Optical Maser Action of Nd^{+3} in a Barium Crown Glass
... density of approximately 3 and a nominal index of refraction of 1.54. Because of the 4f' electron configuration is well shielded in Nd+', the term values are virtually the same as one would find in a crystal or the free ion. The energy level diagram is easily identified by reference to the spectrum ...
... density of approximately 3 and a nominal index of refraction of 1.54. Because of the 4f' electron configuration is well shielded in Nd+', the term values are virtually the same as one would find in a crystal or the free ion. The energy level diagram is easily identified by reference to the spectrum ...
Experiment 1: Fraunhofer Diffraction of Light by a Single Slit
... 2. Light intensity detection by a CCD detector As shown in Fig. 3, the measuring system includes laser, analyzing slit, CCD detecting set and oscilloscope, etc. The CCD detecting set consists of a pair of polarizers, CCD detector, driving circuit, signal processing unit and power supply. The polariz ...
... 2. Light intensity detection by a CCD detector As shown in Fig. 3, the measuring system includes laser, analyzing slit, CCD detecting set and oscilloscope, etc. The CCD detecting set consists of a pair of polarizers, CCD detector, driving circuit, signal processing unit and power supply. The polariz ...
Dual-color total internal reflection fluorescence cross
... significantly improved selectivity and applicability.8 FCCS institutes two differently colored labels and realizes the distinction between coinciding and separated occurrence of these labels. It thus introduces a useful tool to monitor various biological assays including molecular binding between tw ...
... significantly improved selectivity and applicability.8 FCCS institutes two differently colored labels and realizes the distinction between coinciding and separated occurrence of these labels. It thus introduces a useful tool to monitor various biological assays including molecular binding between tw ...
Wales Research and Diagnostic Positron Emission Tomography
... base with interchangeable apertures – incl’ multiple pinhole apertures proprietary reconstruction software better resolution than the size of the pinholes high sensitivity; significant reduction in acquisition time or delivered dose. two focal lengths, accommodating multiple fields of view ...
... base with interchangeable apertures – incl’ multiple pinhole apertures proprietary reconstruction software better resolution than the size of the pinholes high sensitivity; significant reduction in acquisition time or delivered dose. two focal lengths, accommodating multiple fields of view ...
Problem 2
... and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are positive, and refraction phenomenon meeting Snell’s law occurs when light from air strikes obliquely on the surface of such kind of substances. In ...
... and relative permeability ( r ). For conventional materials like water or glass, which are usually optically transparent, both of their r and r are positive, and refraction phenomenon meeting Snell’s law occurs when light from air strikes obliquely on the surface of such kind of substances. In ...
4F system 4F system with defocused input 4F system with defocused
... – Inverse transfer function will multiply the FT of the noise as well as the FT of the original signal ...
... – Inverse transfer function will multiply the FT of the noise as well as the FT of the original signal ...
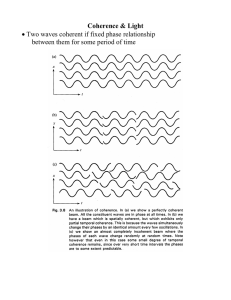
Week 9 Wed. (Lesson 15) Coherence and Optical Tomography
... • Coherence appear in two ways Spatial Coherence • Waves in phase in time, but at different points in space • Required for interference and diffraction • Before lasers need to place slits far from source or pass light through slit so only part of source seen Temporal Coherence • Correlation of phase ...
... • Coherence appear in two ways Spatial Coherence • Waves in phase in time, but at different points in space • Required for interference and diffraction • Before lasers need to place slits far from source or pass light through slit so only part of source seen Temporal Coherence • Correlation of phase ...
Geometric limits to geometric optical imaging with infinite, planar
... Optical instruments are traditionally designed to work in air or at least with an isotropic medium at either end (the oil immersion microscope is an example of the latter, but not the former), and such that a non-pathological (specifically continuous and differentiable “almost everywhere”) incident ...
... Optical instruments are traditionally designed to work in air or at least with an isotropic medium at either end (the oil immersion microscope is an example of the latter, but not the former), and such that a non-pathological (specifically continuous and differentiable “almost everywhere”) incident ...
