Applied Physics - Revision World
... Boyle’s Law: pV = constant - Temperature remains constant (isothermal) - pV = constant and p1V1 = p2V2 - ΔU = 0 because the internal energy is dependent on temperature, which does not change - ΔQ = ΔW. If the gas expands to do work ΔW, & amount of heat ΔQ must be supplied - compression or expansion ...
... Boyle’s Law: pV = constant - Temperature remains constant (isothermal) - pV = constant and p1V1 = p2V2 - ΔU = 0 because the internal energy is dependent on temperature, which does not change - ΔQ = ΔW. If the gas expands to do work ΔW, & amount of heat ΔQ must be supplied - compression or expansion ...
Gill_chapter4
... 16. Since Td = increase in heat content (of the system), then if the process is isentropic and reversible, then it is also called adiabatic. In our case, we assume “reversible processes,” so isentropic = adiabatic. Thermodynamic Definition: An adiabatic process a process in which no heat is transfe ...
... 16. Since Td = increase in heat content (of the system), then if the process is isentropic and reversible, then it is also called adiabatic. In our case, we assume “reversible processes,” so isentropic = adiabatic. Thermodynamic Definition: An adiabatic process a process in which no heat is transfe ...
Lecture_1_ Heat and - Arizona State University
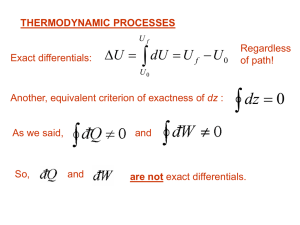
... this unfortunate convention work is positive if the engine is doing its job. Note that some textbooks e.g., Equilibrium Thermodynamics by Adkins will write the first law as dU Q W which is more in line with results in the opposite sign convention for work. In this convention positive work is ...
... this unfortunate convention work is positive if the engine is doing its job. Note that some textbooks e.g., Equilibrium Thermodynamics by Adkins will write the first law as dU Q W which is more in line with results in the opposite sign convention for work. In this convention positive work is ...
Z004 - THERMODYNAMICS
... gas if 2,000 joules of work are done on the gas and 6,000 joules of work is allowed to exit the system by cooling? -The enclosed gas in the previous question is .02 kg of atmospheric air. If the gas starts at 308 K what is its final temperature? -How much heat is required to increase the temperature ...
... gas if 2,000 joules of work are done on the gas and 6,000 joules of work is allowed to exit the system by cooling? -The enclosed gas in the previous question is .02 kg of atmospheric air. If the gas starts at 308 K what is its final temperature? -How much heat is required to increase the temperature ...
AP Physics 2
... out of an ideal gas at a constant volume so that its pressures drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then, the gas expands at a constant pressure, from a volume of 5.9 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. a. Calculate the total work done by the gas in the process. ...
... out of an ideal gas at a constant volume so that its pressures drops from 2.2 atm to 1.4 atm. Then, the gas expands at a constant pressure, from a volume of 5.9 L to 9.3 L, where the temperature reaches its original value. a. Calculate the total work done by the gas in the process. ...
Q - UCSB Physics
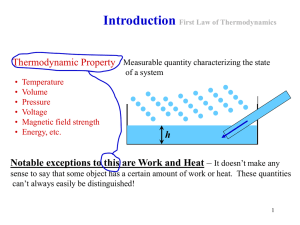
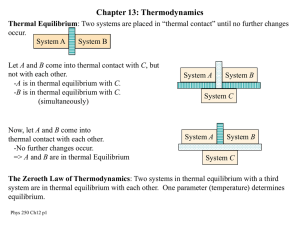
... Thermodynamic Concepts • Thermodynamic system: able to exchange heat with its surroundings • State variables: p, V, T, ... describe the thermodynamic system • Thermodynamic process: changes the state ( p, V, T, ...) of the system ...
... Thermodynamic Concepts • Thermodynamic system: able to exchange heat with its surroundings • State variables: p, V, T, ... describe the thermodynamic system • Thermodynamic process: changes the state ( p, V, T, ...) of the system ...
0.1 Minimum Principles and Thermodynamic Potentials
... the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 in an irreversible process. The Gibbs free energy is very useful because most prac ...
