lecture2
... Next, step back from the single crystal and look at groupings of crystals. A material may have different levels of crystalline. a. Single crystal: entire substance formed from one large crystal ...
... Next, step back from the single crystal and look at groupings of crystals. A material may have different levels of crystalline. a. Single crystal: entire substance formed from one large crystal ...
AP Physics 2
... - liquid -Takes the shape of its container, yet has a definite volume. - gas - Takes the shape and volume of its container. Special "states - Plasma, Bose-Einstein Condensate ...
... - liquid -Takes the shape of its container, yet has a definite volume. - gas - Takes the shape and volume of its container. Special "states - Plasma, Bose-Einstein Condensate ...
Microwave Oven
... actuating functions and are capable of adapting to changes in the environment. In other words, smart materials can change themselves in response to an outside stimulus or respond to the stimulus by producing a signal of some sort. By utilizing these materials, a complicated part in a system consisti ...
... actuating functions and are capable of adapting to changes in the environment. In other words, smart materials can change themselves in response to an outside stimulus or respond to the stimulus by producing a signal of some sort. By utilizing these materials, a complicated part in a system consisti ...
Chapter 12
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
Chapter 12
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
... an object of mass M is the force Mg acting at the center of gravity of the object If g is uniform over the object, then the center of gravity of the object coincides with its center of mass If the object is homogeneous and symmetrical, the center of gravity coincides with its geometric center ...
The Hydrodynamics of Flow Stimuli - McHenry Lab
... the hydrodynamic regime of a flow field by approximating the relative magnitude of these forces. The Reynolds number serves as a key hydrodynamic index that may be easily calculated from measurements of length and speed. For example, the Reynolds number for a gliding fish (e.g., Astyanax fasciatus; ...
... the hydrodynamic regime of a flow field by approximating the relative magnitude of these forces. The Reynolds number serves as a key hydrodynamic index that may be easily calculated from measurements of length and speed. For example, the Reynolds number for a gliding fish (e.g., Astyanax fasciatus; ...
pdf file - Wayne State University Physics and Astronomy
... Example: Depressing the brake pedal in a car pushes on a piston with crosssectional area 3.0 cm2. The piston applies pressure to the brake fluid, which is connected to two pistons, each with area 12.0 cm2. Each of these pistons presses a brake pad against one side of a rotor attached to one of the r ...
... Example: Depressing the brake pedal in a car pushes on a piston with crosssectional area 3.0 cm2. The piston applies pressure to the brake fluid, which is connected to two pistons, each with area 12.0 cm2. Each of these pistons presses a brake pad against one side of a rotor attached to one of the r ...
Fluids - Teach Engineering
... Archimedes’ Principle: The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the displaced water. ...
... Archimedes’ Principle: The buoyant force is equal to the weight of the displaced water. ...
estimation of subsurface residual stress depth profiles via wideband
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
... altering the way that magnetic domain walls move; this results in a quantifiable change in the MBN emitted by the sample in the presence of an externally applied alternating magnetic field. The effective depth of emission of MBN for traditionally used frequency bands is very near the surface, hence ...
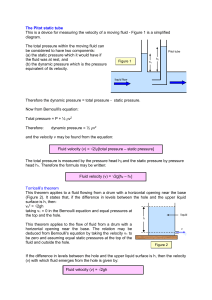
Pitot and Toricelli
... The Pitot static tube This is a device for measuring the velocity of a moving fluid - Figure 1 is a simplified diagram. The total pressure within the moving fluid can be considered to have two components: (a) the static pressure which it would have if the fluid was at rest, and (b) the dynamic press ...
... The Pitot static tube This is a device for measuring the velocity of a moving fluid - Figure 1 is a simplified diagram. The total pressure within the moving fluid can be considered to have two components: (a) the static pressure which it would have if the fluid was at rest, and (b) the dynamic press ...
Fluid Power
... and transmit power Pneumatic Power Uses gas, usually air, to convert, store, and transmit power. ...
... and transmit power Pneumatic Power Uses gas, usually air, to convert, store, and transmit power. ...
1-2 Section Summary
... particles of a fluid begin to flow, transferring heat energy from one part of the fluid to another. Heat transfer by convection is caused by differences in temperature and density within a fluid. Density is a measure of how much mass there is in a volume of a substance. When a liquid or gas is heate ...
... particles of a fluid begin to flow, transferring heat energy from one part of the fluid to another. Heat transfer by convection is caused by differences in temperature and density within a fluid. Density is a measure of how much mass there is in a volume of a substance. When a liquid or gas is heate ...
MUCOOl_Absorber_Feb._03
... • In a parallel flow heat exchanger, the coldest temperature of the warm stream is always higher the warmest temperature of the cold stream. This restriction does not apply for a counter flow heat exchanger. • For a given heat exchanger U factor and heat exchanger area, a counter flow heat exchanger ...
... • In a parallel flow heat exchanger, the coldest temperature of the warm stream is always higher the warmest temperature of the cold stream. This restriction does not apply for a counter flow heat exchanger. • For a given heat exchanger U factor and heat exchanger area, a counter flow heat exchanger ...
Load Duration Curves (LDCs)
... Load Duration Curves Allowable or desired concentration Primary Contract Recreation Standard E. coli 126 cfu/100 mL General Use Screening Level Nitrate 1.95 mg/L ...
... Load Duration Curves Allowable or desired concentration Primary Contract Recreation Standard E. coli 126 cfu/100 mL General Use Screening Level Nitrate 1.95 mg/L ...
STATE UNIVERSITY OF NEW YORK COLLEGE OF TECHNOLOGY CANTON, NEW YORK
... GOALS (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES): By the end of this course, the student will be able to: Course Objective a. Describe simple crystal structure and interatomic bonding. b. Integrate the structure of solids with their thermal, mechanical, electrical, optical and magnetic properties. c. Explain the g ...
... GOALS (STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES): By the end of this course, the student will be able to: Course Objective a. Describe simple crystal structure and interatomic bonding. b. Integrate the structure of solids with their thermal, mechanical, electrical, optical and magnetic properties. c. Explain the g ...
Fluid Mechanics Lab
... 3. Install the 5mm nozzle and 45o target. 4. Position the weight carrier on the weight platform. Add weights until the target is free of the stop and is about midpoint between target and nozzle. Record the weight on the carrier. Align the pointer with the weight platform for reference. Measure the d ...
... 3. Install the 5mm nozzle and 45o target. 4. Position the weight carrier on the weight platform. Add weights until the target is free of the stop and is about midpoint between target and nozzle. Record the weight on the carrier. Align the pointer with the weight platform for reference. Measure the d ...
PowerPoint Slides - University of Toronto Physics
... A. broadens as it falls. B. narrows as it falls. C. does not change its cross-sectional shape. D. slows before hitting the bottom of the sink. ...
... A. broadens as it falls. B. narrows as it falls. C. does not change its cross-sectional shape. D. slows before hitting the bottom of the sink. ...