acknowledgements
... detected by liquid crystals.Central part of the image was blocked by a mirror. Setup to make the reconstruction is shown in Fig. 5. The second example that is of interest used the ellipse of Figure 1a as the input object. A part of the DOE written by the IR laser beam is shown in Figure 6a. This par ...
... detected by liquid crystals.Central part of the image was blocked by a mirror. Setup to make the reconstruction is shown in Fig. 5. The second example that is of interest used the ellipse of Figure 1a as the input object. A part of the DOE written by the IR laser beam is shown in Figure 6a. This par ...
Direct measurement of standing evanescent waves with a photon
... collection efficiency E and the distance offset Az as fitting parameters. For the other parameters we used the values given in Section 2 and kept them fixed for the fitting procedure. There are several points that we should note here: (1) For 0 < z < 325 nm the data show an excellent fit by Eq. (3) ...
... collection efficiency E and the distance offset Az as fitting parameters. For the other parameters we used the values given in Section 2 and kept them fixed for the fitting procedure. There are several points that we should note here: (1) For 0 < z < 325 nm the data show an excellent fit by Eq. (3) ...
Optical Activity
... Optically active organic molecules have a spiral structure like a right-handed or lefthanded screw. It is this spiral nature of the molecule, which rotates the plane of polarization of light passing through it. Right-handed molecules will rotate the plane of polarization clockwise as viewed in the d ...
... Optically active organic molecules have a spiral structure like a right-handed or lefthanded screw. It is this spiral nature of the molecule, which rotates the plane of polarization of light passing through it. Right-handed molecules will rotate the plane of polarization clockwise as viewed in the d ...
Inverse scattering for frequency-scanned full-field
... within a coherence length of the focal plane produce scattered fields that will interfere with the reference. By recording the interference, an image of a slice of the sample around the focal plane is obtained, and the out-of-focus contributions are removed by coherence gating. The usual technique i ...
... within a coherence length of the focal plane produce scattered fields that will interfere with the reference. By recording the interference, an image of a slice of the sample around the focal plane is obtained, and the out-of-focus contributions are removed by coherence gating. The usual technique i ...
Chapter 25: Interference and Diffraction
... Coherent waves can become out of phase if they travel different distances to the point of observation. P ...
... Coherent waves can become out of phase if they travel different distances to the point of observation. P ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1E Instructions:
... For each question below, choose the single best response and write the corresponding capital letter in the box provided. There is no penalty for guessing the wrong answer. 1. UGA waves weren’t covered in class, but they do obey Snell’s law! They have a speed of wave propagation vA = 2097m/s in apple ...
... For each question below, choose the single best response and write the corresponding capital letter in the box provided. There is no penalty for guessing the wrong answer. 1. UGA waves weren’t covered in class, but they do obey Snell’s law! They have a speed of wave propagation vA = 2097m/s in apple ...
5.3.2 Processing Light
... Wollaston prism All those "prisms" use birefringent (or tensor) materials, typically the easy to get or make calcite CaCO3. The incoming beam splits into an ordinary and extraordinary beam that can be fully polarized. In the Nicol prism the geometry is chosen in such a way that the extraordinary bea ...
... Wollaston prism All those "prisms" use birefringent (or tensor) materials, typically the easy to get or make calcite CaCO3. The incoming beam splits into an ordinary and extraordinary beam that can be fully polarized. In the Nicol prism the geometry is chosen in such a way that the extraordinary bea ...
Joule Expansion Imaging Techniques on Microlectronic Devices
... reference and probe beams are modulated at two different frequencies and the detection is made at the frequency difference. Due to the acquisition system[17], this set-up is at present limited to displacement imaging for f frequency higher than 20 kHz. The laser probe after reflection on the sample ...
... reference and probe beams are modulated at two different frequencies and the detection is made at the frequency difference. Due to the acquisition system[17], this set-up is at present limited to displacement imaging for f frequency higher than 20 kHz. The laser probe after reflection on the sample ...
Light and Telescopes
... the area of the primary light gathering element. Since area is proportional to the square of the diameter, two telescopes of different diameters will have light gathering power that scales with D2. LGPA/ LGPB = (DA/ DB)2 Thus, for two telescopes of comparable optical quality at the same location, if ...
... the area of the primary light gathering element. Since area is proportional to the square of the diameter, two telescopes of different diameters will have light gathering power that scales with D2. LGPA/ LGPB = (DA/ DB)2 Thus, for two telescopes of comparable optical quality at the same location, if ...
Faraday Optical Rotation
... Having described optical rotation in terms of the index of refraction, we must now find a relationship between an applied magnetic field and its effect on the optical properties. Although the Faraday effect was discovered over 160 years ago, textbook explanations3, 4 of the underlying physics are no ...
... Having described optical rotation in terms of the index of refraction, we must now find a relationship between an applied magnetic field and its effect on the optical properties. Although the Faraday effect was discovered over 160 years ago, textbook explanations3, 4 of the underlying physics are no ...
LATTICE IMAGING IN TRANSMISSION ELECTRON MICROSCOPY
... and neutron techniques fail for this task, because of a non-periodic character of nanostructures. Only fast electrons are scattered sufficiently strongly with matter to provide local information at the atomic scale. One of the most commonly used high-resolution techniques in transmission electron mi ...
... and neutron techniques fail for this task, because of a non-periodic character of nanostructures. Only fast electrons are scattered sufficiently strongly with matter to provide local information at the atomic scale. One of the most commonly used high-resolution techniques in transmission electron mi ...
Chapter 4
... due to “smearing out” of the signal. • Mechanisms responsible for distortion are “modal” and “material” dispersion. Input signal ...
