Summary presentation 10.2 File
... In order to distinguish between heat and work in thermodynamic processes Heat is defined as a process in which thermal energy is transferred due to a temperature difference. Work is defined as the process in which thermal energy is transferred by means that are independent of a temperature differenc ...
... In order to distinguish between heat and work in thermodynamic processes Heat is defined as a process in which thermal energy is transferred due to a temperature difference. Work is defined as the process in which thermal energy is transferred by means that are independent of a temperature differenc ...
Heat vs Temperature
... Expansion: mercury, metal, gas, alcohol Chromatic: color emitted by hot object Thermocouple: small electrical flow ...
... Expansion: mercury, metal, gas, alcohol Chromatic: color emitted by hot object Thermocouple: small electrical flow ...
IB Physics
... gas appreciate that if a system and its surroundings are at different temperatures and the system undergoes a process, the energy transferred by nonmechanical means to or from the system is referred to as thermal energy (heat). ...
... gas appreciate that if a system and its surroundings are at different temperatures and the system undergoes a process, the energy transferred by nonmechanical means to or from the system is referred to as thermal energy (heat). ...
Model Question Paper – 1
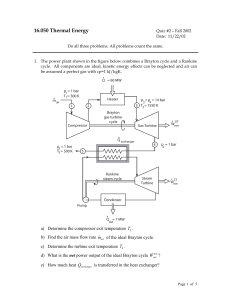
... a) If expansion is quasi-static, find heat transfer, work transfer and change in internal energy. b) In another process the same system expands according to the same P-v relation as in part (a); and between same initial and final states; but heat transfer in this case is 30 kJ. Find work transfer c) ...
... a) If expansion is quasi-static, find heat transfer, work transfer and change in internal energy. b) In another process the same system expands according to the same P-v relation as in part (a); and between same initial and final states; but heat transfer in this case is 30 kJ. Find work transfer c) ...
Topic 3
... gas appreciate that if a system and its surroundings are at different temperatures and the system undergoes a process, the energy transferred by nonmechanical means to or from the system is referred to as thermal energy (heat). ...
... gas appreciate that if a system and its surroundings are at different temperatures and the system undergoes a process, the energy transferred by nonmechanical means to or from the system is referred to as thermal energy (heat). ...
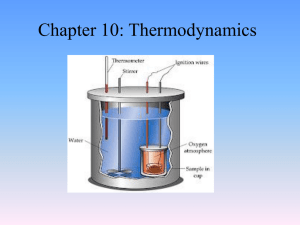
Chapter 10: Thermodynamics
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
... • Adiabatic process: a thermodynamic process during which heat energy is transferred to or from the system. ex: usually a fast process like filling a tank • Isobaric process: a process that takes place at a constant pressure. ex: heating an open pot of water ...
Mass Balance for Open System
... Define, discuss, apply and analyze internal energy, first law, energy balance-closed system, thermodynamic state and state function, equilibrium, the Phase Rule, reversible process, constant-V and constant-P processes, enthalpy and heat capacity. 3. Chapter 3: Volumetric properties of pure fluids 4. ...
... Define, discuss, apply and analyze internal energy, first law, energy balance-closed system, thermodynamic state and state function, equilibrium, the Phase Rule, reversible process, constant-V and constant-P processes, enthalpy and heat capacity. 3. Chapter 3: Volumetric properties of pure fluids 4. ...
Thermodynamics - StrikerPhysics
... by boundaries or surfaces. Boundaries need not have definite shape or volume. • Thermally Isolated System – system in which no heat is transferred into or out of the system. • Heat Reservoir – a large separate system with unlimited heat capacity (any amount of heat can be withdrawn or added without ...
... by boundaries or surfaces. Boundaries need not have definite shape or volume. • Thermally Isolated System – system in which no heat is transferred into or out of the system. • Heat Reservoir – a large separate system with unlimited heat capacity (any amount of heat can be withdrawn or added without ...
Course 2 – Mathematical Tools and Unit Conversion Used in
... Heat - the form of energy transferred from hot to cold objects It is energy in transit, not stored in the system as heat but as kinetic and potential energy of the atoms The rate of heat transfer from one body to another is proportional to the difference in temperature 1 calorie = the quantity of h ...
... Heat - the form of energy transferred from hot to cold objects It is energy in transit, not stored in the system as heat but as kinetic and potential energy of the atoms The rate of heat transfer from one body to another is proportional to the difference in temperature 1 calorie = the quantity of h ...
Phases of Pure Substance
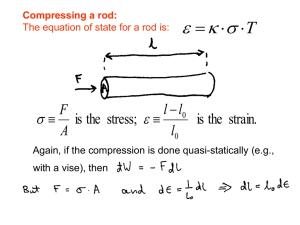
... when a fluid expands pushing a piston outwards, the work is said to be positive. i.e., Work output of the system = + W If the work is done on the system by the surroundings, e.g., when a force is applied to a rotating handle, or to a piston to compress a fluid, the work is said to be negative. i.e., ...
... when a fluid expands pushing a piston outwards, the work is said to be positive. i.e., Work output of the system = + W If the work is done on the system by the surroundings, e.g., when a force is applied to a rotating handle, or to a piston to compress a fluid, the work is said to be negative. i.e., ...