You want to project a real image of an object using
... An image must be projected onto a screen from a picture slide that is 3.50 cm high. The focal length of the projector’s converging lens is 15.00 cm. The screen is placed 615 cm away from the lens. What is the height of the projected image? ...
... An image must be projected onto a screen from a picture slide that is 3.50 cm high. The focal length of the projector’s converging lens is 15.00 cm. The screen is placed 615 cm away from the lens. What is the height of the projected image? ...
Refractive Index Measurement Principle - K
... The measuring prism provides the interface between the instrument and the medium which is measured. The geometry of the optical system is such that light rays at a certain selection of angles α are projected onto the prism surface. The actual angles are chosen so that the desired refractive index ra ...
... The measuring prism provides the interface between the instrument and the medium which is measured. The geometry of the optical system is such that light rays at a certain selection of angles α are projected onto the prism surface. The actual angles are chosen so that the desired refractive index ra ...
Advantages of Holographic Optical Tweezers
... Stimulated by the work in the area of cooling atoms the first schemes of using light for trapping microscopic particles were used in the 1970s?, ? . In most of these experiments two laser beams were used to accomplish a stable trap. In 1986 Ashkin et al.? realized a single beam gradient force optica ...
... Stimulated by the work in the area of cooling atoms the first schemes of using light for trapping microscopic particles were used in the 1970s?, ? . In most of these experiments two laser beams were used to accomplish a stable trap. In 1986 Ashkin et al.? realized a single beam gradient force optica ...
A History of Imaging
... the British Royal Society to support a similar British effort on glass. British support of Faraday led to further improvements in glass homogeneity. However, Faraday did little to advance the link between glass composition and its optical properties. Instead, advances in glass chemistry were conducte ...
... the British Royal Society to support a similar British effort on glass. British support of Faraday led to further improvements in glass homogeneity. However, Faraday did little to advance the link between glass composition and its optical properties. Instead, advances in glass chemistry were conducte ...
Physical Optics - Old Mill High School
... the soap bubble in the figure, have a multicolored appearance that often changes while you are watching them. Why are such films multicolored and why do they change with time? ...
... the soap bubble in the figure, have a multicolored appearance that often changes while you are watching them. Why are such films multicolored and why do they change with time? ...
Lab
... appear to be moving in a circle as it approached you. If while looking at the source, the electric vector of the light coming toward you appears to be rotating clockwise, the light is said to be right-circularly polarized. If counterclockwise, then left-circularly polarized light. The electric field ...
... appear to be moving in a circle as it approached you. If while looking at the source, the electric vector of the light coming toward you appears to be rotating clockwise, the light is said to be right-circularly polarized. If counterclockwise, then left-circularly polarized light. The electric field ...
Properties of a 4Pi confocal fluorescence microscope
... observed from one side (Fig. 1). The objective lens transforms the illumination wave front into a segment of a spherical wave front. For technical reasons, the maximum aperture of an oil immersion lens is 1.4, i.e., the aperture angle is below 2 X 68° = 136°o3,4 This fact leads to a geometry for the ...
... observed from one side (Fig. 1). The objective lens transforms the illumination wave front into a segment of a spherical wave front. For technical reasons, the maximum aperture of an oil immersion lens is 1.4, i.e., the aperture angle is below 2 X 68° = 136°o3,4 This fact leads to a geometry for the ...
What is Light?
... Use of a photopic correction filter is important when measuring the perceived brightness of a source to a human. The filter weights incoming light in proportion to the effect it would produce in the human eye. Regardless of the color or spectral distribution of the source, the photopic detector can ...
... Use of a photopic correction filter is important when measuring the perceived brightness of a source to a human. The filter weights incoming light in proportion to the effect it would produce in the human eye. Regardless of the color or spectral distribution of the source, the photopic detector can ...
Supplementary Information (doc 4223K)
... to achieve large optical nonlinearity to reduce the pump power for ultrafast optical tunability. Gold triangles have stronger surface plasmon polariton resonances according to our previous work (see Cuicui Lu, et al. Plasmonics, 7, 159 (2011)). Thirdly, it is flexible to use triangle dimer to achiev ...
... to achieve large optical nonlinearity to reduce the pump power for ultrafast optical tunability. Gold triangles have stronger surface plasmon polariton resonances according to our previous work (see Cuicui Lu, et al. Plasmonics, 7, 159 (2011)). Thirdly, it is flexible to use triangle dimer to achiev ...
Physics 1252 Sec.B Exam #1D Instructions:
... A. will not undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will not undergo tota ...
... A. will not undergo total internal reflection if incident from below the interface with an angle of incidence of 8.5o . B. will have an angle of refraction greater than the angle of incidence if the beam is incident from above the interface without total internal reflection. C. will not undergo tota ...
Physics116_L22
... What is the angular separation between the refracted red and refracted blue beams while they are in the glass? (The respective indices of refraction for the blue light and the red light are 1.4636 and ...
... What is the angular separation between the refracted red and refracted blue beams while they are in the glass? (The respective indices of refraction for the blue light and the red light are 1.4636 and ...
P5.3.2.3 - LD Didactic
... According to the common principle which characterizes these experiments, wave-optical methods − such as reflection, refraction, blocking and beam spitting − allow the creation of two interfering light bundles from the light emitted by a source. Therefore this method of superimposing light is called ...
... According to the common principle which characterizes these experiments, wave-optical methods − such as reflection, refraction, blocking and beam spitting − allow the creation of two interfering light bundles from the light emitted by a source. Therefore this method of superimposing light is called ...
Notebook and Assignment Guidelines
... In this part of the lab, you will test your equation by using it to calculate the wavelength of a laser light shining through small slits. The directions for this section of the lab will need to be followed exactly in order to prevent injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to ask your teacher if ...