... due to “smearing out” of the signal. • Mechanisms responsible for distortion are “modal” and “material” dispersion. Input signal ...
How do Dichroic Filters work?
... Figure 6 shows the energy distribution from an incandescent lamp, extended beyond the visible range. Note that most of the energy (80%) is emitted in the infrared region, 12.5% in the UV range and only 6.5% are used to produce light. The dichroic lamp has an optical multi-layer coating, which reflec ...
... Figure 6 shows the energy distribution from an incandescent lamp, extended beyond the visible range. Note that most of the energy (80%) is emitted in the infrared region, 12.5% in the UV range and only 6.5% are used to produce light. The dichroic lamp has an optical multi-layer coating, which reflec ...
Reflectivity measurements of a quantum well
... range – from helium to room temperature (using the heater built in the temperature controller), liquid helium is transferred to the cryostat and cool the sample - focusing lens 3 - focuses the signal on the entrance slit of the monochromator - monochromator - spectrometer analyzing the radiation and ...
... range – from helium to room temperature (using the heater built in the temperature controller), liquid helium is transferred to the cryostat and cool the sample - focusing lens 3 - focuses the signal on the entrance slit of the monochromator - monochromator - spectrometer analyzing the radiation and ...
Chapt23_VG0
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
... Different colors are associated with light of different wavelengths. However, color is a perception, and most of that perception is based on the way our eyes and brain work. For example combinations of light with different wavelengths appear to have colors different from those of the original compo ...
... Optically active organic molecules have a spiral structure like a right-handed or lefthanded screw. It is this spiral nature of the molecule, which rotates the plane of polarization of light passing through it. Right-handed molecules will rotate the plane of polarization clockwise as viewed in the d ...
All Optical Networks
... cladding layer, which is covered by protective jacket ray of light travels through by reflecting along the interface between the two transparent mediums. ...
... cladding layer, which is covered by protective jacket ray of light travels through by reflecting along the interface between the two transparent mediums. ...
Light Scattering Spectroscopy
... Summary of LSS • LSS contrasts: • Polarization: single vs. multiple scattering • Angle: small vs. large particles • Spectrum: size and refractive index • Advantages: • Strong signal - allows use of lower cost components components. • Sensitive to important chromophores that are not fluorescent: e.g ...
... Summary of LSS • LSS contrasts: • Polarization: single vs. multiple scattering • Angle: small vs. large particles • Spectrum: size and refractive index • Advantages: • Strong signal - allows use of lower cost components components. • Sensitive to important chromophores that are not fluorescent: e.g ...
Two-dimensional control of light with light on metasurfaces
... wave relative to the metasurface. This way, any part of the structure can be illuminated by a single beam (A or B) or by both coherent waves, where the phase modulator allows tuning from constructive to destructive interference at the metasurface position; that is from enhanced to negligible light-m ...
... wave relative to the metasurface. This way, any part of the structure can be illuminated by a single beam (A or B) or by both coherent waves, where the phase modulator allows tuning from constructive to destructive interference at the metasurface position; that is from enhanced to negligible light-m ...
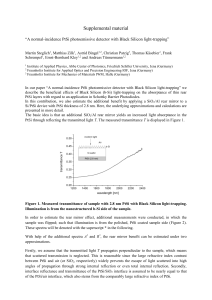
supplemental_material
... Figure 1. Measured transmittance of sample with 2.8 nm PtSi with Black Silicon light-trapping. Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination ...
... Figure 1. Measured transmittance of sample with 2.8 nm PtSi with Black Silicon light-trapping. Illumination is from the nanostructured b-Si side of the sample. In order to estimate the rear mirror effect, additional measurements were conducted, in which the sample was flipped; such that illumination ...
N. Qureshi, H. Schmidt, A. Hawkins, “Near
... In the polar magneto-optic Kerr effect, linearly polarized light impinging normal to the surface of a reflective magnetized material experiences a rotation in the plane of polarization upon reflection6. This results from the fact that the material has different refractive indices for the two circula ...
... In the polar magneto-optic Kerr effect, linearly polarized light impinging normal to the surface of a reflective magnetized material experiences a rotation in the plane of polarization upon reflection6. This results from the fact that the material has different refractive indices for the two circula ...
Parallelized STED fluorescence nanoscopy
... 25. G. Donnert, C. Eggeling, and S. W. Hell, “Major signal increase in fluorescence microscopy through dark-state relaxation,” Nat. Methods 4(1), 81–86 (2007). ...
... 25. G. Donnert, C. Eggeling, and S. W. Hell, “Major signal increase in fluorescence microscopy through dark-state relaxation,” Nat. Methods 4(1), 81–86 (2007). ...
Bright-Field Microscopy
... was coined by Giovanni Faber on April 13, 1625. The brightfield microscope is, perhaps, one of the most elegant instruments ever invented, and the first microscopists used the technologically advanced increase in the resolving power of the human eye to reveal that the workmanship of the Creator can ...
... was coined by Giovanni Faber on April 13, 1625. The brightfield microscope is, perhaps, one of the most elegant instruments ever invented, and the first microscopists used the technologically advanced increase in the resolving power of the human eye to reveal that the workmanship of the Creator can ...
1 Janaky Narayanan PC 5213 AY 2004
... stereochemistry. A molecule may be identified first by its chemical formula, then by its chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determin ...
... stereochemistry. A molecule may be identified first by its chemical formula, then by its chemical structure, and finally by its molecular structure. For example, C2H6O is the chemical formula of ethyl alcohol. CH3-CH2-OH is the chemical structure of ethyl alcohol. The molecular structure is determin ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.