Understanding wing lift
... flow follows the shape of the surface. Thus the geometry of the aerofoil profile together with the friction force and Coanda effect are the primary causes of the streamline velocity distribution around an aerofoil. At the lower surface, the wing has initially a short convex profile that becomes conc ...
... flow follows the shape of the surface. Thus the geometry of the aerofoil profile together with the friction force and Coanda effect are the primary causes of the streamline velocity distribution around an aerofoil. At the lower surface, the wing has initially a short convex profile that becomes conc ...
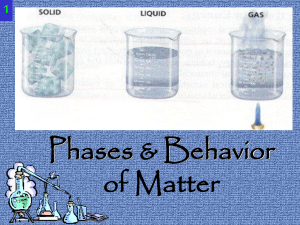
Phases and Behavior of Matter ppt
... • His most important work considered the basic properties of fluid flow, pressure, density and velocity, and gave the Bernoulli principle. ...
... • His most important work considered the basic properties of fluid flow, pressure, density and velocity, and gave the Bernoulli principle. ...
Impact of Wind Generation on ERCOT Operations
... South have large oscillations and trip during disturbances which degrade system reliability and lead to firm load shed or islanding. • “Why” do we need to concern system oscillation? – Many static exciters in system are designed to help voltage regulation, but also induce “undesired” negative dampin ...
... South have large oscillations and trip during disturbances which degrade system reliability and lead to firm load shed or islanding. • “Why” do we need to concern system oscillation? – Many static exciters in system are designed to help voltage regulation, but also induce “undesired” negative dampin ...
Stylolite formation process: Surface Roughness
... The cross over scale L∗ = γE/(βp0σs) is function of the pressure during formation, through p0 and σs. Determining the cross over L∗ at lab allows to determine such stress value during formation, and consequently depth of the rock during stylolite formation. Assuming as an order of magnitude p0 ∼ σs ...
... The cross over scale L∗ = γE/(βp0σs) is function of the pressure during formation, through p0 and σs. Determining the cross over L∗ at lab allows to determine such stress value during formation, and consequently depth of the rock during stylolite formation. Assuming as an order of magnitude p0 ∼ σs ...
Chapter 11 in Review - Garnet Valley School District
... Pressure = Area Units should have two parts, the force slash area ex. N/cm2 , N/m2 (or Pa), lb/in2 (or psi) ...
... Pressure = Area Units should have two parts, the force slash area ex. N/cm2 , N/m2 (or Pa), lb/in2 (or psi) ...
Semiviscosity flow equation with variable parameters under
... that for the same complete semiviscosity materials, the bigger the value of & or rn,, the better its superplasticity. But for different superplastic materials, there are often materials found that alor rn, is bigger, their superplasticity is not better correspondingly, while the mathough their ; or ...
... that for the same complete semiviscosity materials, the bigger the value of & or rn,, the better its superplasticity. But for different superplastic materials, there are often materials found that alor rn, is bigger, their superplasticity is not better correspondingly, while the mathough their ; or ...
lecture 16 - 18 aqui..
... 3. Ground-water discharge occurs in low zones 4. The water table has the same general shape as the surface topography (but less relief change) 5. Ground water generally flows from topographic highs to lows ...
... 3. Ground-water discharge occurs in low zones 4. The water table has the same general shape as the surface topography (but less relief change) 5. Ground water generally flows from topographic highs to lows ...
COMPLEX STRESS TUTORIAL 2 STRESS AND STRAIN This
... The units of change in length and original length must be the same and the strain has no units. Strains are normally very small so often to indicate a strain of 10-6 we use the name micro strain and write it as µε. For example we would write a strain of 7 x 10-6 as 7 µε. Tensile strain is positive a ...
... The units of change in length and original length must be the same and the strain has no units. Strains are normally very small so often to indicate a strain of 10-6 we use the name micro strain and write it as µε. For example we would write a strain of 7 x 10-6 as 7 µε. Tensile strain is positive a ...
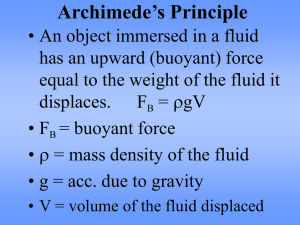
Buoyancy
... particle during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As mass of fluid particles remains constant throughout the motion, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fl ...
... particle during the course of motion with time (fig *) The fluid particles may change their shape, size and state as they move. As mass of fluid particles remains constant throughout the motion, the basic laws of mechanics can be applied to them at all times. The task of following large number of fl ...
Velocity Profiles for Circular Sections and Flow in
... 1. Establish the boundary conditions that define known ...
... 1. Establish the boundary conditions that define known ...
introduction - New Age International
... the kinetic energy of the fluid is converted into either, pressure energy or potential energy or kinetic energy or the combination of any two or all the three forms depending upon the end use in spiral or volute casing, which follows the impeller. In domestic, circulating and in agricultural pumps, ...
... the kinetic energy of the fluid is converted into either, pressure energy or potential energy or kinetic energy or the combination of any two or all the three forms depending upon the end use in spiral or volute casing, which follows the impeller. In domestic, circulating and in agricultural pumps, ...
Bernoulli`s equation
... is “bad news” and causes the flow to separate, leaving a turbulent wake behind the sphere. Very roughly one can estimate the pressure difference upstream and downstream as 1/2 ρU 2 , so that the drag force F ∝ 1/2 ρU 2 × A, where A is the cross-sectional area. The ratio F CD = 1 2 ...
... is “bad news” and causes the flow to separate, leaving a turbulent wake behind the sphere. Very roughly one can estimate the pressure difference upstream and downstream as 1/2 ρU 2 , so that the drag force F ∝ 1/2 ρU 2 × A, where A is the cross-sectional area. The ratio F CD = 1 2 ...
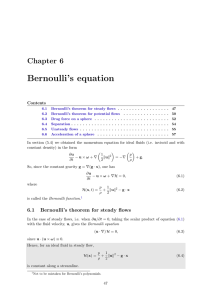
Chapter 6
... Heterogeneous materials can become homogeneous by diffusion. For an active diffusion to occur, temp. should be high enough to overcome energy barriers to atomic motion. ...
... Heterogeneous materials can become homogeneous by diffusion. For an active diffusion to occur, temp. should be high enough to overcome energy barriers to atomic motion. ...
Presentation (PowerPoint File)
... What is it? Where do you get it? How do you process it? What can it tell you? ...
... What is it? Where do you get it? How do you process it? What can it tell you? ...
Basics of Electricity
... Provides light, heat, sound, motion . . . Has been practical for use over the last 100 years ...
... Provides light, heat, sound, motion . . . Has been practical for use over the last 100 years ...