Chapter 4 Reactions in Aqueous Solutions
... • Precipitation (formation of a solid from two aqueous solutions) occurs when product is insoluble • Produce insoluble ionic compounds • Double replacement (or metathesis reaction) • Solubility is the maximum amount of a solid that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature ...
... • Precipitation (formation of a solid from two aqueous solutions) occurs when product is insoluble • Produce insoluble ionic compounds • Double replacement (or metathesis reaction) • Solubility is the maximum amount of a solid that can dissolve in a given amount of solvent at a specified temperature ...
الشريحة 1
... components, resulting in an overall increase in randomness of the system. Formation of a homogeneous solution has increased the degree of dispersal, or randomness, because the molecules of each substance are now mixed and distributed in a volume twice as large as that which they occupied individuall ...
... components, resulting in an overall increase in randomness of the system. Formation of a homogeneous solution has increased the degree of dispersal, or randomness, because the molecules of each substance are now mixed and distributed in a volume twice as large as that which they occupied individuall ...
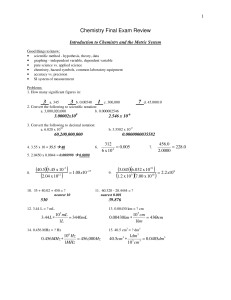
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... PV = nRT → (0.967atm)V = (0.0612mol )(0.0821 mol • K ( 295 K ) → V = 1.53 L ...
... PV = nRT → (0.967atm)V = (0.0612mol )(0.0821 mol • K ( 295 K ) → V = 1.53 L ...
South Pasadena • AP Chemistry
... 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term that refers to a process that never stops – the forward process & reverse processes occur at the same rate giving the appearance that the process has stopped, but that is NOT the case. 8. Dra ...
... 7. What does it mean when an equilibrium system is described as a dynamic system? Explain. Dynamic is a term that refers to a process that never stops – the forward process & reverse processes occur at the same rate giving the appearance that the process has stopped, but that is NOT the case. 8. Dra ...
Chapters 13 and 14
... A solution that is prepared by dissolving 3.150 grams of the substance in 25.00 grams of benzene, C6H6, has a freezing point of 1.12°C. (The normal freezing point of benzene is 5.50°C and the molal freezing-point depression constant, Kf, for benzene is 5.12 C°/molal.) a. Determine the empirical form ...
... A solution that is prepared by dissolving 3.150 grams of the substance in 25.00 grams of benzene, C6H6, has a freezing point of 1.12°C. (The normal freezing point of benzene is 5.50°C and the molal freezing-point depression constant, Kf, for benzene is 5.12 C°/molal.) a. Determine the empirical form ...
Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry (Chapter 4)
... A substance’s solubility is usually expressed in terms of the grams of the solute that can dissolve in 100.00 cm3 of water. Sometimes is it more meaningful to discuss the solubility in terms of moles of solute per liter of solution. A substance’s solubility changes as the solution’s temperature vari ...
... A substance’s solubility is usually expressed in terms of the grams of the solute that can dissolve in 100.00 cm3 of water. Sometimes is it more meaningful to discuss the solubility in terms of moles of solute per liter of solution. A substance’s solubility changes as the solution’s temperature vari ...
Chemistry Final Exam Review
... PV = nRT → (0.967 atm)V = (0.0612mol )(0.0821 mol • K ( 295 K ) → V = 1.53L ...
... PV = nRT → (0.967 atm)V = (0.0612mol )(0.0821 mol • K ( 295 K ) → V = 1.53L ...
Name: 1) At 1 atmosphere and 298 K, 1 mole of H O(l) molecules
... energy generally increases. B) The atomic radius increases, and the first ionization energy generally increases. C) The atomic radius decreases, and the first ionization energy generally decreases. D) The atomic radius increases, and the first ionization energy generally decreases. ...
... energy generally increases. B) The atomic radius increases, and the first ionization energy generally increases. C) The atomic radius decreases, and the first ionization energy generally decreases. D) The atomic radius increases, and the first ionization energy generally decreases. ...
3(aq)
... 2. Strong bases (metal hydroxides) will dissolve completely into OH- ions and a metallic cation. (ex: NaOH and KOH) 3. The net ionic equation for a reaction between a base and an acid is: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(L) 4. There will also be a salt produced, which will remain aqueous, unless it is evapora ...
