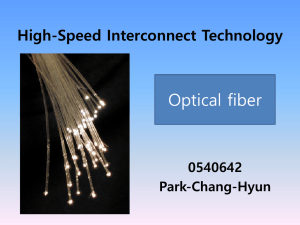
Introduction
... length illuminated uniformly with collimated light. The f-number defines the angle of the cone of light leaving the lens which ultimately forms the image. This is an important concept when the throughput or light-gathering power of an optical system is critical, such as when focusing light into a mo ...
... length illuminated uniformly with collimated light. The f-number defines the angle of the cone of light leaving the lens which ultimately forms the image. This is an important concept when the throughput or light-gathering power of an optical system is critical, such as when focusing light into a mo ...
INTRODUCTION
... The choice of wavelength depends upon the loss profile of the medium. For optical fiber the wavelength has to be 1300nm or 1550nm for low loss. The spectral width has direct bearing on the data rate which the medium can support. Larger the spectral width, smaller is the data rate. A semiconductor la ...
... The choice of wavelength depends upon the loss profile of the medium. For optical fiber the wavelength has to be 1300nm or 1550nm for low loss. The spectral width has direct bearing on the data rate which the medium can support. Larger the spectral width, smaller is the data rate. A semiconductor la ...
Interference effects Thin film interference Phase
... A cd is made out of a plastic with a refractive index of 1.55. If the cd is scanned with a laser with a wavelength of 780 nm how high should the pits on the surface be for destructive interference. d ...
... A cd is made out of a plastic with a refractive index of 1.55. If the cd is scanned with a laser with a wavelength of 780 nm how high should the pits on the surface be for destructive interference. d ...
IO.5 Elliptically Polarized Light - FSU
... For crystals cut as indicated, the two beams will follow the same path inside the crystal, but one will travel with greater speed than the other, hence, when they emerge from the crystal, one will be ahead of the other in phase, and the motion of the end of the resultant electric vector will be elli ...
... For crystals cut as indicated, the two beams will follow the same path inside the crystal, but one will travel with greater speed than the other, hence, when they emerge from the crystal, one will be ahead of the other in phase, and the motion of the end of the resultant electric vector will be elli ...
Chapter 3
... Figure 3.1 A summary of the general laboratory techniques carried out by microbiologists. It is not necessary to perform all the steps shown or to perform them exactly in this order, but all microbiologists participate in at least some of these activities. In some cases, one may proceed right from t ...
... Figure 3.1 A summary of the general laboratory techniques carried out by microbiologists. It is not necessary to perform all the steps shown or to perform them exactly in this order, but all microbiologists participate in at least some of these activities. In some cases, one may proceed right from t ...
Optical Low-pass Filter
... As shown in the figure below, wavelength plates are used mainly for picking up optical information files (DVD, etc) to prevent the back-talk noise of laser beams. ...
... As shown in the figure below, wavelength plates are used mainly for picking up optical information files (DVD, etc) to prevent the back-talk noise of laser beams. ...
Nomarski differential interference-contrast microscopy
... cemented surface of th is prism. (For greater clarity, one of the prism segments is dotted) . If the center plane of the Wollaston prism lies in the iamp-side focal plane of the condenser, the two beams will travel along parallel path s, slightly separated laterally in relati on to each other, after ...
... cemented surface of th is prism. (For greater clarity, one of the prism segments is dotted) . If the center plane of the Wollaston prism lies in the iamp-side focal plane of the condenser, the two beams will travel along parallel path s, slightly separated laterally in relati on to each other, after ...
PDF
... can bind, thus “recognizing” and “detecting” it 关11兴. The problem is to amplify this highly selective binding. We propose to use the LCLC medium with the dissolved antibody that targets the microbe of interest, say, anthrax. When the microbes are present, the antigen-antibody binding causes their ag ...
... can bind, thus “recognizing” and “detecting” it 关11兴. The problem is to amplify this highly selective binding. We propose to use the LCLC medium with the dissolved antibody that targets the microbe of interest, say, anthrax. When the microbes are present, the antigen-antibody binding causes their ag ...
Imaging
... Each CCD is divided into many groups of electrodes called pixels. The exact number of pixels depends on the individual pixel size and the cost of the array. Typically, a low-cost commercial array has dimensions of 600 x 300 pixels, while high cost arrays for scientific applications have dimensions c ...
... Each CCD is divided into many groups of electrodes called pixels. The exact number of pixels depends on the individual pixel size and the cost of the array. Typically, a low-cost commercial array has dimensions of 600 x 300 pixels, while high cost arrays for scientific applications have dimensions c ...
Opto-acoustic Imaging
... laser and ultrasound necessitates new imaging technologies that may provide information related to both the optical and the acoustical properties of the human body. Although several optical methods have been combined with ultrasound, we will concentrate specifically on the application of laser optic ...
... laser and ultrasound necessitates new imaging technologies that may provide information related to both the optical and the acoustical properties of the human body. Although several optical methods have been combined with ultrasound, we will concentrate specifically on the application of laser optic ...
Single camera spectral domain polarization
... technique that can acquire high resolution depth-resolved images in highly scattering tissue specimen. Polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PSOCT) [3–5] enables polarization-dependent detection in OCT and can provide additional imaging contrast such as retardance and fast-axis orient ...
... technique that can acquire high resolution depth-resolved images in highly scattering tissue specimen. Polarization-sensitive optical coherence tomography (PSOCT) [3–5] enables polarization-dependent detection in OCT and can provide additional imaging contrast such as retardance and fast-axis orient ...
