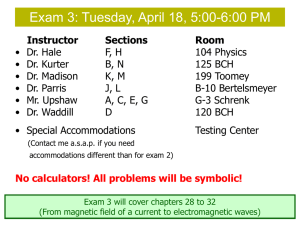
Accurate predictive model for twisted nematic liquid crystal devices. Application
... magnetic field applied. Ø Deformable mirror devices (DMDs). Each pixel is a mirror whose orientation can be electrostatically changed, then reflecting the beam at a different angle. There are also membrane deformable mirrors with no pixelation. Ø Multiple-quantum-well (MQW) SLMs. They take advantage ...
... magnetic field applied. Ø Deformable mirror devices (DMDs). Each pixel is a mirror whose orientation can be electrostatically changed, then reflecting the beam at a different angle. There are also membrane deformable mirrors with no pixelation. Ø Multiple-quantum-well (MQW) SLMs. They take advantage ...
Fun
... When you half-press the shutter release, the activated AF sensor "looks" at the image projected by the lens from two different directions (each line of pixels in the array looks from the opposite direction of the other) and identifies the phase difference of the light from each direction. In one "lo ...
... When you half-press the shutter release, the activated AF sensor "looks" at the image projected by the lens from two different directions (each line of pixels in the array looks from the opposite direction of the other) and identifies the phase difference of the light from each direction. In one "lo ...
Hanan khaled Mofty
... astigmatism) is refractive surgery. In this part we will know how refractive surgery corrects these cases. In general, thicker corneas permit treatment of larger amounts of nearsightedness and farsightedness. Corneas that are too thin may only allow small amounts of nearsightedness and farsightednes ...
... astigmatism) is refractive surgery. In this part we will know how refractive surgery corrects these cases. In general, thicker corneas permit treatment of larger amounts of nearsightedness and farsightedness. Corneas that are too thin may only allow small amounts of nearsightedness and farsightednes ...
Confocal microscopy with a volume holographic filter
... The pinhole preceding the detector in a confocal microscope is a shift-variant optical element. On-axis in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input foc ...
... The pinhole preceding the detector in a confocal microscope is a shift-variant optical element. On-axis in-focus point-source objects are imaged exactly inside the pinhole and give maximal intensity. An out-offocus object, even when it is on axis, is equivalent to an extended source on the input foc ...
A Guide to Acousto
... The Bragg condition would imply that there is only one value of the deflection angle Θ = 2θd allowed, but this is based on the assumption that the acoustic and optical wavefronts are plane waves (i.e. infinitely wide), ...
... The Bragg condition would imply that there is only one value of the deflection angle Θ = 2θd allowed, but this is based on the assumption that the acoustic and optical wavefronts are plane waves (i.e. infinitely wide), ...
MEMS-based handheld confocal microscope for in
... combines a fixed hemisphere front lens directly in contact with the tissue with commercially available air immersion objective lenses to achieve high numerical aperture (NA) and focus control ability without the need for fluid coupling between the objective lens and the sample. Much prior research o ...
... combines a fixed hemisphere front lens directly in contact with the tissue with commercially available air immersion objective lenses to achieve high numerical aperture (NA) and focus control ability without the need for fluid coupling between the objective lens and the sample. Much prior research o ...
Images and Plane Mirrors
... As shown in figure (a), a plane (flat) mirror can form a virtual image of a light source (said to be the object, O) by redirecting light rays emerging from the source. The image can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror ...
... As shown in figure (a), a plane (flat) mirror can form a virtual image of a light source (said to be the object, O) by redirecting light rays emerging from the source. The image can be seen where backward extensions of reflected rays pass through one another. The object’s distance p from the mirror ...
High resolution transmission electron microscopy
... Electrons are focused by simple round magnetic lenses which properties resemble the optical properties of a wine glass…. ...
... Electrons are focused by simple round magnetic lenses which properties resemble the optical properties of a wine glass…. ...
A Simple Classroom Demonstration of Natural Convection
... requires a few hours of preparation time, but very little in materials cost, assuming an overhead projector is already available. It could be prepared by the instructor or by students as part of a class-related project. I explain below the principle behind the schlieren technique, the preparation re ...
... requires a few hours of preparation time, but very little in materials cost, assuming an overhead projector is already available. It could be prepared by the instructor or by students as part of a class-related project. I explain below the principle behind the schlieren technique, the preparation re ...
A Practical Guide to Optical Trapping
... In the last few decades, novel microscopy techniques have been developed to monitor the activity of single enzymes as they perform their biological functions in vitro. Motor proteins such as kinesin, myosin, F1 Fo ATPase, and RNA polymerase have been mercilessly subjected to magnetic, elastic, and o ...
... In the last few decades, novel microscopy techniques have been developed to monitor the activity of single enzymes as they perform their biological functions in vitro. Motor proteins such as kinesin, myosin, F1 Fo ATPase, and RNA polymerase have been mercilessly subjected to magnetic, elastic, and o ...
Module P6.3 Optical elements: prisms, lenses and spherical mirrors
... operation and which can be used in their design. The operation of all these optical elements depends on the known behaviour of light rays when reflected from mirrors or refracted at the boundary between two transparent optical media. The magnifying glass is just one application of a thin lens and th ...
... operation and which can be used in their design. The operation of all these optical elements depends on the known behaviour of light rays when reflected from mirrors or refracted at the boundary between two transparent optical media. The magnifying glass is just one application of a thin lens and th ...
Mirrors and Lenses - mrphysicsportal.net
... Examine the inside surface of a spoon. It acts like a concave mirror. A concave mirror reflects light from its inner ("caved in") surface. In a spherical concave mirror, the mirror is part of the inner surface of a hollow sphere, Figure 18-4. The sphere of radius r has a geometric center, C. Point A ...
