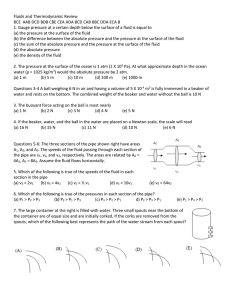
Unit 1.3 Key Terms Active Solar Energy Collection A type of system
... The unit of electric current in the meter-kilogram-second system of units. Referred to as amp and symbolized as A. The transfer of heat within an object or between objects by molecular activity, without any net external motion. Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass w ...
... The unit of electric current in the meter-kilogram-second system of units. Referred to as amp and symbolized as A. The transfer of heat within an object or between objects by molecular activity, without any net external motion. Process by which, in a fluid being heated, the warmer part of the mass w ...
Lacture №1. Chemical thermodynamics. The first law of
... The given heat for the system spents on the change of the internal energy and producing the work: Q = ▲U + W The internal energy of the system can be changed In two ways: a) By allowing heat to flow into the system or out of the system b) By work done on the system or work done by the system. ...
... The given heat for the system spents on the change of the internal energy and producing the work: Q = ▲U + W The internal energy of the system can be changed In two ways: a) By allowing heat to flow into the system or out of the system b) By work done on the system or work done by the system. ...
File - Elements of Mechanical Engineering
... Q9. A reversible engine working in a cycle takes 4500 kJ of heat from a source at 750K per minute and develops a power of 15kw. The engine rejects heat to two reservoirs at 300K and 400K. Determine the thermal efficiency and heat rejected to each sink. Q10. Two Carnot engines work in series between ...
... Q9. A reversible engine working in a cycle takes 4500 kJ of heat from a source at 750K per minute and develops a power of 15kw. The engine rejects heat to two reservoirs at 300K and 400K. Determine the thermal efficiency and heat rejected to each sink. Q10. Two Carnot engines work in series between ...
CHAPTER I
... on the system and its internal energy is increased. If the piston moves out, then dV is positive, so W is positive and the system does work on its environment and its internal energy is reduced. This is a general expression of work for a gas, it isn’t piston and cylinder specific. For example, in a ...
... on the system and its internal energy is increased. If the piston moves out, then dV is positive, so W is positive and the system does work on its environment and its internal energy is reduced. This is a general expression of work for a gas, it isn’t piston and cylinder specific. For example, in a ...
Problem Set 2 3.20 MIT Professor Gerbrand Ceder Fall 2003
... transforms of the energy. For those of you familiar with statistical mechanics you may notice that the Massieu functions are the Hamiltonians for the different ensembles. Problem 1.2 Prove that the Cp for an ideal gas is independent of pressure. Problem 1.3 For a gas whose Helmholtz free energy is g ...
... transforms of the energy. For those of you familiar with statistical mechanics you may notice that the Massieu functions are the Hamiltonians for the different ensembles. Problem 1.2 Prove that the Cp for an ideal gas is independent of pressure. Problem 1.3 For a gas whose Helmholtz free energy is g ...
New Microsoft Office Word Document
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
... Depends on the path followed from initial to final state of the system ...
PPT
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
... Joule’s Law states: “if a gas expands without doing any work, and under adiabatic conditions, the temperature of the gas remains constant.” Corollary: Molecules of an ideal gas do not exert any attractive or repulsive forces ...
Application , First, Law of Thermodynamics
... d. Show the PV diagram; the curve for which the temperature is constant is called an isotherm. e. Have real life examples of isothermal processes (e.g., phase changes). 6. Isochoric process a. A system undergoes a thermodynamic process at a constant volume with no work done during the process. b. Fo ...
... d. Show the PV diagram; the curve for which the temperature is constant is called an isotherm. e. Have real life examples of isothermal processes (e.g., phase changes). 6. Isochoric process a. A system undergoes a thermodynamic process at a constant volume with no work done during the process. b. Fo ...
lecture1424085736
... This document does not claim any originality and cannot be used as a substitute for prescribed textbooks. The information presented here is merely a collection by the committee members for their respective teaching assignments. Various sources as mentioned at the reference of the document as well as ...
... This document does not claim any originality and cannot be used as a substitute for prescribed textbooks. The information presented here is merely a collection by the committee members for their respective teaching assignments. Various sources as mentioned at the reference of the document as well as ...
Thermal Physics Tutorial
... Note: when a bubble rises from the bottom of a beer glass, the pressure experience by this bubbles decreases. Assuming there is no change in the temperature, there will be an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass ...
... Note: when a bubble rises from the bottom of a beer glass, the pressure experience by this bubbles decreases. Assuming there is no change in the temperature, there will be an increase in the volume of the bubble. However, to have its volume doubled solely due to decreases in pressure, the beer glass ...
Mechanical Engineering
... A change in the system state is called a process. When the initial and final states of a process are the same, the process is called a cycle. If a process can be run in reverse with no change in the system as well as surroundings, then the process is called a reversible process. If a process is not ...
... A change in the system state is called a process. When the initial and final states of a process are the same, the process is called a cycle. If a process can be run in reverse with no change in the system as well as surroundings, then the process is called a reversible process. If a process is not ...
Equivalence of Kelvin-Planck and Clausius statements
... gas to chamber A. The vacuum pump is then removed. • But the vacuum pump has increased the internal energy of the gas by an amount equal to the electrical work consumed by it. • Therefore, only after an equal amount of heat has to be rejected by the gas to the surroundings will the gas be restored t ...
... gas to chamber A. The vacuum pump is then removed. • But the vacuum pump has increased the internal energy of the gas by an amount equal to the electrical work consumed by it. • Therefore, only after an equal amount of heat has to be rejected by the gas to the surroundings will the gas be restored t ...
The Laws of Thermodinamics
... A state variable related to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, the entropy Let Qr be the energy absorbed or expelled during a reversible, constant temperature process between two equilibrium states. Then the change in entropy during any constant temperature process connecting the two equilibrium stat ...
... A state variable related to the Second Law of Thermodynamics, the entropy Let Qr be the energy absorbed or expelled during a reversible, constant temperature process between two equilibrium states. Then the change in entropy during any constant temperature process connecting the two equilibrium stat ...
15-2 Thermodynamic Processes and the First Law
... The process above does not violate the first law of thermodynamics and the law of conservation of energy. Since this process does not occur in nature, the second law of thermodynamics was ...
... The process above does not violate the first law of thermodynamics and the law of conservation of energy. Since this process does not occur in nature, the second law of thermodynamics was ...
Notes on the First Law of Thermodynamics Chemistry CHEM 213W
... In other words, the energy of our classical system of particles doesn’t change in time or is conserved. The same is true under the laws of quantum mechanics. What happens if, in addition to the forces acting between the particles, the particles are subjected to an external forces? The first law of t ...
... In other words, the energy of our classical system of particles doesn’t change in time or is conserved. The same is true under the laws of quantum mechanics. What happens if, in addition to the forces acting between the particles, the particles are subjected to an external forces? The first law of t ...
Thermo I
... Water with a mass of 2.0 kg is held at constant volume in a container while 10,000 J of heat is slowly added by a flame. The container is not well insulated, and as a result 2,000 J of heat leaks out to the surroundings. a) What is the increase in internal energy? b) What is the increase in temperat ...
... Water with a mass of 2.0 kg is held at constant volume in a container while 10,000 J of heat is slowly added by a flame. The container is not well insulated, and as a result 2,000 J of heat leaks out to the surroundings. a) What is the increase in internal energy? b) What is the increase in temperat ...