5, 6]. Fresnel lenses have strong ...
... As a result, Fresnel lenses are typically used as optical collimators or concentrators and not as imaging lens [3]. Other common applications include chromatic aberration compensation using doublets with refractive lenses [4], and as an element in X-Ray microscopes [5, 6]. Fresnel lenses have strong ...
LABORATORY TECHNIQUES
... (b) focusing a collimated light beam to a point. These lenses are usually achromatic, i.e. consist of two or more elements, and are highly directional: to minimize aberrations they must be aligned with the optical axis of the system and the correct side must face the collimated beam; the side with t ...
... (b) focusing a collimated light beam to a point. These lenses are usually achromatic, i.e. consist of two or more elements, and are highly directional: to minimize aberrations they must be aligned with the optical axis of the system and the correct side must face the collimated beam; the side with t ...
The Optical Design of Miniaturized Microscope Objective for CARS
... to the first power of numerical aperture (NAS). Therefore, in order to decide on an appropriate NAS, we refer to the research of H. Wang and co-workers [17]. They have used the conventional microscope objective with needle-like bill, namely the MicroProbe Objective (MPO) lens from Olympus Inc. with ...
... to the first power of numerical aperture (NAS). Therefore, in order to decide on an appropriate NAS, we refer to the research of H. Wang and co-workers [17]. They have used the conventional microscope objective with needle-like bill, namely the MicroProbe Objective (MPO) lens from Olympus Inc. with ...
ANSWERS - AP Physics Multiple Choice Practice – Torque
... fast vehicle traveling at the speed of sound; the compressions are all right on top of each other. So faster speed means closer compressions and higher frequencies. Choice I must be true because X is a higher frequency so must be going faster. Distance to the person affects the volume but not the pi ...
... fast vehicle traveling at the speed of sound; the compressions are all right on top of each other. So faster speed means closer compressions and higher frequencies. Choice I must be true because X is a higher frequency so must be going faster. Distance to the person affects the volume but not the pi ...
Ch 03 - Aberrations
... In the preceding section on coma, we introduced the terms “tangential” and “sagittal”; a fuller discussion of these terms is appropriate at this point. If a lens system is represented by a drawing of its axial section, rays which lie in the plane of the drawing are called meridional or tangential ra ...
... In the preceding section on coma, we introduced the terms “tangential” and “sagittal”; a fuller discussion of these terms is appropriate at this point. If a lens system is represented by a drawing of its axial section, rays which lie in the plane of the drawing are called meridional or tangential ra ...
An adaptive liquid lens with radial interdigitated
... is a diverging lens. To evaluate the lens performance as its aperture is changed, a bunch of flowers was chosen as the object, as shown in figure 5(a). The object was placed under the lens cell at ∼20 mm distance. A digital camera was used to record the observed image. At V = 0, a clear image was obse ...
... is a diverging lens. To evaluate the lens performance as its aperture is changed, a bunch of flowers was chosen as the object, as shown in figure 5(a). The object was placed under the lens cell at ∼20 mm distance. A digital camera was used to record the observed image. At V = 0, a clear image was obse ...
24 Geometrical Optics
... The focal length f of the lens is given by the Lensmaker’s formula, 1/f = (nl −1)(1/R1 −1/R2 ). In this case f = 1.60 m, R1 = 2.00 m, R2 = ∞ (for the planar surface), which we plug into the formula to solve for nl : nl = 1 + ...
... The focal length f of the lens is given by the Lensmaker’s formula, 1/f = (nl −1)(1/R1 −1/R2 ). In this case f = 1.60 m, R1 = 2.00 m, R2 = ∞ (for the planar surface), which we plug into the formula to solve for nl : nl = 1 + ...
Presentation - University of Arizona
... Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations which measure the distances from focal ...
... Nodal planes have the characteristic of identity angular magnification. When the optical system is in air, nodal points/planes coincide with the principal points/planes. Principal points/planes can be described using Newtonian equations or Gaussian equations which measure the distances from focal ...
Ray tracing yair
... •For instance, windows placed at the Brewster angle are very common in gas lasers. The angles θx and θy paraxial to the optic axis. •However, if the dielectric material is a Brewster's angle window on a gas laser tube, ...
