Energy – Where does it come from and why does it produce waste?
... rub against the wire – creating friction. This resistance creates heat and even light! • But where does this supply of electrons come from? ...
... rub against the wire – creating friction. This resistance creates heat and even light! • But where does this supply of electrons come from? ...
Chapter-18
... graphical integration. 18.20 If an enclosed gas expands 18.23 On a p-V graph of pressure or contracts, calculate the work versus volume for a gas, W done by the gas by integrating identify the algebraic sign of the gas pressure with respect to the work associated with a the volume of the enclosure. ...
... graphical integration. 18.20 If an enclosed gas expands 18.23 On a p-V graph of pressure or contracts, calculate the work versus volume for a gas, W done by the gas by integrating identify the algebraic sign of the gas pressure with respect to the work associated with a the volume of the enclosure. ...
slides - Biology Courses Server
... Energy: ability to do work, with units of joules or calories. E , internal energy. Directly related to temperature and motion of molecules. ∆E , change in internal energy. ∆E = Efinal − Estart w , work done by the surroundings on the system during a process. q, heat flowing into the system from the ...
... Energy: ability to do work, with units of joules or calories. E , internal energy. Directly related to temperature and motion of molecules. ∆E , change in internal energy. ∆E = Efinal − Estart w , work done by the surroundings on the system during a process. q, heat flowing into the system from the ...
Lecture 5 - Chemistry Courses
... Applications/Processes of Thermodynamics Adiabatic Process There is no transfer of heat to or from the system, q = 0, though other characteristics such as the pressure, volume, and temperature of the system may vary. The curve of an adiabatic process on a pV diagram depends on the ...
... Applications/Processes of Thermodynamics Adiabatic Process There is no transfer of heat to or from the system, q = 0, though other characteristics such as the pressure, volume, and temperature of the system may vary. The curve of an adiabatic process on a pV diagram depends on the ...
Science gr.6 - Nawabegh Al-Riyadh International School
... 5. how fast an object's position changes with time at any given moment ____________ 6. the ability to do work ______________ Q5. Fill in the blanks. 1. ___________________ is the chemical building block of all known living things. 2. A physical law stating that the planets, the stars, and the Sun, a ...
... 5. how fast an object's position changes with time at any given moment ____________ 6. the ability to do work ______________ Q5. Fill in the blanks. 1. ___________________ is the chemical building block of all known living things. 2. A physical law stating that the planets, the stars, and the Sun, a ...
Heat and Energy Terms Kinetic Energy: Kinetic energy is the energy
... Potential energy is stored energy due to position. Potential energy can be gravitational due to its position above a reference point and this can be calculated: Ep = mgh. Chemical potential energy due to stored energy within the molecules of substances. Nuclear potential energy held within atoms. Th ...
... Potential energy is stored energy due to position. Potential energy can be gravitational due to its position above a reference point and this can be calculated: Ep = mgh. Chemical potential energy due to stored energy within the molecules of substances. Nuclear potential energy held within atoms. Th ...
The Sun March 2 − We know the most about one star
... • One helium nucleus is produced • 0.7% of mass becomes energy Sun can potentially produce ...
... • One helium nucleus is produced • 0.7% of mass becomes energy Sun can potentially produce ...
P1 mindmap
... The Big Bang and the CMBR The early (much smaller) universe would have had a lot of energy. This energy would have produced radiation. As the universe expanded this radiation also expanded (its wavelength increased). We now observe it as microwaves filling the universe, this is called the cosmic mic ...
... The Big Bang and the CMBR The early (much smaller) universe would have had a lot of energy. This energy would have produced radiation. As the universe expanded this radiation also expanded (its wavelength increased). We now observe it as microwaves filling the universe, this is called the cosmic mic ...
variable specific heat theory
... In addition to the nature of the thermodynamic process, specific heat varies for different gases depending upon molecular atomic structure such as monatomic, diatomic, polyatomic, etc. Thus, specific heat is different for different gases for sam e heating process. Further, specific heat depends on t ...
... In addition to the nature of the thermodynamic process, specific heat varies for different gases depending upon molecular atomic structure such as monatomic, diatomic, polyatomic, etc. Thus, specific heat is different for different gases for sam e heating process. Further, specific heat depends on t ...
Discussion paper on calorific values
... According to the Energy Statistics Manual, “energy content of solid and liquid fossil fuels, and of renewables and wastes is expressed in net calorific value (NCV). Energy content of natural gas and manufactured gases is expressed in gross calorific value (GCV)”. For gases, these values are converte ...
... According to the Energy Statistics Manual, “energy content of solid and liquid fossil fuels, and of renewables and wastes is expressed in net calorific value (NCV). Energy content of natural gas and manufactured gases is expressed in gross calorific value (GCV)”. For gases, these values are converte ...
Unit II - Chemical Thermodynamics
... Zeroth law of thermodynamics discusses about the thermal equilibrium between three bodies. If two systems A and B are in thermal equilibrium with the system C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium with each other.. First law of thermodynamics: The law of conservation of energy. Energy can be neit ...
... Zeroth law of thermodynamics discusses about the thermal equilibrium between three bodies. If two systems A and B are in thermal equilibrium with the system C, then A and B are in thermal equilibrium with each other.. First law of thermodynamics: The law of conservation of energy. Energy can be neit ...
Unit 2 Thermodynamic parameters Ex.1. Read and learn new words
... An idealized thermometer is a sample of an ideal gas at constant pressure. From the ideal gas law PV=nRT, the volume of such a sample can be used as an indicator of temperature; in this manner it defines temperature. Although pressure isdefined mechanically, a pressure-measuring device, called a bar ...
... An idealized thermometer is a sample of an ideal gas at constant pressure. From the ideal gas law PV=nRT, the volume of such a sample can be used as an indicator of temperature; in this manner it defines temperature. Although pressure isdefined mechanically, a pressure-measuring device, called a bar ...
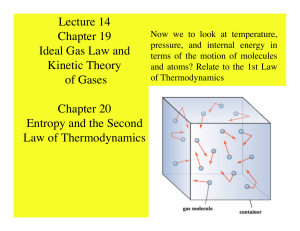
Lecture 14 Chapter 19 Ideal Gas Law and Kinetic Theory of Gases
... • They never will go back together even though energy of conservation is not violated. • Again what controls the direction? ...
... • They never will go back together even though energy of conservation is not violated. • Again what controls the direction? ...