... 2. Strong bases (metal hydroxides) will dissolve completely into OH- ions and a metallic cation. (ex: NaOH and KOH) 3. The net ionic equation for a reaction between a base and an acid is: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(L) 4. There will also be a salt produced, which will remain aqueous, unless it is evapora ...
Exam #2
... (B) Mass of solute (C) Mass of solute and mass of solvent (D) Mass of solute and volume of solvent (E) Mass of solute, mass of solvent, and vapor pressure of solvent 28. Which of the following is probably true for a solid solute with a highly endothermic heat of solution when dissolved in water? (A) ...
... (B) Mass of solute (C) Mass of solute and mass of solvent (D) Mass of solute and volume of solvent (E) Mass of solute, mass of solvent, and vapor pressure of solvent 28. Which of the following is probably true for a solid solute with a highly endothermic heat of solution when dissolved in water? (A) ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... How does an increase in vapor pressure affect the colligative properties of a solution? How would an equation be written for the dissociation of ionic solutes in water? Why does oil not dissolve in water according to the factors that affect solubility? How does an increase in temperature and pressur ...
... How does an increase in vapor pressure affect the colligative properties of a solution? How would an equation be written for the dissociation of ionic solutes in water? Why does oil not dissolve in water according to the factors that affect solubility? How does an increase in temperature and pressur ...
Review Final 111 Lect
... 36. The molar solubility of CaF2(s) in a saturated solution can be increased by adding: a. CaCl2 b. NaF c. HBr d. none of these (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of t ...
... 36. The molar solubility of CaF2(s) in a saturated solution can be increased by adding: a. CaCl2 b. NaF c. HBr d. none of these (Hint: You need to write the equilibrium equation for the solubility of CaF2 given above) 37. When barium chloride is added to a saturated solution of BaSO4(s), which of t ...
AL COS #
... solid compound to dissolve in water. What strategies might she powder, heat the solution, employ to increase the solubility of the solid? and stir the solution vigorously ...
... solid compound to dissolve in water. What strategies might she powder, heat the solution, employ to increase the solubility of the solid? and stir the solution vigorously ...
final-H-2006-07-v1
... following conclusions is supported by this observation? a. All four gases must have the same mass. b. All four gases must have the same pressure. c. All four gases must have equal numbers of particles. d. All four gases must have equal average kinetic energies. Reaction rates 62. A catalyst a. is no ...
... following conclusions is supported by this observation? a. All four gases must have the same mass. b. All four gases must have the same pressure. c. All four gases must have equal numbers of particles. d. All four gases must have equal average kinetic energies. Reaction rates 62. A catalyst a. is no ...
final-H-2006-07-v2
... following conclusions is supported by this observation? a. All four gases must have the same mass. b. All four gases must have the same pressure. c. All four gases must have equal numbers of particles. d. All four gases must have equal average kinetic energies. Reaction rates 66. A catalyst a. is no ...
... following conclusions is supported by this observation? a. All four gases must have the same mass. b. All four gases must have the same pressure. c. All four gases must have equal numbers of particles. d. All four gases must have equal average kinetic energies. Reaction rates 66. A catalyst a. is no ...
Lecture 4
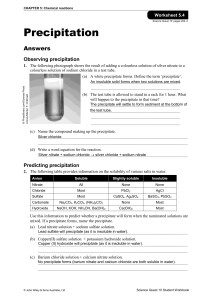
... Solubility Rules for Common Ionic Compounds In water at 25oC 1. All alkali metals (Group 1A) compounds are soluble. 2. All ammonium (NH4+) compounds are soluble. 3. All nitrate (NO3-), chlorate (ClO3-), and perchlorate (ClO4-) compounds are soluble. 4. Most hydroxides (OH-) are insoluble. The excep ...
... Solubility Rules for Common Ionic Compounds In water at 25oC 1. All alkali metals (Group 1A) compounds are soluble. 2. All ammonium (NH4+) compounds are soluble. 3. All nitrate (NO3-), chlorate (ClO3-), and perchlorate (ClO4-) compounds are soluble. 4. Most hydroxides (OH-) are insoluble. The excep ...
Worksheet # 1 Solubility and Saturated Solutions 1. Define and give
... In terms of equilibrium describe the difference between a saturated and unsaturated solution. ...