... •For instance, windows placed at the Brewster angle are very common in gas lasers. The angles θx and θy paraxial to the optic axis. •However, if the dielectric material is a Brewster's angle window on a gas laser tube, ...
lab 1 GEO Optics
... Your group is working to develop and study new proteins. To analyze the composition of a protein mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further anal ...
... Your group is working to develop and study new proteins. To analyze the composition of a protein mixture you have produced, the protein solution is placed in an electric field. Proteins with different total charges will drift at different speeds in the solution, and can be separated for further anal ...
Light consists of electromagnetic waves that have oscillating electric
... These waves carry both energy and momentum. The E and B fields are sinusoidal functions of time and position with a definite frequency and wavelength. Maxwell's equations demonstrate that a time varying magnetic field acts as a source of electric field, and a time-varying electric field acts as a so ...
... These waves carry both energy and momentum. The E and B fields are sinusoidal functions of time and position with a definite frequency and wavelength. Maxwell's equations demonstrate that a time varying magnetic field acts as a source of electric field, and a time-varying electric field acts as a so ...
powerpoint
... An achromatic lens is made of two components made of different kinds of glass and brings the two different wavelengths to the same focus. Other wavelengths are still out of focus. ...
... An achromatic lens is made of two components made of different kinds of glass and brings the two different wavelengths to the same focus. Other wavelengths are still out of focus. ...
Microscope
... optically. Therefore, the following important points should be taken into considerations 1. Always carry a microscope using both hands. 2. When not in use, a microscope should be protected from dust, moisture, direct sunlight and put in microscope case. 3. Keep it standing in place ready for use, bu ...
... optically. Therefore, the following important points should be taken into considerations 1. Always carry a microscope using both hands. 2. When not in use, a microscope should be protected from dust, moisture, direct sunlight and put in microscope case. 3. Keep it standing in place ready for use, bu ...
Galileoscope Optics Guide - Teaching with Telescopes
... 6. Ask the students if light changed direction when it hit the boundary. They should notice light changed direction. If your students are familiar with the term, you can tell them light bent toward the normal. Have the students practice this several times. 7. Tell the students they are going to loo ...
... 6. Ask the students if light changed direction when it hit the boundary. They should notice light changed direction. If your students are familiar with the term, you can tell them light bent toward the normal. Have the students practice this several times. 7. Tell the students they are going to loo ...
Measuring the Complete Transverse Spatial Mode Spectrum
... of freedom of electromagnetic fields with increasing complexity are exploited in applications ranging from communications to medicine. The detailed knowledge of the spatial mode spectrum of these beams, generally emitted by laser devices, is fundamental in optimizing applications as well as in resea ...
... of freedom of electromagnetic fields with increasing complexity are exploited in applications ranging from communications to medicine. The detailed knowledge of the spatial mode spectrum of these beams, generally emitted by laser devices, is fundamental in optimizing applications as well as in resea ...
Optics - MIT Fab Lab
... where f is the focal length of the lens. This is the lens equation, giving the relationship between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance ...
... where f is the focal length of the lens. This is the lens equation, giving the relationship between where a ray starts on the axis on one side of the lens and where it crosses the axis on the other side. Notice that the angles have dropped out of this equation: all rays starting at the same distance ...
Microscope Power Point File
... depths. Of course, with such powerful instruments, both the degree of magnification and the resolution, or sharpness of the image, are very high. Scanning electron microscopes are slightly different in that they scan a gold-plated specimen to give a 3-D view of the surface of an object. This view is ...
... depths. Of course, with such powerful instruments, both the degree of magnification and the resolution, or sharpness of the image, are very high. Scanning electron microscopes are slightly different in that they scan a gold-plated specimen to give a 3-D view of the surface of an object. This view is ...
An Optical ‘‘Janus’’ Device for Integrated Photonics By Xiang Zhang*
... the underlying material properties in a spatial manner. This is possible because of the invariance of Maxwell’s equations[3–5] under a spatial transformation. Therefore, transformation optics opens the possibility to precisely control the flow of light in a medium and thus allow to design novel devi ...
... the underlying material properties in a spatial manner. This is possible because of the invariance of Maxwell’s equations[3–5] under a spatial transformation. Therefore, transformation optics opens the possibility to precisely control the flow of light in a medium and thus allow to design novel devi ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.