Suggested solutions to 2015 MEK2500 Mock Exam
... Assume a linear regime with small strains and no distinction between Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates. Consider a two-dimensional rectangular body of length a (m) and height b (m) with coordinates (x1 , x2 ) ∈ [0, a] × [0, b]. Assume that the body is isotropic and homogeneous with Lamé parameter ...
... Assume a linear regime with small strains and no distinction between Eulerian and Lagrangian coordinates. Consider a two-dimensional rectangular body of length a (m) and height b (m) with coordinates (x1 , x2 ) ∈ [0, a] × [0, b]. Assume that the body is isotropic and homogeneous with Lamé parameter ...
Basic Equations - Earth and Space Sciences at the University of
... This should not be surprising, because early scientists spent most of their time trying to understand the world they could easily observe around them. GFD is a branch of continuum mechanics. This is a statement that the scale is large compared to intermolecular distances. A continuum is a material w ...
... This should not be surprising, because early scientists spent most of their time trying to understand the world they could easily observe around them. GFD is a branch of continuum mechanics. This is a statement that the scale is large compared to intermolecular distances. A continuum is a material w ...
ap physics b lesson 64, 76 fluid mechanics
... atmosphere down to seal level whose cross sectional area is 1m2 is 10, 330kg and its weight is 101300N. Thus the atmospheric pressure is 101,300 Pa or 101.3kPa. ...
... atmosphere down to seal level whose cross sectional area is 1m2 is 10, 330kg and its weight is 101300N. Thus the atmospheric pressure is 101,300 Pa or 101.3kPa. ...
12/10/09
... Temp ↑ 86◦ F for every mile Made of SOLID ROCK 2. MANTLE – largest layer by volume Made of SOLID ROCK that can flow under extreme heat and pressure Upper mantle is called the asthenosphere- a semi-solid substance which the crust floats on Temps. up to 5,500◦ F 3. CORE – a. OUTER CORE LIQ ...
... Temp ↑ 86◦ F for every mile Made of SOLID ROCK 2. MANTLE – largest layer by volume Made of SOLID ROCK that can flow under extreme heat and pressure Upper mantle is called the asthenosphere- a semi-solid substance which the crust floats on Temps. up to 5,500◦ F 3. CORE – a. OUTER CORE LIQ ...
Fluids, elasticity
... (a) the weight of fluid displaced equals the weight of the block (b) the product of the surface area of the bottom of the block, and the gauge pressure there, equals the weight of the block (c) the submerged volume of the block, times the density of water, is equal to the weight of the block (d) bot ...
... (a) the weight of fluid displaced equals the weight of the block (b) the product of the surface area of the bottom of the block, and the gauge pressure there, equals the weight of the block (c) the submerged volume of the block, times the density of water, is equal to the weight of the block (d) bot ...
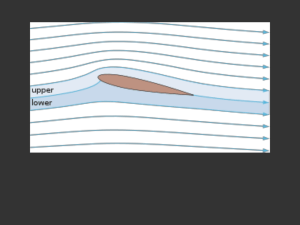
The lift of a wing is proportional to the amount of air diverted down
... To attempt a physical explanation of lift as it applies to an airplane, consider the flow around a 2-D, symmetric airfoil at positive angle of attack in a uniform free stream. Instead of considering the case where an airfoil moves through a fluid as seen by a stationary observer, it is equivalent an ...
... To attempt a physical explanation of lift as it applies to an airplane, consider the flow around a 2-D, symmetric airfoil at positive angle of attack in a uniform free stream. Instead of considering the case where an airfoil moves through a fluid as seen by a stationary observer, it is equivalent an ...
Chapter 6 - Equations of Motion and Energy in Cartesian... Equations of motion of a Newtonian fluid The Reynolds number
... parts. The left side or inertial and potential terms, which dominates for large NRe and the right side or viscous terms, which dominates for small NRe. The potential gradient term could have been on the right side if the dimensionless pressure was defined differently, i.e., normalized with respect t ...
... parts. The left side or inertial and potential terms, which dominates for large NRe and the right side or viscous terms, which dominates for small NRe. The potential gradient term could have been on the right side if the dimensionless pressure was defined differently, i.e., normalized with respect t ...
control volume approach and continuity principle
... just B referenced to mass), and in the volume (if we increase the control volume, we probably include more of the total property B ) Notice also that V in the last term has to be the velocity relative to the control surface. ...
... just B referenced to mass), and in the volume (if we increase the control volume, we probably include more of the total property B ) Notice also that V in the last term has to be the velocity relative to the control surface. ...
Fluid reservoirs in the crust and mechanical coupling between the... lower crust Bruce E Hobbs , Alison Ord
... by high mean stress. The base of the plastic region is at a strong discontinuity in stress difference where localised deformation occurs. Tabular, dilatant fluid filled regions develop at and above this zone in close association with dilatant tensional zones in the hanging-walls of faults and diffus ...