... In this part of the lab, you will test your equation by using it to calculate the wavelength of a laser light shining through small slits. The directions for this section of the lab will need to be followed exactly in order to prevent injury or damage to the equipment. Be sure to ask your teacher if ...
Stellar Activity with SONG
... With a dispersive element, the angle at which the light leaves it, is wavelength dependent. ...
... With a dispersive element, the angle at which the light leaves it, is wavelength dependent. ...
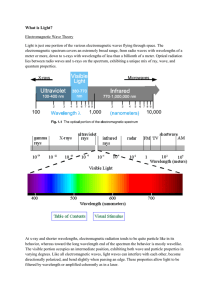
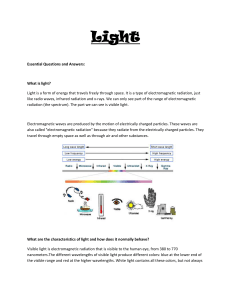
Essential Questions and Answers: What is light? Light is a form of
... Visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, from 380 to 770 nanometers.The different wavelengths of visible light produce different colors: blue at the lower end of the visible range and red at the higher wavelengths. White light contains all these colors, but not al ...
... Visible light is electromagnetic radiation that is visible to the human eye, from 380 to 770 nanometers.The different wavelengths of visible light produce different colors: blue at the lower end of the visible range and red at the higher wavelengths. White light contains all these colors, but not al ...
Supplementary Material for
... Fig. S1 Examples of CCD image of the fringe patterns for single slides. Thinner fringes with uniform spacing are present in all images as a result of interference within the CCD assembly. Measuring the spacing of the thicker fringes, a, yields the wedge angle between the two faces of each slides, wh ...
... Fig. S1 Examples of CCD image of the fringe patterns for single slides. Thinner fringes with uniform spacing are present in all images as a result of interference within the CCD assembly. Measuring the spacing of the thicker fringes, a, yields the wedge angle between the two faces of each slides, wh ...
de Sénarmont Bias Retardation in DIC Microscopy Introduction
... Living cells and other transparent, unstained specimens are often difficult to observe under traditional brightfield illumination using the full aperture and resolution of the microscope objective and condenser system (1, 2). Phase contrast, first developed by Frits Zernike in the 1930s, is often em ...
... Living cells and other transparent, unstained specimens are often difficult to observe under traditional brightfield illumination using the full aperture and resolution of the microscope objective and condenser system (1, 2). Phase contrast, first developed by Frits Zernike in the 1930s, is often em ...
Resolution [from the New Merriam-Webster Dictionary, 1989 ed.]: 3 resolve
... – NO: difficulty increases gradually as feature size shrinks, and difficulty is noise dependent • Apodization can be used to beat the resolution limit imposed by the numerical aperture – NO: watch sidelobe growth and power efficiency loss • The resolution of my camera is N×M pixels – NO: the ma ...
... – NO: difficulty increases gradually as feature size shrinks, and difficulty is noise dependent • Apodization can be used to beat the resolution limit imposed by the numerical aperture – NO: watch sidelobe growth and power efficiency loss • The resolution of my camera is N×M pixels – NO: the ma ...
Confocal optical microscopy
... Contributions from these fields are well worth the attention of the student. 1.2.1. Components. Figure 3 shows the basic components of a microscope. This thin lens schematic shows the two optical systems that reside in any instrument. One system is the set of planes conjugate to the object, and ther ...
... Contributions from these fields are well worth the attention of the student. 1.2.1. Components. Figure 3 shows the basic components of a microscope. This thin lens schematic shows the two optical systems that reside in any instrument. One system is the set of planes conjugate to the object, and ther ...
Lenses: Bending Light
... converge). The rays of light refract as they move between the air and the lens - the shape of the convex causes the rays to converge at one point called the focal point.The distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called the focal length. Images are formed by placing objects at ...
... converge). The rays of light refract as they move between the air and the lens - the shape of the convex causes the rays to converge at one point called the focal point.The distance between the focal point and the centre of the lens is called the focal length. Images are formed by placing objects at ...
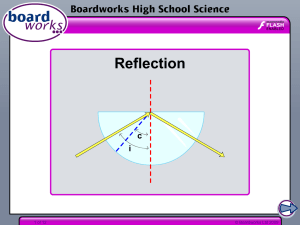
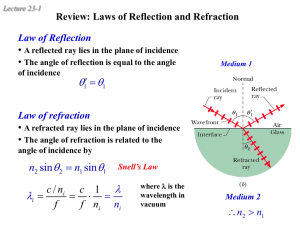
law of reflection
... There are two conditions for total internal reflection: 1. The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. 2. The light must be passing from a high refractive index to a low one. Sometimes only part of a light ray will be reflected, while the rest crosses the boundary and is refracte ...
... There are two conditions for total internal reflection: 1. The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle. 2. The light must be passing from a high refractive index to a low one. Sometimes only part of a light ray will be reflected, while the rest crosses the boundary and is refracte ...
Guided Discovery and Lesson Notes on Mirrors and Applications
... 3. Point C is the center of curvature of the mirror (all points on the surface of the mirror are a distance r from this point). 4. The point F is the focal point of the mirror. Any ray traveling close to & parallel to the principal axis will be reflected through F. F is mid-way between C & A. 5. The ...
... 3. Point C is the center of curvature of the mirror (all points on the surface of the mirror are a distance r from this point). 4. The point F is the focal point of the mirror. Any ray traveling close to & parallel to the principal axis will be reflected through F. F is mid-way between C & A. 5. The ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.












![Resolution [from the New Merriam-Webster Dictionary, 1989 ed.]: 3 resolve](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008540150_1-c5b41598686a834a8b54abcabe9102c4-300x300.png)