Viscosity Measurement - Northern Illinois University
... are controlled to some degree by fluid viscosity. Viscosity is defined as the internal friction of a fluid. The microscopic nature of internal friction in a fluid is analogous to the macroscopic concept of mechanical friction in the system of an object moving on a stationary planar surface. Energy m ...
... are controlled to some degree by fluid viscosity. Viscosity is defined as the internal friction of a fluid. The microscopic nature of internal friction in a fluid is analogous to the macroscopic concept of mechanical friction in the system of an object moving on a stationary planar surface. Energy m ...
PM5 RHEOLOGY
... fact strictly speaking none do if the relevant parameters are varied widely enough. In this lecture we are going to look at some of the more complicated behaviour one can get. To start we consider the fluids that do not obey Newton's law - the non-newtonian fluids. For these, the shear stress is not ...
... fact strictly speaking none do if the relevant parameters are varied widely enough. In this lecture we are going to look at some of the more complicated behaviour one can get. To start we consider the fluids that do not obey Newton's law - the non-newtonian fluids. For these, the shear stress is not ...
Viscosity
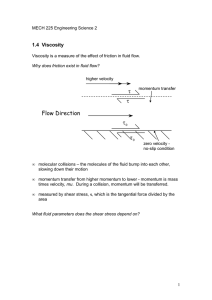
... The shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity, also called du the velocity gradient. We can write this as: τ ∝ dy So near the surface, the shear stress is high, while on moving further into the stream the shear stress gets smaller. ...
... The shear stress is proportional to the rate of change of velocity, also called du the velocity gradient. We can write this as: τ ∝ dy So near the surface, the shear stress is high, while on moving further into the stream the shear stress gets smaller. ...
Fluids, Shear Zones and Continental Rheology
... weakening and consequent deformation (i.e. shear zones), but this will be followed by incorporation of fluid into mineral lattices, and hence strengthening of the rock mass once more. As a result, from the perspective of a relatively small rock mass, deformation will be sporadic as rock strengths al ...
... weakening and consequent deformation (i.e. shear zones), but this will be followed by incorporation of fluid into mineral lattices, and hence strengthening of the rock mass once more. As a result, from the perspective of a relatively small rock mass, deformation will be sporadic as rock strengths al ...
Fluid Friction in Pipes
... In Chemical engineering process operations , fluids are typically conveyed through pipelines, in which viscous action. Such friction is normally overcome either by means of the pressure generated by a pump or by the fluid falling under gravity from a higher to a lower elevation. In both cases it ...
... In Chemical engineering process operations , fluids are typically conveyed through pipelines, in which viscous action. Such friction is normally overcome either by means of the pressure generated by a pump or by the fluid falling under gravity from a higher to a lower elevation. In both cases it ...
Abstract-Sumer PEKER - ic-rmm1
... the secondary bonds toward stretching. Extensional viscosity arises on the increase of velocity when the cross sectional area of flow is reduced in the flow direction. Velocity of the molecules with negligible interaction forces increase independently in the case of Newtonian fluids. In the case of ...
... the secondary bonds toward stretching. Extensional viscosity arises on the increase of velocity when the cross sectional area of flow is reduced in the flow direction. Velocity of the molecules with negligible interaction forces increase independently in the case of Newtonian fluids. In the case of ...
Final Exam Time: 120 min Course: 58:160, Fall 2006 Name
... Course: 58:160, Fall 2006 Name:------------------------- ...
... Course: 58:160, Fall 2006 Name:------------------------- ...
form_sheet_final_che..
... Print this document on a single sheet of paper and bring it to the exam; there will be no spare sheets at the exam. You are allowed to add information on the side of the sheet you printed on; the reverse side should be blank ...
... Print this document on a single sheet of paper and bring it to the exam; there will be no spare sheets at the exam. You are allowed to add information on the side of the sheet you printed on; the reverse side should be blank ...
Rheology 7
... • The viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids changes according to the rate of shear, thus non-Newtonian systems have no constant viscosity. • non-Newtonian systems can be of three general types, such as plastic, pseudo plastic and dilatants. ...
... • The viscosity of non-Newtonian fluids changes according to the rate of shear, thus non-Newtonian systems have no constant viscosity. • non-Newtonian systems can be of three general types, such as plastic, pseudo plastic and dilatants. ...
fluid_pr
... For water, k =2.2 Gpa, meaning that when a pressure of 0.1Mpa acts upon a cubic metre of water, the change in volume resulting is 1/22000 m 3. ...
... For water, k =2.2 Gpa, meaning that when a pressure of 0.1Mpa acts upon a cubic metre of water, the change in volume resulting is 1/22000 m 3. ...
10-10 Viscosity
... like a layer of plastic around water. • Surface tension =g …or gamma. • g = F/L …where F is force applied on a line of any fluid’s surface of length L. • g = W/DA …work is done resulting in surface energy. • See sample problem 10-14 p298. • Surfactants can reduce surface tension. • Adhesion…sticking ...
... like a layer of plastic around water. • Surface tension =g …or gamma. • g = F/L …where F is force applied on a line of any fluid’s surface of length L. • g = W/DA …work is done resulting in surface energy. • See sample problem 10-14 p298. • Surfactants can reduce surface tension. • Adhesion…sticking ...