... by high mean stress. The base of the plastic region is at a strong discontinuity in stress difference where localised deformation occurs. Tabular, dilatant fluid filled regions develop at and above this zone in close association with dilatant tensional zones in the hanging-walls of faults and diffus ...
Theories of Failure
... • For uneven materials; tensile strength is due to the presence of microscopic flaws in the castings, which when subjected to tensile loading, serve as nuclei for crack formation. • when subjected to compressive stress, these flaws are pressed together, increasing the resistance to slippage from sh ...
... • For uneven materials; tensile strength is due to the presence of microscopic flaws in the castings, which when subjected to tensile loading, serve as nuclei for crack formation. • when subjected to compressive stress, these flaws are pressed together, increasing the resistance to slippage from sh ...
Puncture of the knee joint
... drape" and the use of disposable equipment, the needle is introduced at an angle to the lateral upper pole of the patella. After around 1 to 2 centimetres, the needle enters the joint as evidenced by the aspiration of a small amount of fluid with the syringe. The joint fluid is either evacuated (to ...
... drape" and the use of disposable equipment, the needle is introduced at an angle to the lateral upper pole of the patella. After around 1 to 2 centimetres, the needle enters the joint as evidenced by the aspiration of a small amount of fluid with the syringe. The joint fluid is either evacuated (to ...
Phy_103_-3
... 3.3.1 Characteristics of a Fluid Considering the motion of real fluids, it is very complex and not fully understood. When fluid is in motion, its flow can be characterized as being one of 2 main types. Steady or laminar flow. The flow is steady if the overall flow pattern does not change with time. ...
... 3.3.1 Characteristics of a Fluid Considering the motion of real fluids, it is very complex and not fully understood. When fluid is in motion, its flow can be characterized as being one of 2 main types. Steady or laminar flow. The flow is steady if the overall flow pattern does not change with time. ...
Continuity equation and Bernoulli`s equation
... However, the thrust is also equal to the mass flow times the change in speed. The mass flow is ρSd (V0 + Va1 ), and the change in speed is simply equal to Vat . So: ...
... However, the thrust is also equal to the mass flow times the change in speed. The mass flow is ρSd (V0 + Va1 ), and the change in speed is simply equal to Vat . So: ...
Corelite-1 - Waymond Scott
... Difference lies in the fact that Corelite does not send congestion notifications until flows are close to respective fair share rates, thus eliminating the need for re-entry into slow-start ...
... Difference lies in the fact that Corelite does not send congestion notifications until flows are close to respective fair share rates, thus eliminating the need for re-entry into slow-start ...
Pressure gradient
... - Use these properties of turbulent flows in the Navier Stokes equations -The only terms that have products of fluctuations are the advection terms - All other terms remain the same, e.g., u t u t u ' t u t ...
... - Use these properties of turbulent flows in the Navier Stokes equations -The only terms that have products of fluctuations are the advection terms - All other terms remain the same, e.g., u t u t u ' t u t ...
Flow Directions in Sedimentary, Volcanic and Plutonic Rocks
... the magnetic foliation is always oriented near the bedding, while the magnetic lineation is mostly roughly parallel to the near-bottom water current directions. Less frequently, the magnetic lineation may be perpendicular to the current direction, which is typical of the flysch sediments of the lowe ...
... the magnetic foliation is always oriented near the bedding, while the magnetic lineation is mostly roughly parallel to the near-bottom water current directions. Less frequently, the magnetic lineation may be perpendicular to the current direction, which is typical of the flysch sediments of the lowe ...
smart ceramics
... They include rocks and clays, cement, concrete, glass and precious gemstones. They are a group of materials that generally speaking are strong, particularly in compression and hard, they have high melting points, so can be used in hot environments and they are good electrical and thermal insulators. ...
... They include rocks and clays, cement, concrete, glass and precious gemstones. They are a group of materials that generally speaking are strong, particularly in compression and hard, they have high melting points, so can be used in hot environments and they are good electrical and thermal insulators. ...
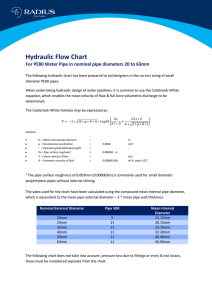
Hydraulic Flow Chart
... The following hydraulic chart has been prepared to aid designers in the correct sizing of small diameter PE80 pipes. When undertaking hydraulic design of water pipelines, it is common to use the Colebrook-White equation, which enables the mean velocity of flow & full bore volumetric discharge to be ...
... The following hydraulic chart has been prepared to aid designers in the correct sizing of small diameter PE80 pipes. When undertaking hydraulic design of water pipelines, it is common to use the Colebrook-White equation, which enables the mean velocity of flow & full bore volumetric discharge to be ...
Fluids
... Two empty pop cans are placed about ¼” apart on a frictionless surface. If you blow air between the cans, what happens? A) The cans move toward each other. B) The cans move apart. C) The cans don’t move at all. ...
... Two empty pop cans are placed about ¼” apart on a frictionless surface. If you blow air between the cans, what happens? A) The cans move toward each other. B) The cans move apart. C) The cans don’t move at all. ...