... the equilibrium state is that for which G is a minimum. The proof is very similar to that for A: the second law states that ∆Q ≤ T ∆S or 0 ≥ T ∆S + ∆U + P ∆V , if P is held fixed. But dG = dU − T dS + P dV , so dG ≤ 0 in an irreversible process. The Gibbs free energy is very useful because most prac ...
Engineering Building Room 2303 Mail Code Phone: 818-677
... inlet and one outlet. In this case the inlet and outlet mass flow rates must be the same and . The first law for this system then becomes. can be given the single symbol, m ...
... inlet and one outlet. In this case the inlet and outlet mass flow rates must be the same and . The first law for this system then becomes. can be given the single symbol, m ...
More Carnot Cycle March 4, 2010 Efficiency = W/Qin = Qin
... In the diagram the gas starts at V1, P1 then it was expanded isothermally to V2, P2 then compressed at constant pressure to V3, P3. In this case, V3 = V1. Heat was added to bring it back to its original state at constant volume. The total work by the system is equal to the sum of the works done in e ...
... In the diagram the gas starts at V1, P1 then it was expanded isothermally to V2, P2 then compressed at constant pressure to V3, P3. In this case, V3 = V1. Heat was added to bring it back to its original state at constant volume. The total work by the system is equal to the sum of the works done in e ...
15-1 The First Law of Thermodynamics
... When the gas temperature reaches 90°C, the equilibrium, the pressure of piston is at a new equilibrium position, but the pressure the gas is given by in the cylinder is the same as it was before – nothing has , where A is changed on the free-body diagram. Thus, to satisfy the ideal gas law, the volu ...
... When the gas temperature reaches 90°C, the equilibrium, the pressure of piston is at a new equilibrium position, but the pressure the gas is given by in the cylinder is the same as it was before – nothing has , where A is changed on the free-body diagram. Thus, to satisfy the ideal gas law, the volu ...
Heat Work
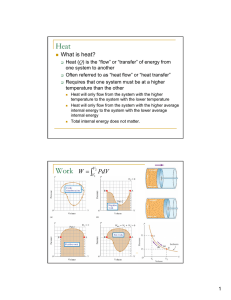
... When temperature changes, internal energy has changed – may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the system ΔU = Q ...
... When temperature changes, internal energy has changed – may happen through heat transfer or through mechanical work First law is a statement of conservation of energy Change in internal energy of system equals the difference between the heat added to the system and the work done by the system ΔU = Q ...
Course name Thermodynamics Course code ENG.I.011 Department
... Applying thermodynamic properties using Boyle’s, Charls and Gay Lussac’s law. 3. Calculations of gas parameters using equations of state for an ideal gas. Representation of various processes on P-v diagram. 4. Calculation of work done in various thermodynamic processes. 5. Calculation of enthalpy in ...
... Applying thermodynamic properties using Boyle’s, Charls and Gay Lussac’s law. 3. Calculations of gas parameters using equations of state for an ideal gas. Representation of various processes on P-v diagram. 4. Calculation of work done in various thermodynamic processes. 5. Calculation of enthalpy in ...
Basic thermodynamics` definitions. Units and conversions.
... 2. Basic gas laws (Boyle’s, Charls, Gay Lussac). 3. Volume and the number of molecules: Avogadro's law. Ideal gas equation of state (P-V-T relation). 4. Total air conditioning applications (psychrometrics). Mollier chart 5. First Law of Thermodynamics. Energy, internal energy as a property, componen ...
... 2. Basic gas laws (Boyle’s, Charls, Gay Lussac). 3. Volume and the number of molecules: Avogadro's law. Ideal gas equation of state (P-V-T relation). 4. Total air conditioning applications (psychrometrics). Mollier chart 5. First Law of Thermodynamics. Energy, internal energy as a property, componen ...
Using the “Clicker” - Boston University: Physics
... being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temperature re-sets the engine so another cycle can begin. In a full cycle, three things happen: Heat QH is added at a relatively high temperature TH. Some of this ene ...
... being done every cycle. Two temperatures are required. The higher temperature causes the system to expand, doing work, and the lower temperature re-sets the engine so another cycle can begin. In a full cycle, three things happen: Heat QH is added at a relatively high temperature TH. Some of this ene ...