
The Second Law of Thermodynamics
... The above equation is the Clausius definition of the entropy S. The first law of thermodynamics can be now expressed as for a reversible process ...
... The above equation is the Clausius definition of the entropy S. The first law of thermodynamics can be now expressed as for a reversible process ...
12.1 Thermodynamic Systems, States, and Processes 12.3
... system must change, (b) heat must be transferred from the system, (c) the internal energy of the system must change and/or heat must be transferred from the system, (d) heat must be transferred to the system. (c) MC When heat is added to a system of ideal gas during an isothermal expansion process, ...
... system must change, (b) heat must be transferred from the system, (c) the internal energy of the system must change and/or heat must be transferred from the system, (d) heat must be transferred to the system. (c) MC When heat is added to a system of ideal gas during an isothermal expansion process, ...
Summary - Clarkson University
... C. Heat and work 1. A system can absorb heat (Q) from the surroundings. Q > 0, if heat is absorbed by the system. Q < 0, if heat is evolved from the system to the surroundings. Heat appears only at the system boundary. Heat appears only during a change of state. Strictly speaking, it is incorrect t ...
... C. Heat and work 1. A system can absorb heat (Q) from the surroundings. Q > 0, if heat is absorbed by the system. Q < 0, if heat is evolved from the system to the surroundings. Heat appears only at the system boundary. Heat appears only during a change of state. Strictly speaking, it is incorrect t ...
15-3 Constant Volume and Constant Pressure Processes
... 15-3 Constant Volume and Constant Pressure Processes Let’s consider once again two different thermodynamic processes, one in which heat is added to a system at constant volume, and the other when heat is added at constant pressure. EXPLORATION 15.3A – A constant-volume process A sample of monatomic ...
... 15-3 Constant Volume and Constant Pressure Processes Let’s consider once again two different thermodynamic processes, one in which heat is added to a system at constant volume, and the other when heat is added at constant pressure. EXPLORATION 15.3A – A constant-volume process A sample of monatomic ...
Energy & Power
... The system follows the isotherm and does work W by lifting the weight The internal energy U (which depends only on temperature for an ideal gas), does not change during this isothermal expansion ...
... The system follows the isotherm and does work W by lifting the weight The internal energy U (which depends only on temperature for an ideal gas), does not change during this isothermal expansion ...
Thermodynamic Laws/Definition of Entropy Carnot Cycle
... cP > cV because the volume expands at constant pressure and the system does work which means it stores less energy. Note that for non P V T systems analogous heat capacities can be defined. In a magnetic system, P → H and V → M and we can define cH and cM . A statistical approach can be used to obta ...
... cP > cV because the volume expands at constant pressure and the system does work which means it stores less energy. Note that for non P V T systems analogous heat capacities can be defined. In a magnetic system, P → H and V → M and we can define cH and cM . A statistical approach can be used to obta ...
Q - W
... A pressurized gas bottle (V = 0.05 m3), contains helium gas (an ideal monatomic gas) at a pressure p = 1×107 Pa and temperature T = 300 K. What is the internal thermal energy of this gas? ...
... A pressurized gas bottle (V = 0.05 m3), contains helium gas (an ideal monatomic gas) at a pressure p = 1×107 Pa and temperature T = 300 K. What is the internal thermal energy of this gas? ...
Laws of Thermodynamics - Ohio Wesleyan University
... cycle (a cycle in which system can be returned to its initial state along the same path) called the Carnot cycle – Note that a truly reversible process is an idealization, and real processes are irreversible (although some are close to being reversible) ...
... cycle (a cycle in which system can be returned to its initial state along the same path) called the Carnot cycle – Note that a truly reversible process is an idealization, and real processes are irreversible (although some are close to being reversible) ...
Fluids – Lecture 11 Notes
... Definition and implications A compressible flow is a flow in which the fluid density ρ varies significantly within the flowfield. Therefore, ρ(x, y, z) must now be treated as a field variable rather than simply a constant. Typically, significant density variations start to appear when the flow Mach number exc ...
... Definition and implications A compressible flow is a flow in which the fluid density ρ varies significantly within the flowfield. Therefore, ρ(x, y, z) must now be treated as a field variable rather than simply a constant. Typically, significant density variations start to appear when the flow Mach number exc ...
Vocabulary
... gases within the cylinders of an automobile engine is nearly adiabatic. __TRUE TRUE__ 8. What happens to a gas when it adiabatically expands and does work on its surroundings? It loses internal energy and cools down 9. Circle the letter that describes the adiabatic form of the first law of thermodyn ...
... gases within the cylinders of an automobile engine is nearly adiabatic. __TRUE TRUE__ 8. What happens to a gas when it adiabatically expands and does work on its surroundings? It loses internal energy and cools down 9. Circle the letter that describes the adiabatic form of the first law of thermodyn ...
幻灯片 1
... rises. Is this a heat or work interaction? 2. On a P-v diagram, what does the area under the process curve represent? 3. Determine the energy required to accelerate a 2000-kg car from 20 to 70 km/h on an uphill road with a vertical rise of 40m. ...
... rises. Is this a heat or work interaction? 2. On a P-v diagram, what does the area under the process curve represent? 3. Determine the energy required to accelerate a 2000-kg car from 20 to 70 km/h on an uphill road with a vertical rise of 40m. ...
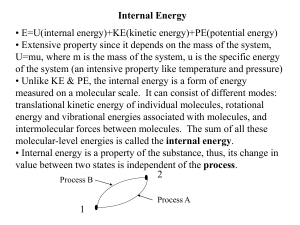











![[2013 question paper]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008881813_1-433cb609ef4aa3f6141509bf2df16e48-300x300.png)