... In terms of equilibrium describe the difference between a saturated and unsaturated solution. ...
Reaction Systems Engineering II (part 1)
... Solution to Exercise 1.3 rG° = 77.1 + (–131.2) – (–109.8) = 55.7 kJ mol–1 b[A+(aq)]b[B–(aq)] = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–55.71000 / (8.3145298)] = 1.72510–10 mol2 kg–2 S = (1.72510–10)1/2 = 1.3110–5 mol kg–1 hardly soluble salt well approximated by an ideal solution * Solubility difficult to me ...
... Solution to Exercise 1.3 rG° = 77.1 + (–131.2) – (–109.8) = 55.7 kJ mol–1 b[A+(aq)]b[B–(aq)] = exp(–rG° / RT) = exp[–55.71000 / (8.3145298)] = 1.72510–10 mol2 kg–2 S = (1.72510–10)1/2 = 1.3110–5 mol kg–1 hardly soluble salt well approximated by an ideal solution * Solubility difficult to me ...
CHAPTER 6: Earth science
... 1. The following photograph shows the result of adding a colourless solution of silver nitrate to a colourless solution of sodium chloride in a test tube. (a) A white precipitate forms. Define the term ‘precipitate’. An insoluble solid forms when two solutions are mixed. ...
... 1. The following photograph shows the result of adding a colourless solution of silver nitrate to a colourless solution of sodium chloride in a test tube. (a) A white precipitate forms. Define the term ‘precipitate’. An insoluble solid forms when two solutions are mixed. ...
Ch1-2
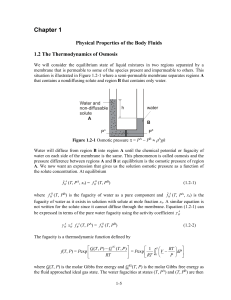
... The term osmole is defined as one mole of a nondiffusing and nondissociating substance. One mole of a dissociating substance such as NaCl is equivalent to two osmoles. The number of osmoles per liter of solution is called osmolarity. For physiological solutions, it is convenient to work in terms of ...
... The term osmole is defined as one mole of a nondiffusing and nondissociating substance. One mole of a dissociating substance such as NaCl is equivalent to two osmoles. The number of osmoles per liter of solution is called osmolarity. For physiological solutions, it is convenient to work in terms of ...
Physical properties
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
... • Distillation is used to purify a compound by separating it from a non-volatile or less-volatile material. When different compounds in a mixture have different boiling points, they separate into individual components when the mixture is carefully distilled. • Distillation is the process of heating ...
CHM1 Review for Exam 9 Topics 1. Reaction Types a. Combustion
... 7. Which equation represents a double replacement reaction? (1) 2 Na + 2 H2O 2 NaOH + H2 (2) CaCO3 CaO + CO2 (3) AgNO3 + HCl LiCl + HNO3 (4) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O 8. One hundred grams of water is saturated with NH4Cl at 50°C. According to Table G, if the temperature is lowered to 10°C. what ...
... 7. Which equation represents a double replacement reaction? (1) 2 Na + 2 H2O 2 NaOH + H2 (2) CaCO3 CaO + CO2 (3) AgNO3 + HCl LiCl + HNO3 (4) CH4 + 2 O2 CO2 + 2 H2O 8. One hundred grams of water is saturated with NH4Cl at 50°C. According to Table G, if the temperature is lowered to 10°C. what ...
chapter 9: aqueous solutions
... Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ...
... Show that the ions separate from each other in solution. Steps: 1. write the separate aqueous ions (including their correct charges) on the right side 2. write the formula of the compound followed by an arrow 3. balance using coefficients 4. add state symbols (state of pure substance on the left, ...
Chapter 4 - GEOCITIES.ws
... the attractions between the ions are so large that the water molecule will not separate the ion, and the substance remains mostly ...
... the attractions between the ions are so large that the water molecule will not separate the ion, and the substance remains mostly ...
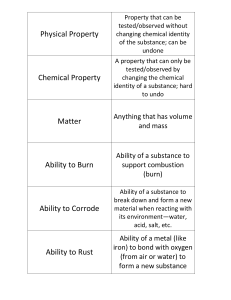
Physical Property
... Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid ...
... Temperature at which a solid turns to liquid AND Temperature at which a liquid turns to solid ...