The s-Block Elements
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
... 2. For Group II sulphates, the cations are much smaller than the anions. The changing in size of cations does not cause a significant change in H lattice (proportional to 1/(r+ + r-). However, the changing in size of cations does cause H hydration (proportional to 1/r+ and 1/r-) to become less exo ...
EKSIKA JOINT EVALUATION TEST. Kenya Certificate
... Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above. Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above. Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided above. All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary. Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used ...
... Write your name and index number in the spaces provided above. Sign and write the date of examination in the spaces provided above. Answer ALL questions in the spaces provided above. All workings MUST be clearly shown where necessary. Mathematical tables and silent electronic calculators may be used ...
Compulsory textbook Recommended textbooks Topics of the first
... to the analyte until the reaction between the analyte and the reagent is complete Equivalence point – the point in the titration, when the amount of reagennt added to thge solution is exactly equivalent to the amount of the analyte (theoretical value) End point – the point in the titration, when a p ...
... to the analyte until the reaction between the analyte and the reagent is complete Equivalence point – the point in the titration, when the amount of reagennt added to thge solution is exactly equivalent to the amount of the analyte (theoretical value) End point – the point in the titration, when a p ...
Name ……………………………..………...… …….. Index No
... Name the type of polymerization these monomers would undergo to form a polymer.(1mk) ...
... Name the type of polymerization these monomers would undergo to form a polymer.(1mk) ...
GC-Final-Review-2014
... d. Contains less solute that a saturated solution e. Maximum amount of solvent dissolved in a solute at a certain temperature e. Maximum amount of solvent dissolved in a solute at a certain temperature f. small amount of solute in large amount of solvent g. Moles per liter, represents solution conce ...
... d. Contains less solute that a saturated solution e. Maximum amount of solvent dissolved in a solute at a certain temperature e. Maximum amount of solvent dissolved in a solute at a certain temperature f. small amount of solute in large amount of solvent g. Moles per liter, represents solution conce ...
Barnard Castle School Chemistry Department
... A solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution. A solution is a mixture of a solute and a solvent, and is clear in appearance. An example of a common solution is sea water. The solute is salt (sodium chloride) and the solvent is water. A substance is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves in it, b ...
... A solute dissolves in a solvent to form a solution. A solution is a mixture of a solute and a solvent, and is clear in appearance. An example of a common solution is sea water. The solute is salt (sodium chloride) and the solvent is water. A substance is soluble in a solvent if it dissolves in it, b ...
use-2012_review_sheettest_form_c_reactions
... lead. According to the activity series, does this reaction actually take place? ...
... lead. According to the activity series, does this reaction actually take place? ...
Notes_Solutions - Anderson High School
... miscible—When two or more liquids mix (ex. Water and food coloring) immiscible—When two or more liquids DON’T mix.--they usually layer if allowed to set for a while. (ex. Water and oil) ...
... miscible—When two or more liquids mix (ex. Water and food coloring) immiscible—When two or more liquids DON’T mix.--they usually layer if allowed to set for a while. (ex. Water and oil) ...
Chapter 13: Properties of Solutions
... As temperature increases, the solubility of gases in water decrease. Ex: Boiling water releases gas molecules ...
... As temperature increases, the solubility of gases in water decrease. Ex: Boiling water releases gas molecules ...
Chapter 13…States of Matter
... 18. Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) will dissociate into __4___(how many) ions and will cause a (greater/smaller) change boiling point than MgCl2. 19. In the solvation of solids, solubility rate increases with (high/low) temperatures and (high /low) pressure. Pressure does not affect solids,only gases ...
... 18. Aluminum chloride (AlCl3) will dissociate into __4___(how many) ions and will cause a (greater/smaller) change boiling point than MgCl2. 19. In the solvation of solids, solubility rate increases with (high/low) temperatures and (high /low) pressure. Pressure does not affect solids,only gases ...
Molar Heat of Reaction
... (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
... (which is usually water) Expressed in kilojoules per mole (kJ/mol) of dissolved solute In this reaction heat can be either released or absorbed ...
Spring 2014 Chemistry Review
... 98) In the solvation of solids, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures. 99) In the solvation of gases, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures and (high / low) pressure. 100) Agitation of a solution will (increase / decrease) the dissolving rate of a solid; whereas ...
... 98) In the solvation of solids, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures. 99) In the solvation of gases, solubility rates increase with (high / low) temperatures and (high / low) pressure. 100) Agitation of a solution will (increase / decrease) the dissolving rate of a solid; whereas ...
Extraction lecture - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... – Water is removed from the organic layer using saturated sodium chloride solution (bulk) or a drying agent (for smaller amounts of water) ...
... – Water is removed from the organic layer using saturated sodium chloride solution (bulk) or a drying agent (for smaller amounts of water) ...