... Examine the inside surface of a spoon. It acts like a concave mirror. A concave mirror reflects light from its inner ("caved in") surface. In a spherical concave mirror, the mirror is part of the inner surface of a hollow sphere, Figure 18-4. The sphere of radius r has a geometric center, C. Point A ...
24.1 Physics 6C Geometrical Optics
... Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then bounces off the mirror and goes through the focal point (f). Ray 3 is the tricky one. Si ...
... Where is her image and how large is it? Notice the 3 rays in the diagram. They all start at the object and go toward the mirror. Ray 1 through the center is easy to draw. So is ray 2, which starts out flat, then bounces off the mirror and goes through the focal point (f). Ray 3 is the tricky one. Si ...
Chapter 33 . Aberration Curves in Lens Design
... astigmatism is present, the image planes for the tangential and sagittal fans are located at different distances along the chief ray. This is manifested in the ray intercept curves by different slopes at the origin for the tangential and sagittal curves. In Fig. 3 the slopes at the origins of the tw ...
... astigmatism is present, the image planes for the tangential and sagittal fans are located at different distances along the chief ray. This is manifested in the ray intercept curves by different slopes at the origin for the tangential and sagittal curves. In Fig. 3 the slopes at the origins of the tw ...
5377 17paper
... pupil is different for each example and shows how a test object can be designed for particular sensitivity to an aberration order. The diffraction energy distribution of Figure 2(c), for example, is most sensitive to third order (or primary) aberration and the sizing values of this example are used ...
... pupil is different for each example and shows how a test object can be designed for particular sensitivity to an aberration order. The diffraction energy distribution of Figure 2(c), for example, is most sensitive to third order (or primary) aberration and the sizing values of this example are used ...
Optical System design
... followed with the release of PreDesigner – a simple free optical layout program, designed to help find answers to that very first stage of the optical design task. Most recently, WinLens has been extended to handle non-rotationally symmetric systems. Many optical systems include prisms and/or tilts ...
... followed with the release of PreDesigner – a simple free optical layout program, designed to help find answers to that very first stage of the optical design task. Most recently, WinLens has been extended to handle non-rotationally symmetric systems. Many optical systems include prisms and/or tilts ...
Spectacle lens design following Hamilton, Maxwell
... We have a very useful way to characterize magnification and distortion. However, how to compute the point eikonal matrix S? Recall that we need to compute it for many gaze directions, and do so very fast, since it must be done at each iteration of the optimization process. Clearly, this cannot be do ...
... We have a very useful way to characterize magnification and distortion. However, how to compute the point eikonal matrix S? Recall that we need to compute it for many gaze directions, and do so very fast, since it must be done at each iteration of the optimization process. Clearly, this cannot be do ...
BioE 123 Teaching Material Stanford University
... direction of light wavefronts (see red vectors, wavefronts are in blue in diagram at right). These are “light rays.” The bending of light at interfaces between materials results in shifting in the direction of wavefronts and thus it is easy to use vectors to show where the peaks of the wavefronts wi ...
... direction of light wavefronts (see red vectors, wavefronts are in blue in diagram at right). These are “light rays.” The bending of light at interfaces between materials results in shifting in the direction of wavefronts and thus it is easy to use vectors to show where the peaks of the wavefronts wi ...
Generation of a dark hollow beam by a four
... one can obtain that formula (5) and (6) are overlying of Laguerre-Gaussian functions LG0l . It is easy to see that intensity is zero on z axis and the maximum of the intensity around z axis generates DHBOP. When illuminated by the light beam showed in Fig.1(c), two DHBOPs will cross vertically and a ...
... one can obtain that formula (5) and (6) are overlying of Laguerre-Gaussian functions LG0l . It is easy to see that intensity is zero on z axis and the maximum of the intensity around z axis generates DHBOP. When illuminated by the light beam showed in Fig.1(c), two DHBOPs will cross vertically and a ...
Exposing Digital Forgeries Through Chromatic Aberration
... Most images contain a variety of aberrations that result from imperfections and artifacts of the optical imaging system. In an ideal imaging system, light passes through the lens and is focused to a single point on the sensor. Optical systems, however, deviate from such ideal models in that they fai ...
... Most images contain a variety of aberrations that result from imperfections and artifacts of the optical imaging system. In an ideal imaging system, light passes through the lens and is focused to a single point on the sensor. Optical systems, however, deviate from such ideal models in that they fai ...
Expressive Chromatic Accumulation Buffering for Defocus Blur
... where B1 , B2 , B3 , C1 , C2 , and C3 are empirically chosen constants of optical materials and can be found from open databases [19]. For instance, BK7 (one of the most common glasses) for the current implementation is characterized by B1 = 1.040, B2 = 0.232, B3 = 1.010, C1 = 0.006, C2 = 0.020, and ...
... where B1 , B2 , B3 , C1 , C2 , and C3 are empirically chosen constants of optical materials and can be found from open databases [19]. For instance, BK7 (one of the most common glasses) for the current implementation is characterized by B1 = 1.040, B2 = 0.232, B3 = 1.010, C1 = 0.006, C2 = 0.020, and ...
Lens (optics)
A lens is a transmissive optical device that affects the focus of a light beam through refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (elements), usually along a common axis. Lenses are made from transparent materials such as glass, ground and polished to a desired shape. A lens can focus light to form an image, unlike a prism, which refracts light without focusing. Devices that similarly refract radiation other than visible light are also called lenses, such as microwave lenses or acoustic lenses.