Integration of a semiconductor laser source on silicon
... because it is only a couple of hundred nanometers thick, making it compatible with established IBM technology which allows only a thickness of 400 nm for the laser to be integrated within. ...
... because it is only a couple of hundred nanometers thick, making it compatible with established IBM technology which allows only a thickness of 400 nm for the laser to be integrated within. ...
microscope instructions ppt
... specimen using the normal fine focus on the side of the scope. Now close the right eye, and focus the other eye using the ocular focus (not the normal focus). The scope should now be set for you eyes. Look at the focus setting for that ocular (- to +) and remember it. You can always set it there whe ...
... specimen using the normal fine focus on the side of the scope. Now close the right eye, and focus the other eye using the ocular focus (not the normal focus). The scope should now be set for you eyes. Look at the focus setting for that ocular (- to +) and remember it. You can always set it there whe ...
EVERYDAY ENGINEERING EXAMPLES FOR SIMPLE CONCEPTS
... reflected. We can see objects through translucent materials but because some of the light is scattered or absorbed we cannot see them clearly. iii) Opaque materials, such as cardboard or wood, scatter, absorb or reflect most light and transmit almost no light. Thus, we cannot see through them. The l ...
... reflected. We can see objects through translucent materials but because some of the light is scattered or absorbed we cannot see them clearly. iii) Opaque materials, such as cardboard or wood, scatter, absorb or reflect most light and transmit almost no light. Thus, we cannot see through them. The l ...
Quasi Light Fields: A Model of Coherent Image Formation
... The light field represents radiance as a function of position and direction, thereby decomposing optical power flow along rays. The light field is an important tool in incoherent imaging applications, where it is used to dynamically generate different viewpoints for computer graphics rendering, comp ...
... The light field represents radiance as a function of position and direction, thereby decomposing optical power flow along rays. The light field is an important tool in incoherent imaging applications, where it is used to dynamically generate different viewpoints for computer graphics rendering, comp ...
Investigation of nanoscale structural alterations of cell nucleus as an
... On the other hand, the nanoscale structural properties, also referred to as “nano-morphology”, show the potential to become a new class of morphological markers for earlier and more accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis. It is well recognized that cancer is a complex disease involving early change ...
... On the other hand, the nanoscale structural properties, also referred to as “nano-morphology”, show the potential to become a new class of morphological markers for earlier and more accurate cancer diagnosis and prognosis. It is well recognized that cancer is a complex disease involving early change ...
Chapter 8 Wave Optics
... The results are involved in interferences and diffractions. It is known that for the interference of the double-slit, the fringes are equally bright. But when we consider the diffraction by a slit, the final pattern actually observed is a combination of both effects. The interference pattern locates ...
... The results are involved in interferences and diffractions. It is known that for the interference of the double-slit, the fringes are equally bright. But when we consider the diffraction by a slit, the final pattern actually observed is a combination of both effects. The interference pattern locates ...
AP Physics Ch 24 : Physical Optics
... In the formula we will use, there is a variable, “n”, that is a count of how many bright fringes you are away from the central fringe. o The central fringe is n = 0. o The fringe to either side of the central fringe has an order of n = 1 (the first order fringe). o The order of the next fringe out o ...
... In the formula we will use, there is a variable, “n”, that is a count of how many bright fringes you are away from the central fringe. o The central fringe is n = 0. o The fringe to either side of the central fringe has an order of n = 1 (the first order fringe). o The order of the next fringe out o ...
12. Infrared and Visible Waves
... When a light ray hits the boundary between two materials of different densities (e.g. glass and air), the ray is normally bent or refracted. This occurs because the speed of light changes in different materials. ...
... When a light ray hits the boundary between two materials of different densities (e.g. glass and air), the ray is normally bent or refracted. This occurs because the speed of light changes in different materials. ...
Three-Dimensional Mapping of Near-Field Interactions via Single-Photon Tomography Benjamin D. Mangum,
... and detected by an APD (Perkin-Elmer). The laser focus is aligned onto an AFM probe; when the excitation polarization is longitudinal, an enhancement in the optical intensity is expected at the tip apex due to a nonresonant lightning-rod effect (i.e., far from any plasmon resonance). Topographical a ...