Solute
... in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, ionized phase of matter as found on the sun. ...
... in fixed positions. Liquid – definite volume but indefinite shape; particles close together but not in fixed positions Gas – neither definite volume nor definite shape; particles are at great distances from one another Plasma – high temperature, ionized phase of matter as found on the sun. ...
Complex Ions and Free Energy
... 2. A solution containing 0.010 M Ba2+ and 0.10 M Ag+, which solid will precipitate first when Na2SO4 is added to the solution? Justify your reasoning with calculations. NOTE the Ksp (BaSO4) = 1.1 x 10-10 and Ksp (AgSO4) = 1.1 x 10-5. ...
... 2. A solution containing 0.010 M Ba2+ and 0.10 M Ag+, which solid will precipitate first when Na2SO4 is added to the solution? Justify your reasoning with calculations. NOTE the Ksp (BaSO4) = 1.1 x 10-10 and Ksp (AgSO4) = 1.1 x 10-5. ...
- Solubility products -Thermochemistry
... show the reaction of one mole of the compound with sufficient oxygen to convert all of the carbon and hydrogen present to gaseous CO2 and liquid H2O. • C6H6(l) + 7½O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) H° = -3274 kJ • CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ...
... show the reaction of one mole of the compound with sufficient oxygen to convert all of the carbon and hydrogen present to gaseous CO2 and liquid H2O. • C6H6(l) + 7½O2(g) 6CO2(g) + 3H2O(l) H° = -3274 kJ • CH4(g) + 2O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(l) ...
IPC Semester Exam Review – Chemistry Topics
... 103. double replacement: CuCl2 + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2AgCl 104. At the surface of the solute, solvent particles surround solute particles (due to +/- attractions) and pull them away into the solution. 105. stirring, increased surface area, high temperature 106. no stirring/shaking, high pressure, lo ...
... 103. double replacement: CuCl2 + 2AgNO3 Cu(NO3)2 + 2AgCl 104. At the surface of the solute, solvent particles surround solute particles (due to +/- attractions) and pull them away into the solution. 105. stirring, increased surface area, high temperature 106. no stirring/shaking, high pressure, lo ...
Chapter 14…Kinetic Theory
... 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, __________ kPa or __________mmHg 13. What is the relationship between: volume and density: temperature and density: pressure and density Calculate the following: 14. A sample of argon gas is cooled and its volume went from ...
... 11. Standard temperature = __________ 12. Standard pressure = __________ atm, __________ kPa or __________mmHg 13. What is the relationship between: volume and density: temperature and density: pressure and density Calculate the following: 14. A sample of argon gas is cooled and its volume went from ...
semester two review sheet
... 1. Define the following terms: polarity, surface tension, vapor pressure, specific heat, and capillary action. 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. ...
... 1. Define the following terms: polarity, surface tension, vapor pressure, specific heat, and capillary action. 2. Draw four water molecules. Label the types of bonds (covalent vs. hydrogen), oxygen atoms, hydrogen atoms, and respective charges on the atoms. 3. Is water polar or nonpolar? Explain. 4. ...
The s-Block Elements - GCG-42
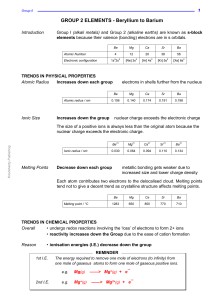
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
... BeCl2 is essentially covalent, with comparatively low m.pt. The lower members in group II form essentially ionic chlorides, with Mg having intermediate properties. ...
Physical Properties
... • A substance dissolves faster if it is stirred or –The particles are made smaller. shaken. –The temperature is increased. Why? ...
... • A substance dissolves faster if it is stirred or –The particles are made smaller. shaken. –The temperature is increased. Why? ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
... Strong and Weak Acids and Bases • Strong acids ionize completely to H+ • HCl (aq) → H+ (aq) + Cl- (aq) • In a solution of 1.0 M HCl, there is 1M H+ and 1M Cl• No HCl is left un-ionized • Other strong acids ionize in similar fashion ...
CHEMISTRY EXAM 2 REVIEW
... Define the following chemistry terms: [Chemistry Dictionary] 1. alloy a mixture of metals 2. brittleness the property of matter that is how easily the substance breaks or shatters when force is applied to it. 3. compound a substance made up of two or more elements that are combined chemically. 4. de ...
... Define the following chemistry terms: [Chemistry Dictionary] 1. alloy a mixture of metals 2. brittleness the property of matter that is how easily the substance breaks or shatters when force is applied to it. 3. compound a substance made up of two or more elements that are combined chemically. 4. de ...
Honors Chemistry Final Review
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...
... apart on the _________________ In fact, the further apart, the more ionic! A covalent bond forms from the combination of ______________________, including ___________ It has an electronegativity difference that is ___________ which means that the two combining elements will not be far apart on the p ...