Lecture 1/ Chapter 1/ Measurements
... 2) Huygens’ principle 3) Young’s Interference Experiment: Double slit Announcements: - HW 8 due today - HW 9 given out In chapter 34, we considered the propagation of light along a straight path Ray Optics”. However we learned in chapter 33, that light is an electromagnetic wave. This means that i ...
... 2) Huygens’ principle 3) Young’s Interference Experiment: Double slit Announcements: - HW 8 due today - HW 9 given out In chapter 34, we considered the propagation of light along a straight path Ray Optics”. However we learned in chapter 33, that light is an electromagnetic wave. This means that i ...
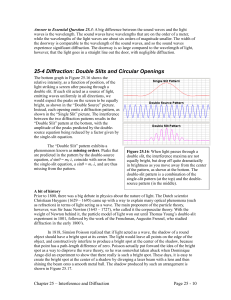
25-4 Diffraction: Double Slits and Circular Openings
... Figure 25.17: The bright spot at the center of the shadow of a ball bearing, demonstrating that light acts as a wave. Photo credit: A. Duffy. Diffraction by a circular opening A related and common phenomenon is diffraction by a circular opening (commonly called a circular aperture), such as the one ...
... Figure 25.17: The bright spot at the center of the shadow of a ball bearing, demonstrating that light acts as a wave. Photo credit: A. Duffy. Diffraction by a circular opening A related and common phenomenon is diffraction by a circular opening (commonly called a circular aperture), such as the one ...
TAPERED OPTICAL FIBER PLATFORM FOR HIGH SENSITIVITY
... University of Dayton Abstract Sparse aperture image synthesis requires proper phasing between sub-apertures. Phasing can be difficult due to hardware misalignments, atmospheric turbulence, and many other causes of optical path differences (OPD). Common synthesis techniques include incoherent and coh ...
... University of Dayton Abstract Sparse aperture image synthesis requires proper phasing between sub-apertures. Phasing can be difficult due to hardware misalignments, atmospheric turbulence, and many other causes of optical path differences (OPD). Common synthesis techniques include incoherent and coh ...
Presentation
... • Material loss, Metal loading loss, Substrate loss • Channel wall-roughness loss, Epi/substrate interface loss • The loss that occurs when the index difference is not large enough to confine the NA of the input beam completely or when the proportions of rib do not produce good mode confinement • Th ...
... • Material loss, Metal loading loss, Substrate loss • Channel wall-roughness loss, Epi/substrate interface loss • The loss that occurs when the index difference is not large enough to confine the NA of the input beam completely or when the proportions of rib do not produce good mode confinement • Th ...
Statistical Optics. Second Edition. Wiley Series in Pure and Applied... Brochure
... - An expansion of the chapter on imaging with partially coherent light, including several new examples - An expanded section on speckle and its properties - New sections on the cross–spectrum and bispectrum techniques for obtaining images free from atmospheric distortions - A new section on imaging ...
... - An expansion of the chapter on imaging with partially coherent light, including several new examples - An expanded section on speckle and its properties - New sections on the cross–spectrum and bispectrum techniques for obtaining images free from atmospheric distortions - A new section on imaging ...
mirrors and lenses - Appoquinimink High School
... As light passes from one material to another where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
... As light passes from one material to another where the index of refraction is less (water into air for example), the light bends away from the normal. At a particular incident angle, the angle of refraction will be 90 degrees. This is called the critical angle. ...
The `IEC` LASERVIEW – kit of shapes
... run along parallel to the rear face of the block and then it will not exit the block at all and it will be fully internally reflected. At this point, it has reached the ‘critical angle’. There is always a very small amount of light lost when it ‘zig zags’ at the sharp corners of a rectangular shaped ...
... run along parallel to the rear face of the block and then it will not exit the block at all and it will be fully internally reflected. At this point, it has reached the ‘critical angle’. There is always a very small amount of light lost when it ‘zig zags’ at the sharp corners of a rectangular shaped ...
The Focal Length of a Thin Converging Lens
... The ability of a lens to focus light is a consequence of its shape and optical density relative to that of the surrounding environment. For example, a thin converging lens, typically made from some type of glass, is fabricated into the shape of two spherical caps of relatively small curvature with t ...
... The ability of a lens to focus light is a consequence of its shape and optical density relative to that of the surrounding environment. For example, a thin converging lens, typically made from some type of glass, is fabricated into the shape of two spherical caps of relatively small curvature with t ...
Introduction to light 2
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
... Dispersion and Refractive Index For the normal dispersion of the refractive indices, the index of refraction decreases with increasing wavelength. To describe the dispersion of a particular material it is necessary to report the index of refraction at several wavelengths. By convention indices of r ...
Chapter 3: Telescopes
... • X rays can be focused, but very differently than visible light. • Gamma rays can be detected but not imaged. ...
... • X rays can be focused, but very differently than visible light. • Gamma rays can be detected but not imaged. ...
LASERPULSE™ LIGHT ARM FOR PIV MODEL 610015
... applications, the YAG laser beam is delivered through TSI light sheet generation optics attached to the arm exit. The lens system included with the arm offers a choice of several laser sheet divergence angles and light sheet thicknesses. ...
... applications, the YAG laser beam is delivered through TSI light sheet generation optics attached to the arm exit. The lens system included with the arm offers a choice of several laser sheet divergence angles and light sheet thicknesses. ...
Jens Prescher, Establishment and Optimization of Super
... Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with a resolution up to 3 nm, X-ray tomography (5 nm) or Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) (0.1 nm). However, optical microscopy holds significant advantages compared to these other methods, so that this slight loss on resolution is acceptable. Not only can it ...
... Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) with a resolution up to 3 nm, X-ray tomography (5 nm) or Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) (0.1 nm). However, optical microscopy holds significant advantages compared to these other methods, so that this slight loss on resolution is acceptable. Not only can it ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.