... and detected by an APD (Perkin-Elmer). The laser focus is aligned onto an AFM probe; when the excitation polarization is longitudinal, an enhancement in the optical intensity is expected at the tip apex due to a nonresonant lightning-rod effect (i.e., far from any plasmon resonance). Topographical a ...
Study the Effect of the Sugar Solutions on the Rotation of the
... It is the rotation of linearly polarized light as it travels through materials. It appears in solutions of chiral molecules such as sucrose (sugar), solid with rotated crystal planes such as quartz, and spin-polarized gases of atoms or molecules. Chirality is the property of an object of being non-s ...
... It is the rotation of linearly polarized light as it travels through materials. It appears in solutions of chiral molecules such as sucrose (sugar), solid with rotated crystal planes such as quartz, and spin-polarized gases of atoms or molecules. Chirality is the property of an object of being non-s ...
Lecture 2
... What is a Microscope? A microscope is an instrument designed to make fine details visible. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: 1. To produce a magnified image of the specimen (magnification). 2. To separate the details in the image (resolution). 3. To render the details visible to the eye, ...
... What is a Microscope? A microscope is an instrument designed to make fine details visible. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: 1. To produce a magnified image of the specimen (magnification). 2. To separate the details in the image (resolution). 3. To render the details visible to the eye, ...
Modeling, Simulation and Application of the Probe Beam Deflection
... • PBDT is implemented by focusing probe beams through an enclosure filled with a propagation medium. As an acoustic wave travels through the medium the refractive index is changed relative to the pressure gradient produced by the wave. The probe beam deflects and refracts as it interacts with the re ...
... • PBDT is implemented by focusing probe beams through an enclosure filled with a propagation medium. As an acoustic wave travels through the medium the refractive index is changed relative to the pressure gradient produced by the wave. The probe beam deflects and refracts as it interacts with the re ...
Visualizing Bacterial Cell Walls and Biofilms
... and its astounding ability to interact with and configure molecular ingredients. However, advances in cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryoTEM) are helping to overcome this difficulty because they allow investigators to examine native, hydrated structures in bacteria and their associated biofi ...
... and its astounding ability to interact with and configure molecular ingredients. However, advances in cryo-transmission electron microscopy (cryoTEM) are helping to overcome this difficulty because they allow investigators to examine native, hydrated structures in bacteria and their associated biofi ...
d - Madison Public Schools
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
... Although principal rays help guide us to locate the image, we cannot forget the important fact that each point on the object emits rays in all directions. The lens is completely filled with rays from every point of the object! ...
Polarization microscopy with the LC-PolScope
... was dominated by techniques such as phase contrast, differential interference contrast and polarized light microscopy which do not require the introduction of exogenous dyes or markers. Fluorescence microscopy, on the other hand, often required the killing and fixation of cells and then labeling the ...
... was dominated by techniques such as phase contrast, differential interference contrast and polarized light microscopy which do not require the introduction of exogenous dyes or markers. Fluorescence microscopy, on the other hand, often required the killing and fixation of cells and then labeling the ...
Telescopes
... the area of the primary light gathering element. Since area is proportional to the square of the diameter, two telescopes of different diameters will have light gathering power that scales with D2. LGPA/ LGPB = (DA/ DB)2 Thus, for two telescopes of comparable optical quality at the same location, if ...
... the area of the primary light gathering element. Since area is proportional to the square of the diameter, two telescopes of different diameters will have light gathering power that scales with D2. LGPA/ LGPB = (DA/ DB)2 Thus, for two telescopes of comparable optical quality at the same location, if ...
Microscopy

Microscopy is the technical field of using microscopes to view objects and areas of objects that cannot be seen with the naked eye (objects that are not within the resolution range of the normal eye). There are three well-known branches of microscopy: optical, electron, and scanning probe microscopy.Optical and electron microscopy involve the diffraction, reflection, or refraction of electromagnetic radiation/electron beams interacting with the specimen, and the collection of the scattered radiation or another signal in order to create an image. This process may be carried out by wide-field irradiation of the sample (for example standard light microscopy and transmission electron microscopy) or by scanning of a fine beam over the sample (for example confocal laser scanning microscopy and scanning electron microscopy). Scanning probe microscopy involves the interaction of a scanning probe with the surface of the object of interest. The development of microscopy revolutionized biology and remains an essential technique in the life and physical sciences.